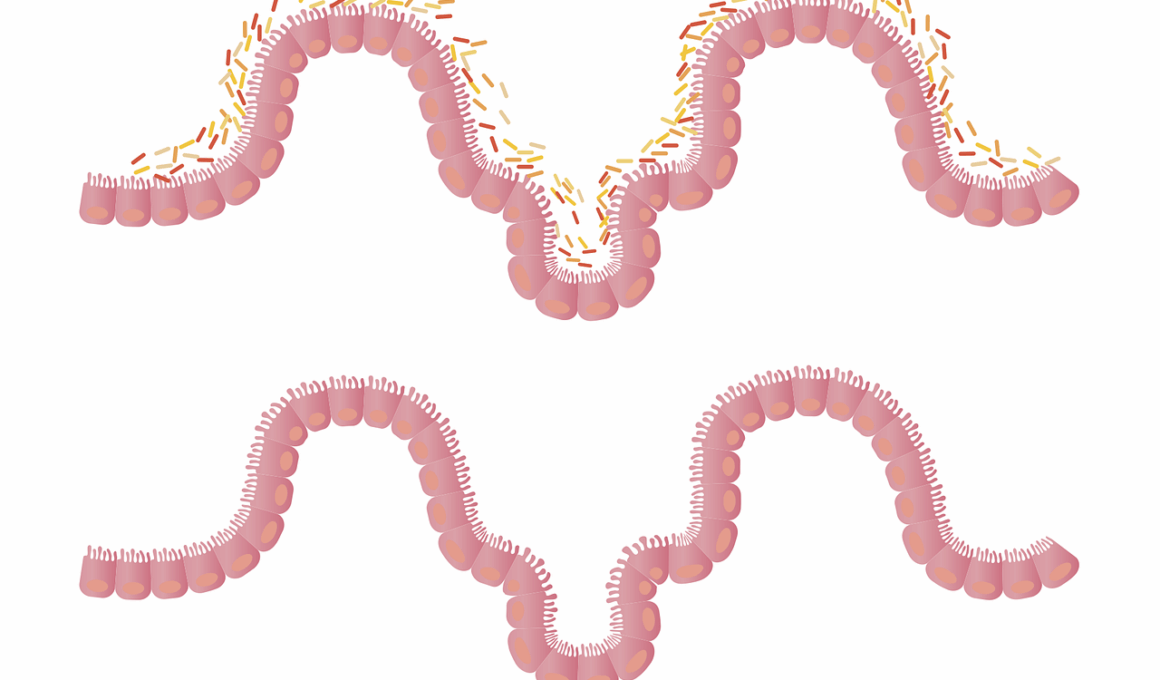
Gut Inflammation Symptoms: When to See a Doctor
Gut inflammation can manifest in various ways, and recognizing the symptoms is crucial for your health. The digestive tract is sensitive, so any signs like cramps or bloating may indicate inflammation. Typical symptoms include persistent abdominal pain, frequent heartburn, and changes in bowel habits. Some may experience fatigue, which often surprises individuals, as they associate gut health more with physical discomfort. It’s vital not to ignore consistent gastrointestinal symptoms, as they can lead to further complications if left untreated. Another tell-tale sign is experiencing unexplained weight loss, where it becomes increasingly challenging to maintain a healthy weight. Additionally, individuals might notice alterations in their appetite. Moreover, mood swings are frequently linked to gut health, showing the connection between emotional and digestive wellness. If you observe these symptoms persisting over time or worsening, it is advisable to consult a healthcare professional. Often, they will perform tests or examinations to determine the underlying cause of your symptoms. Seeking early guidance can enhance treatment outcomes and lead to a more favorable recovery.
Inflammation in the gut may also lead to overt signs that shouldn’t be overlooked. These signs can escalate in their severity and intensify discomfort over time. Look out for symptoms like diarrhea, especially if it’s chronic, as this can severely impact hydration and nutrition levels. Another critical indicator is blood in your stool, which can be alarming and requires immediate medical evaluation. Alongside that, mucus in the stool may also point to inflammation, and persistent visits to the restroom or fecal urgency can occur as well. Ultimately, maintaining awareness of these gut-related symptoms presents a proactive approach to health. While many individuals may experience occasional digestive discomfort, consistent symptoms should initiate a visit to a healthcare provider. In severe cases, mucosal inflammation may develop, leading to conditions like IBD. In this regard, keeping a symptom diary can be beneficial. By documenting any irregular changes, you provide your doctor with invaluable information, aiding in diagnosis. By addressing these issues early, you decrease the possibility of developing chronic conditions that can significantly disrupt daily life.
Physical Symptoms of Gut Inflammation
Physical symptoms accompanying gut inflammation can vary widely between individuals. Some common signs include noticeable abdominal pain, which can be sharp or dull, often escalating post meals. Bloating, the feeling of fullness, and gas are also prevalent, leading to discomfort. These symptoms occur due to the digestion process breaking down food inconsistently. Along with this, nausea or vomiting may occur, making it difficult to eat properly. These persistent digestive disturbances can affect your appetite adversely, causing drastic weight fluctuations. People dealing with gut inflammation may also report chronic fatigue, frequently attributing their tiredness to other causes. It’s essential to gauge your body’s signals critically. Underlying inflammation can lead to far more significant conditions like Crohn’s disease or ulcerative colitis, so recognizing these symptoms is vital. Furthermore, skin issues such as rashes or acne may sometimes arise, giving insight into the interconnectedness between gut and skin health. If you’re noting consistent inflammation signs combined with skin or mood changes, it’s intricately linked. Such manifestations should prompt a comprehensive medical assessment for appropriate intervention methods tailored to your needs.
