Time-Restricted Eating and Its Impact on Gut Health
In recent years, time-restricted eating (TRE) has gained considerable attention as a dietary approach that might enhance gut health. Time-restricted eating involves limiting food intake to specific hours of the day, typically ranging from an 8 to a 10-hour window. Some proponents argue that this eating pattern can foster a more significant balance within gut microbiota. These microorganisms play a pivotal role in digestion, metabolism, and overall health. TRE can help mitigate inflammation, regulate gut permeability, and improve metabolic health. Studies suggest that aligning eating patterns with circadian rhythms may optimize digestive processes. By restricting eating hours, individuals may experience better blood sugar regulation and hormonal balance, which are crucial factors in gut health. It also allows the gut to have adequate time for repair and regeneration. When food is consumed in a limited time frame, it may support weight management and reduce caloric intake. This article explores the various mechanisms by which TRE can influence gut health positively. Understanding these associations illuminates the potential benefits of adopting a time-restricted eating regimen for those looking to enhance their gut health significantly.
Research has demonstrated that time-restricted eating may help mitigate gastrointestinal disorders such as bloating, indigestion, and even irritable bowel syndrome (IBS). Many of these disorders are attributed to imbalances in gut bacteria that occur due to excessive eating patterns. By adopting TRE, individuals allow their digestive systems to rest, which can alleviate symptoms associated with these conditions. Moreover, research indicates that natural hunger cues may become more pronounced under this regime, allowing individuals to recognize when they are genuinely hungry. The practice of eating within a defined time frame may encourage healthier food choices since individuals often plan their meals more thoughtfully. Furthermore, limiting eating hours aligns with the body’s natural circadian rhythms. This means that digestion happens when the body is prepared for it, limiting disturbances caused by late-night eating. While incorporating TRE offers benefits, it’s essential to recognize individual needs and variations in responses. Not everyone will achieve the same results when implementing TRE. Therefore, consultation with a healthcare professional is advisable before starting any new dietary regimen to ensure it aligns with personal health goals.
Effects on Gut Microbiota
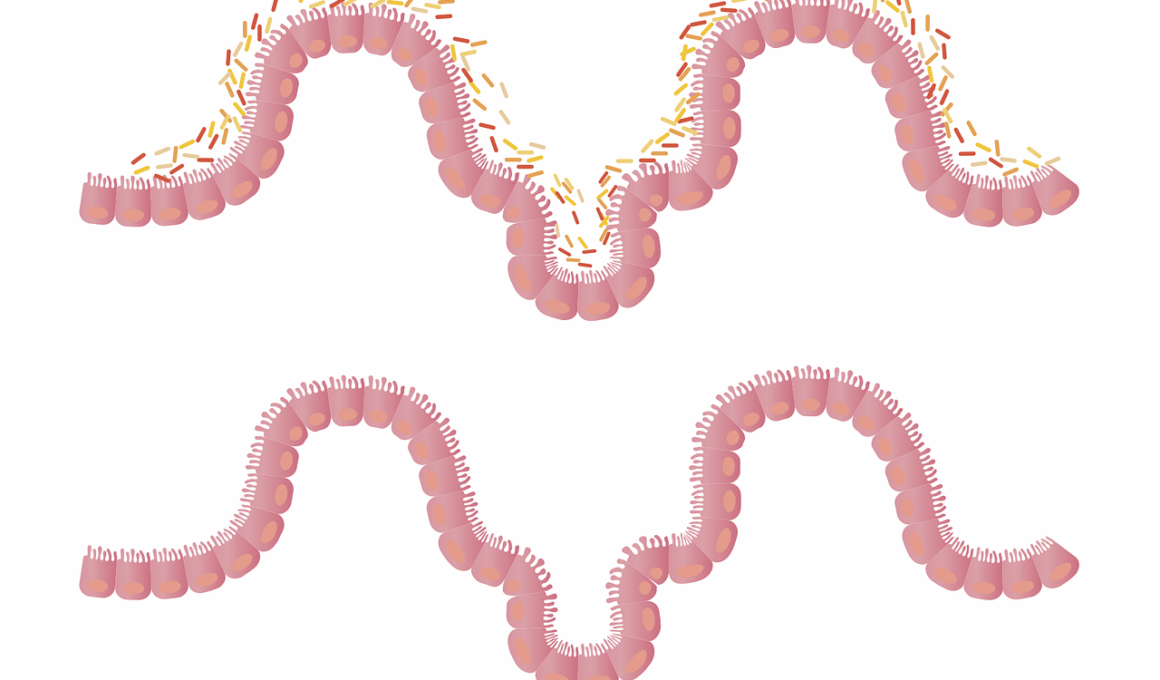
Studies on time-restricted eating indicate significant modulation of gut microbiota composition. Gut microbiota play an intricate role in metabolism and health, contributing to immune function, digestion, and synthesis of certain vitamins. Some researchers found that a limited eating window could lead to increased diversity of beneficial gut bacteria. Greater diversity in gut microbiota is often linked to improved metabolic health and lower inflammation levels. When food is consumed in a close window, gut bacteria adapt to this routine, optimizing their efficiency in fermentation and nutrient absorption. Furthermore, studies suggest that certain bacterial populations might thrive within these eating patterns, enhancing the breakdown of complex carbohydrates. These beneficial bacterial strains can produce short-chain fatty acids (SCFAs), which are vital for colon health. SCFAs help manage gut inflammation and support gut barrier function. A healthy gut barrier prevents harmful substances from entering the bloodstream. By fine-tuning eating patterns, it’s possible to make positive changes to the gut microbiome, which can reflect favorable health outcomes. Thus, TRE represents a promising prospect for managing gut health through dietary manipulation.
