The Relationship Between Androgens and Gut Health
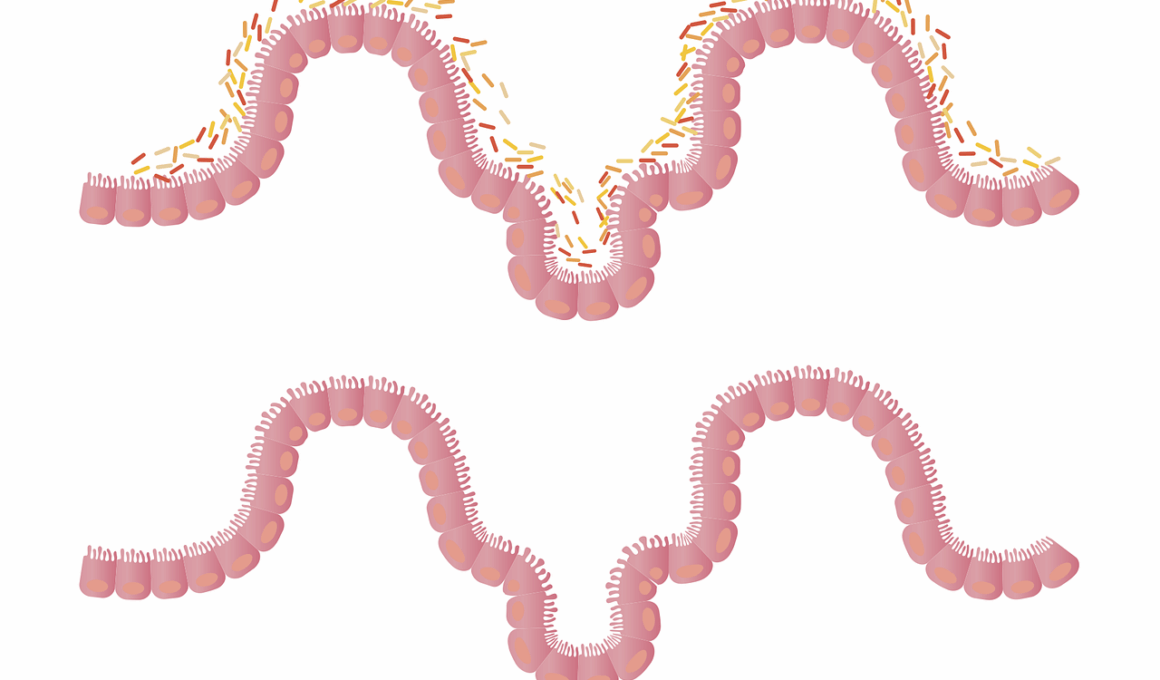
Androgens, commonly associated with male biological functions, play a significant role in both male and female health. These hormones, including testosterone, impact numerous bodily systems, including our digestive health. Understanding how androgens interact with gut function is critical for recognizing broader hormonal health. Research indicates a complex relationship exists between androgens and the gut microbiome, which is the collection of microorganisms residing in the gastrointestinal tract. A balanced gut microbiome is vital for optimal digestion, metabolism, and overall health. Androgens influence the microbiome composition and the gut lining through their action on various receptors throughout the digestive system. They can modulate inflammation, alter gut permeability, and affect the secretion of digestive enzymes, which can impact how nutrients are absorbed. Furthermore, gut health also influences androgen levels, making the relationship bidirectional. For example, dysbiosis, an imbalance in gut bacteria, may lead to lower testosterone levels in men and women. This two-way street highlights the importance of maintaining a healthy gut for hormonal balance, emphasizing the need for dietary and lifestyle interventions that promote gut health effectively.
Impact of Gut Health on Androgen Levels
Those interested in hormonal health should consider the impact that gut health has on androgen levels. The gut microbiome affects hormone metabolism, which includes androgens. Gut bacteria aid in the metabolism of hormones, converting testosterone into its more active form, dihydrotestosterone (DHT). A healthy gut microbiome ensures this conversion occurs optimally, leading to effective testosterone activity. Conversely, an unhealthy gut influenced by poor diet and lifestyle choices can lead to dysbiosis or microbial imbalances. This imbalance can hinder proper hormonal conversion and result in decreased testosterone levels. Moreover, inflammation originating from gut issues may disrupt the hypothalamic-pituitary-gonadal (HPG) axis, which regulates testosterone production. Certain strains of beneficial bacteria are known to enhance enzyme activity for hormone regulation, creating a positive feedback loop. This means promoting gut health could potentially increase androgen levels. Dietary choices rich in prebiotics and probiotics can support this microbiome balance. Foods like yogurt, sauerkraut, and fibrous vegetables contribute to a healthier gut microbiome, ultimately supporting hormone metabolism. Thus, prioritizing gut health is essential for anyone looking to manage their androgen levels and overall hormonal health.