Psychological symptoms can significantly correlate with gut inflammation, highlighting the gut-brain connection’s impact. Many individuals report increased anxiety or depression alongside digestive issues. This link indicates that inflammation may not solely affect physical well-being but also emotional health. Chronic discomfort and dietary restrictions can lead to frustration and feelings of isolation or defeat. Understanding that psychological symptoms can complement physical issues allows individuals to approach their health holistically. It’s essential to recognize emotional distress as a symptom of a larger issue, potentially stemming from gut inflammation. Additionally, irritability and mood swings can occur, impacting daily life and interpersonal relationships. Sometimes, treating the root cause—gut inflammation—can lead to improvements in mood and overall mental health. Incorporating stress management techniques and maintaining a balanced diet can be helpful strategies to improve gut health while supporting emotional stability. Suppose this emotional turmoil persists alongside physical discomfort. In that case, it is crucial to seek an integrated treatment plan from healthcare professionals who understand both the physical and psychological aspects of gut inflammation.
Long-Term Consequences of Ignoring Symptoms
Long-term consequences can result from ignoring ongoing signs of gut inflammation. Chronic conditions such as inflammatory bowel disease may develop if inflammation persists untreated. This can lead to severe complications, including osteoporosis, malnutrition, and an increased risk of colon cancer over time. Ignoring initial warning signs can accumulate, making the condition more difficult to manage and treat. Patients may find themselves in situations where surgical interventions become necessary due to the severity of damage. Gaining awareness surrounding these long-term implications emphasizes the importance of early detection. Consistent inflammation can also disrupt electrolyte levels, which can lead to further health complications. Moreover, hormonal imbalances may occur as the body struggles to cope with chronic inflammation. Severe imbalances can create an array of health issues, ranging from metabolic disorders to issues with reproductive health. Lastly, being unaware of these long-term impacts may result in a decreased quality of life. The goal is to maintain optimal gut health and prevent chronic ailments that could otherwise be avoided by recognizing initial symptoms and seeking timely medical assistance.
Diet plays a crucial role in managing gut inflammation and can significantly influence symptomatology. Identifying specific food triggers is essential for alleviating inflammation symptoms effectively. Common culprits such as dairy, gluten, and refined sugars may aggravate inflammation for many individuals. Therefore, keeping a food diary can help determine which foods spark adverse reactions. Incorporating anti-inflammatory foods into your diet, such as fatty fish, leafy greens, and spices like turmeric, can create a strong counterbalance. Adopting a diet rich in fiber also promotes a healthy gut microbiome, which plays a pivotal role in preventing inflammation. Moreover, it’s advisable to stay well-hydrated to support digestion and overall health. Over time, these dietary changes can bring about a significant decrease in gut inflammation symptoms. Consultation with a registered dietitian can offer personalized advice tailored to your specific needs, ultimately optimizing your digestion and well-being. Remember, understanding the impact of your food choices empowers you to take control over your gut health. A focused approach to nutrition can help pave the path for recovery and improved quality of life.
When to Seek Medical Advice
Recognizing when to seek medical advice regarding gut inflammation is crucial for optimal health. If symptoms persist for weeks or worsen, consulting a healthcare professional should be your priority. Unexplained weight loss, in particular, is a concerning sign that should prompt immediate evaluation. Any signs of gastrointestinal bleeding or severe pain that disrupts your daily life should also lead to urgent medical consultation. Additionally, if you observe a significant change in bowel habits, especially prolonged diarrhea or constipation, do not hesitate to seek advice. In some cases, experiencing fever along with abdominal pain can signal a more serious underlying condition. Furthermore, complications from chronic inflammation need to be thoroughly assessed, as they can lead to more significant health issues. Having an open dialogue with your doctor enables a clearer understanding of any changes or symptoms you’re experiencing. By approaching your gut health proactively and seeking advice when needed, you can receive early interventions. Ultimately, early medical intervention can be the key to preventing more severe conditions and ensuring that your gut health remains in a stable state.
In conclusion, maintaining awareness of gut inflammation symptoms empowers individuals to act sooner and seek necessary medical attention. Recognizing early signs such as pain, diarrhea, or emotional disturbances is critical. Ignoring these signs can result in severe consequences, possibly leading to chronic conditions. Additionally, developing a better understanding of diet and its impact can play a significant role in preventing inflammation. Incorporating soothing foods and hydration benefits overall health and well-being. If symptoms persist, don’t hesitate to consult with a healthcare provider who can guide a thorough evaluation. Documenting symptoms can further assist in identifying underlying issues. Guided diet modifications can also lead to comprehensive benefits, ensuring you are on the path to recovery rather than facing escalating health challenges. Being vigilant about your gut health is a crucial component of comprehensive wellness. Foster open communication between yourself and your healthcare provider. Being informed about when to seek help ultimately leads to better health outcomes. Your gut health is integral to overall quality of life, so prioritizing awareness and action is necessary for thriving wellness.