How Probiotics Enhance Your Immune System
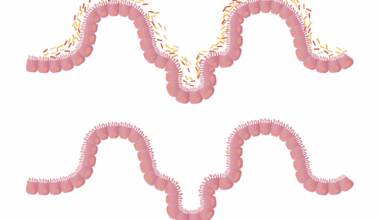
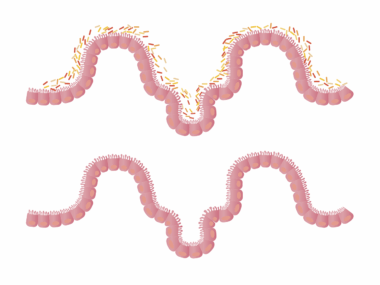
The human immune system plays a crucial role in protecting the body from pathogens, hence maintaining good gut health is essential. Probiotics, which are live microorganisms found in certain foods and supplements, contribute significantly to improving gut health. They help maintain a balanced gut microbiome, which can enhance the immune system’s ability to combat infections. Many studies suggest that when gut flora is healthy, the immune system can respond more effectively to pathogens. Notably, probiotics improve the intestinal barrier function, inhibiting harmful bacteria from entering the bloodstream. This balancing act allows for a robust immune defense, particularly during cold and flu seasons. Nutrient-rich foods such as yogurt, kefir, and fermented vegetables are excellent sources of probiotics that can enrich your gut flora. Furthermore, prebiotics, which are fibers that feed probiotics, also play a vital role. This means that consuming probiotic and prebiotic-rich foods together offers the best support for immune system health. Integrating these dietary elements can pave the way for resilience against common infections.
Research indicates that the benefits of probiotics extend beyond gut health to significantly impact overall immunity. Various strains of probiotics have shown promise in boosting the immune response during stress and illness. Some studies specifically highlight the role of Lactobacillus and Bifidobacterium in enhancing immune functions. These strains help balance the immune response, thus preventing it from becoming overactive, which can lead to autoimmune issues. By modulating immune function, probiotics provide a targeted way to promote health. Additionally, by producing short-chain fatty acids during digestion, probiotics contribute to lower inflammation in the body. This is particularly beneficial for individuals with inflammatory diseases. For optimal results, experts recommend providing the body with diverse probiotic strains, which can be achieved by consuming a variety of foods. Moreover, achieving the right balance of gut bacteria can amplify the effects of vaccinations. Thus, probiotic supplementation is not just a preventive measure; it can also improve response to immune challenges. Those looking to boost their health may consider integrating probiotics into their daily routine for enhanced immunity.
The Gut-Immune System Connection
The gut microbiome is known to be a significant player in immune function, acting as a bridge between digestion and immunity. The gut houses approximately 70% of the body’s immune cells, which interact significantly with the gut microbiota. A well-balanced gut microbiome allows for optimal immune cell development and function. Thus, an imbalance can lead to a weakened immune response and increased susceptibility to diseases. Through the production of metabolites, probiotics foster a protective environment in the gut. These metabolites can strengthen the intestinal barrier, thereby minimizing the risk of pathogens penetrating the gut lining. Furthermore, probiotics can also modulate the production of antibodies, fostering a quicker response to pathogens. Studies indicate that individuals with higher levels of beneficial gut bacteria tend to experience fewer infections. Additionally, including probiotics in your diet may help alleviate gastrointestinal disorders, fostering overall gut health. A well-functioning gut is essential for a healthy immune system. Therefore, one’s diet should focus on foods rich in probiotics and antioxidants to ensure a healthy intestinal microbiome.
The timing of probiotic intake may also play a crucial role in their effectiveness. Research suggests that taking probiotics during or after the onset of illness can support the immune system proactively. This means that maintaining consistent intake, especially during high-stress periods, can enhance immune responses. Probiotics should be viewed as a long-term health strategy. For maximum benefit, it is recommended to include fermented foods in daily meals. These include options like kimchi, sauerkraut, and kombucha, all rich in beneficial bacteria. Additionally, supplements can offer a concentrated dose of probiotics for specific needs. It is essential to choose high-quality strains based on research and clinical evidence for enhanced efficacy. Furthermore, integrating foods rich in vitamins and minerals, such as zinc and vitamin C, will further support immune health. The partnership between probiotics, a balanced diet, and lifestyle choices creates a comprehensive approach to wellness. Therefore, it is vital to remain informed and consult healthcare providers for personalized recommendations. This holistic strategy can significantly improve health outcomes, particularly concerning immune function.
Dietary Sources of Probiotics
There are many dietary sources of probiotics that can easily be incorporated into your daily meal plan. Fermented dairy products, such as yogurt and kefir, are among the most popular sources. These products contain live cultures that help foster beneficial gut bacteria. In addition, plant-based options like sauerkraut or kimchi are excellent as they also provide probiotics while offering various nutrients and fibers. Another important consideration is the inclusion of miso and tempeh, which are fermented soy products rich in beneficial bacteria. Furthermore, pickled vegetables that are fermented naturally can also contribute to gut health while adding flavor to meals. Some brands now produce probiotic-fortified foods, which add another source for obtaining these beneficial organisms. It’s essential to read labels to ensure that products contain live cultures. Another option includes taking probiotic supplements, which can deliver targeted benefits for specific health issues. As always, one should consider dietary preferences and tolerances. Incorporating these sources leads to improved gut flora and a more robust immune system, ultimately promoting better health.
Awareness of potential probiotics’ limitations is essential for informed health choices. While many people experience positive benefits, not everyone reacts the same. Probiotics may not be suitable for individuals with compromised immune systems or those on antibiotics, as these can hinder effectiveness. Resistance to certain strains might also occur, leading to reduced efficacy. Moreover, using probiotics without the necessary dietary fiber can stifle their benefits. Prebiotics nourish probiotics, allowing them to thrive. Consequently, a balanced intake of both is crucial for maintaining gut health. Furthermore, it is important to consult with healthcare professionals before starting any new supplement regimen. Individual needs may vary, requiring personalized approaches for effectiveness. Ensuring that probiotic strains suit one’s health goals and lifestyle can improve overall outcomes significantly. Research continues to evolve, leading to new findings about probiotics’ potential and effectiveness. Staying updated with reliable sources of information ensures that individuals make knowledgeable decisions about their health. Generally, integrating a combination of probiotics and a balanced diet leads to a resilient immune system, equipped to tackle everyday health challenges.
Conclusion
In conclusion, incorporating probiotics into your daily diet can significantly enhance your immune system health. The connection between gut health and immunity cannot be underestimated, as the gut microbiome plays a vital role in maintaining overall bodily functions. Regular consumption of fermented foods and possibly supplements can help balance gut bacteria and improve immune responses. Individual dietary choices, activity levels, and health conditions should guide personal approaches to probiotic intake. Consulting healthcare professionals may provide guidance tailored to individual needs, maximizing the benefits of probiotics. The synergistic effects of probiotics and a fiber-rich diet enhance digestive health and strengthen immunity. As research continues, the understanding of probiotics’ role in health will evolve, opening even more possibilities for preventive wellness strategies. Taking proactive steps in diet and nutrition can lead to improved health and resilience against infections. As evidence mounts about the benefits of maintaining a healthy gut, individuals should embrace changes in their eating habits. Ultimately, supporting gut health lays the foundation for longevity and vitality, ensuring a better quality of life.