Effects of Artificial Sweeteners on Gut Microbiome and Metabolism
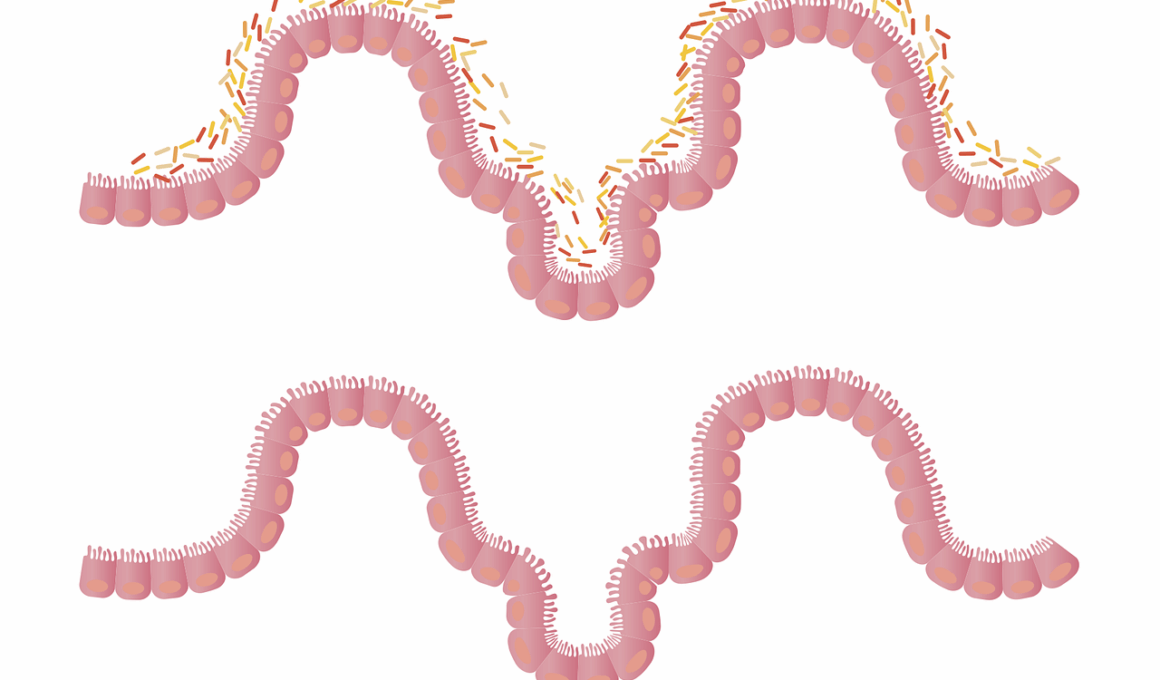
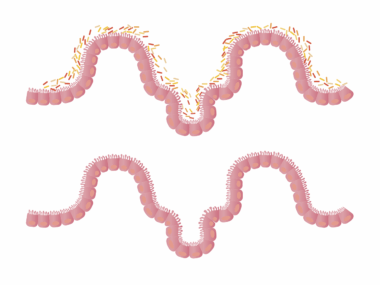
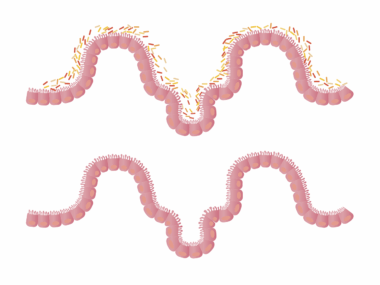
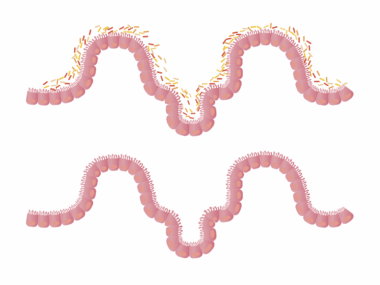
Artificial sweeteners have become a popular alternative to sugar, offering the sweetness without the calories. However, their impact on the gut microbiome and metabolism raises significant concerns. Research indicates that these sweeteners, while low in calories, can alter the composition of gut bacteria, leading to dysbiosis. Dysbiosis is an imbalance in gut bacteria that might contribute to various metabolic disorders. Furthermore, studies suggest that the consumption of artificial sweeteners may lead to increased cravings for sweet foods, potentially leading to weight gain. Importantly, the effects can vary based on individual responses, indicating the complexity of the human microbiome. Understanding the intricate relationship between these sweeteners and gut health is essential in making informed dietary choices. Moreover, the replacement of natural sugars with artificial substitutes might not be as beneficial as initially thought. It’s crucial to look beyond the surface benefits of calorie reduction to explore the long-term health consequences. Research is ongoing, and individuals are encouraged to consider their own experiences when integrating artificial sweeteners into their diet.
The role of gut microbiome extends beyond digestion, influencing overall health and metabolism significantly. As artificial sweeteners wade into this realm, it’s essential to examine specific metabolic pathways that can be disrupted. For instance, artificial sweeteners have been shown to affect glucose metabolism, potentially leading to increased insulin resistance. Insulin resistance is a condition that can pave the way for type 2 diabetes over time. The types of sweeteners consumed, such as aspartame, sucralose, or saccharin, each possess unique qualities that may diferentes affect gut bacteria. Some research suggests that certain artificial sweeteners may promote the growth of harmful bacteria while inhibiting beneficial strains. This shift not only disturbs gut health but may also influence metabolic functions throughout the body. Understanding this dynamic relationship is crucial, as the gut microbiome is increasingly recognized as a central player in metabolic health. As more studies delve into these connections, consumers are left to ponder whether the potential benefits of artificial sweeteners outweigh the negative impacts on gut microbiome and metabolism.