A study focusing on athletes showed that those with better gut microbiome diversity had higher testosterone levels. This finding suggests that athletes’ performance and recovery may be improved by supporting gut health. Factors such as exercise and diet certainly contribute to this relationship; however, gut health itself may play a crucial role in regulating hormonal health as well. Additionally, mental health and stress levels have been linked to both gut health and androgen production. Chronic stress can negatively affect gut permeability and lead to inflammation, which may reduce androgen levels. Implementing stress-reducing practices like yoga, meditation, and proper nutrition can positively impact gut health, subsequently supporting hormone levels. Scientific literature indicates that the gut-brain axis, the communication pathway between the gut and the brain, is also pivotal in maintaining hormonal balance. The microbiome sends signals that communicate with the brain, potentially influencing anxiety and stress responses. As a result, managing mental health through diet and lifestyle choices can lead to enhanced gut health and, consequently, better hormonal regulation.
Dietary Interventions for Gut and Hormonal Health
Individuals seeking to improve their androgen levels through gut health can benefit from specific dietary interventions. Incorporating foods rich in omega-3 fatty acids, such as salmon and walnuts, may lower gut inflammation and support hormonal regulation. Furthermore, engaging in a fiber-rich diet can promote a healthy gut microbiome. Foods like whole grains, legumes, fruits, and vegetables provide essential nutrients to nurture beneficial bacteria, contributing to better digestion and hormone balance. Fermented foods, like kefir and kimchi, introduce important probiotics that promote microbial richness in the gut. Studies have also shown that antioxidants, found in various fruits and vegetables, help combat oxidative stress, which can negatively affect androgen levels and overall health. Consuming a balanced diet with adequate micronutrients, such as zinc and magnesium, is important as well. These minerals are involved in testosterone production and can influence androgen levels. In conclusion, focusing on a well-rounded diet can support both gut health and hormonal balance, making it a crucial part of any hormonal health strategy.
Supplementation is another approach individuals might consider for hormonal balance through gut health. Many studies show that probiotics can have a positive impact on hormone levels. However, it is crucial to select strains that specifically support androgen activity. For instance, Lactobacillus and Bifidobacterium strains have demonstrated effectiveness in addressing gut issues associated with hormonal imbalances. These beneficial bacteria can help reduce inflammation and improve gut health, leading to better testosterone levels. Additionally, certain dietary supplements, such as zinc and vitamin D, may support androgen levels as well. Zinc deficiency has been linked to decreased testosterone production in both men and women, while vitamin D can enhance testosterone synthesis in the body. Before starting any supplementation, it is essential to consult with a healthcare professional. They can evaluate individual needs and ensure a targeted approach that addresses specific gut and hormonal health concerns. The process of restoring gut health is not instantaneous; it requires commitment to dietary changes and possibly supplementation. However, the long-term benefits are significant, as maintaining hormone balance can enhance overall health and well-being.
Conclusion: The Importance of Holistic Approaches
Understanding the relationship between androgens and gut health emphasizes the need for a holistic approach to hormonal health. Many individuals may recognize the importance of hormones in relation to mood, energy, and overall well-being. However, few realize how significantly gut health impacts these hormonal levels. By recognizing the interconnectedness of these systems, individuals can employ strategies that not only support hormone balance but also improve digestive health. Strategies that promote a healthy microbiome, such as dietary interventions, stress management, and targeted supplementation, can enhance overall hormonal health. Furthermore, it is essential to remember that health is a complex tapestry, affected by various lifestyle choices, environment, and genetics. Therefore, personalized plans are necessary to address the unique needs of each individual effectively. Regularly working with healthcare providers to assess gut health and hormonal levels can also provide additional guidance. As research progresses in this area, approaching hormonal health from a holistic perspective will likely deliver better outcomes. Engaging with this knowledge can empower individuals to take proactive steps toward achieving optimal hormonal balance.
In conclusion, the intricate connection between androgens and gut health is a critical aspect of hormonal health that deserves greater attention. By understanding how these two factors interact, individuals can make more informed decisions regarding their diet, lifestyle, and overall health. Factors such as stress management, dietary interventions, and targeted supplementation can lead to better gut health, which in turn supports balanced androgen levels. This holistic perspective not only addresses immediate concerns but also paves the way for long-term wellness. As findings emerge about the relationship between gut microbiota and hormones, it is increasingly clear that maintaining gut health is essential to achieving optimal hormonal balance. Whether you are an athlete looking for performance enhancement or simply aiming to feel better overall, recognizing this relationship is vital. Nurturing your gut microbiome can be a transformative step in promoting better androgen levels, thereby enhancing energy, mood, and quality of life. Emphasizing gut health can lead to a positive ripple effect across other body systems, confirming that an integrated approach to health fosters overall well-being.
Further Research and Future Directions
Finally, ongoing research into the gut-hormone relationship offers exciting potential for future strategies in hormonal health management. Understanding specific mechanisms through which gut health affects androgen levels will enhance our ability to tailor interventions that maximize health outcomes. For instance, ongoing studies examine the role of specific gut bacteria strains in testosterone metabolism. Identifying these pathways might open doors for targeted probiotics or dietary modifications to optimize hormone production. Additionally, integrative approaches combining nutrition, supplementation, and stress management strategies can create a multi-faceted plan for individuals striving for hormonal balance. This holistic approach, grounded in evidence-based research, will be essential to developing comprehensive health strategies. Working closely with healthcare providers will ensure that individuals are receiving appropriate guidance based on their unique health profiles. As science continues to unfurl the relationship between gut health and androgen levels, it is crucial for individuals to stay engaged and informed. In doing so, they can leverage this knowledge to foster their own health, empower informed decisions, and potentially reduce the frequency of hormonal disruptions.