Incorporating time-restricted eating into daily habits can also lead to improved overall metabolic responses. By restricting the timing of meals, individuals may experience enhanced insulin sensitivity, which plays a pivotal role in metabolic health. This improved sensitivity is particularly essential for those concerned with weight management or metabolic syndrome. Additionally, TRE may support weight loss efforts by naturally reducing caloric intake without strict calorie counting. As a person’s time window for eating shrinks, there is often a decrease in excessive snacking throughout the day. This can lead to a more sustainable weight loss strategy. Furthermore, metabolic benefits might also stem from the potential reduction of late-night eating, which has been associated with weight gain and poor health outcomes. Some individuals may find that they feel bloated or uncomfortable after eating extensively during late hours. By adopting a time-restricted eating pattern, individuals gain the ability to harness their natural energy peaks while minimizing negative effects on gut health. Listening to one’s body and recognizing proper training can dramatically change one’s dietary approach and the overall gut experience.
Benefits Beyond Gut Health
The implications of time-restricted eating extend beyond just gut health benefits. Many participants in TRE studies reported enhanced energy levels and reduced fatigue. These effects may be attributed to improved metabolic processes stemming from consuming food during daylight hours, which coincides with natural circadian cycles. As energy utilization improves, so does overall well-being. Additionally, individuals following TRE often report better sleep quality, which is crucial for gut health and overall health. Good sleep can enhance metabolic regulation and contribute to the vitality of gut bacteria. Furthermore, the practice has been linked to positive changes in biomarkers associated with cardiovascular health. Studies have shown reductions in blood pressure and cholesterol levels among those engaging in TRE. This suggests that a time-restricted approach has multifaceted benefits that encompass not just gut health but cardiovascular and metabolic health as well. Embracing such a dietary approach can foster a holistic attitude towards well-being and enhance quality of life. However, it is important to combine such eating patterns with a balanced diet to fully reap the benefits.
While time-restricted eating shows promising results in gut health, it is vital for participants to tailor the approach to their lifestyles. It is essential to balance the quality of food consumed within the eating window to maximize gut benefits. Whole foods, including fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, and healthy fats, should be prioritized during these meals. Moreover, it’s advisable to avoid processed foods high in sugar and unhealthy fats, as they can contribute to gut dysbiosis. Additionally, drinking adequate amounts of water remains crucial during fasting and eating periods. Hydration supports digestion and helps flush out toxins from the body. Listening to one’s body and adjusting meal timing or content based on individual responses can also enhance outcomes. Everyone’s body responds differently to dietary changes, and it’s critical to be aware of these reactions. Tracking changes in digestion and overall health can provide insights that encourage positive adjustments to dietary habits. Adopting a flexible approach to time-restricted eating can lead to long-term improvements and a sustainable lifestyle.
Conclusion
In conclusion, time-restricted eating presents a compelling approach to improving gut health through both physiological and behavioral mechanisms. By creating an eating regimen that limits food intake to specific hours, individuals can experience an array of benefits, including improved metabolic health, better gut microbiota composition, and enhanced overall well-being. As the research on time-restricted eating continues to evolve, further studies are needed to identify the long-term effects and optimal eating windows for different populations. Overall, TRE offers an exciting dietary approach that allows individuals to align their eating habits with their body’s natural rhythms. For anyone interested in enhancing their gut health and achieving a balanced lifestyle, adopting a time-restricted eating pattern may be a beneficial option. As always, it’s advisable to seek guidance from healthcare professionals when making substantial dietary changes. They can provide personalized recommendations tailored to individual health needs and goals. Embracing time-restricted eating could be a key step toward sustaining a healthier, vibrant life.
As you consider incorporating time-restricted eating into your routine, remember that patience and persistence are essential. Making significant lifestyle changes takes time, and results may not be immediate. Tracking your progress, whether it’s improvements in digestion, energy levels, or overall health, can motivate you along the journey. Being aware of any challenges that may arise is similarly important. Adapting to a new eating schedule can be tricky at first, and some may experience hunger during fasting periods. However, it’s crucial to differentiate between actual hunger and habitual snacking habits. Gradually adjusting your eating window can help ease this transition. Attending to your body’s hunger signals can help you develop a more intuitive relationship with food. Overall, time-restricted eating offers a promising avenue for balancing gut health and metabolic wellness. Pairing this dietary approach with mindful eating practices and balanced consumables can yield optimal results. As we advance our understanding of nutrition, conditions like gut health continue to gain importance in holistic well-being. Adopting innovative eating methods such as TRE can be instrumental in nurturing health, including a healthy gut microbiome.