Moreover, gut health contributes to many bodily functions, including immune response and even mental health. The introduction of artificial sweeteners has the potential to disturb the delicate balance of this ecosystem. While some people may find artificial sweeteners beneficial for weight management, others may experience unwanted consequences. Reports of gastrointestinal discomfort, a common complaint among consumers of these products, can signal a disruption in the gut microbiome caused by these sweeteners. Moreover, prolonged exposure may lead to long-term health risks, including cardiovascular issues and obesity. As awareness about the impacts on gut health increases, questions arise regarding the long-term feasibility of substituting sugar for artificial alternatives. Nutritional scientists advocate for greater exploration into natural sweeteners like honey or maple syrup, which may provide a more favorable effect on gut microbiome composition. Such alternatives not only satiate sweet cravings but also come with additional nutritional benefits that artificial options lack. Continued discourse and research are essential in guiding consumers toward healthier sweetening choices.
The Need for Further Research
Despite the growing body of evidence suggests potential negative impacts, the research surrounding artificial sweeteners remains inconsistent. Some studies report minimal or no effects on the gut microbiome, while others highlight significant changes. This disparity calls for further extensive investigation into the mechanisms by which artificial sweeteners interact with gut bacteria. Understanding the specific characteristics of different artificial sweeteners is also crucial since their metabolic effects are likely not uniform. Additionally, factors such as individual genetics, existing diet, and lifestyle can all influence the extent to which artificial sweeteners affect one’s microbiome. As researchers continue to uncover the complexities surrounding diet and gut health, it becomes increasingly important to inform consumers of the potential risks and benefits. With more clarity on these topics, individuals will be better equipped to make well-informed decisions regarding their sugar intake. For now, it is advisable for consumers to approach artificial sweeteners with caution and to stay attuned to their body’s responses following their consumption.
Furthermore, the subjective experiences of individuals must play a role in the understanding of artificial sweeteners’ effects. Some may find them invaluable for managing caloric intake, while others may experience adverse reactions. The interaction between artificial sweeteners and gut microbiome is a personal journey, and methodologies for study must consider this variability. It’s vital to recognize that what works for one person may not necessarily apply to another. The traditional view of calorie counting and weight management is evolving, with a more profound appreciation for how diets impact gut health, a core part of holistic wellness. As individuals navigate their dietary choices, self-awareness becomes increasingly vital. Keeping a food journal can help track the impacts of artificial sweeteners and establish patterns in how they affect overall health. Additionally, experimenting with temporary eliminations of sweeteners can provide insights into how elimination may affect energy levels, cravings, and digestive health. Such practices can lead to valuable personal revelations regarding the consumption of artificial sweeteners.
Balancing Sweetness and Health
Ultimately, finding balance between enjoying sweetness and maintaining gut health is crucial in today’s society, where sugar alternatives are prevalent. Artificial sweeteners promise reduced calories but can also lead to unexpected consequences on gut microbiome and metabolic health. The journey toward a healthy gut is multifaceted, requiring attention not only to what is consumed but how different foods can interact within the body. Advocating for a dietary paradigm that incorporates a variety of whole foods over strict reliance on artificial replacements can foster an environment conducive to a thriving microbiome. In addition to whole foods, incorporating fermented items such as yogurt or sauerkraut can promote a healthy gut, improving digestion and overall wellness. As more services recognize the importance of gut health, shifting the cultural narrative toward more natural food choices will become imperative. Emphasizing nutrient-rich options can allow for enjoyment without the potential negative impact of artificial sweeteners. Awareness, education, and mindfulness about dietary choices remain the foundation for a healthier relationship with food.
In conclusion, the effects of artificial sweeteners on gut microbiome and metabolism warrant careful consideration. As the scientific community continues to explore these relationships, consumers should be proactive in evaluating their dietary choices. Artificial sweeteners may offer short-term benefits, but their long-term impact on gut health could lead to complications that should not be overlooked. Striking a balance between enjoying sweet flavors and fostering a healthy gut microbiome is possible through informed decisions. It is critical for everyone to assess individual responses and consult with healthcare providers if needed. By prioritizing gut health and considering the implications of artificial sweeteners, individuals can contribute to their overall well-being. Navigating the complexities of diet in the modern world requires a multifaceted approach. It is more than merely considering calories; it extends into understanding how food shapes our microbial landscape. Gathering knowledge, being intentional about dietary choices, and promoting gut health will remain vital in successfully integrating sweeteners into a healthy lifestyle.
In conclusion, the effects of artificial sweeteners on gut microbiome and metabolism warrant careful consideration. As the scientific community continues to explore these relationships, consumers should be proactive in evaluating their dietary choices. Artificial sweeteners may offer short-term benefits, but their long-term impact on gut health could lead to complications that should not be overlooked. Striking a balance between enjoying sweet flavors and fostering a healthy gut microbiome is possible through informed decisions. It is critical for everyone to assess individual responses and consult with healthcare providers if needed. By prioritizing gut health and considering the implications of artificial sweeteners, individuals can contribute to their overall well-being. Navigating the complexities of diet in the modern world requires a multifaceted approach. It is more than merely considering calories; it extends into understanding how food shapes our microbial landscape. Gathering knowledge, being intentional about dietary choices, and promoting gut health will remain vital in successfully integrating sweeteners into a healthy lifestyle.