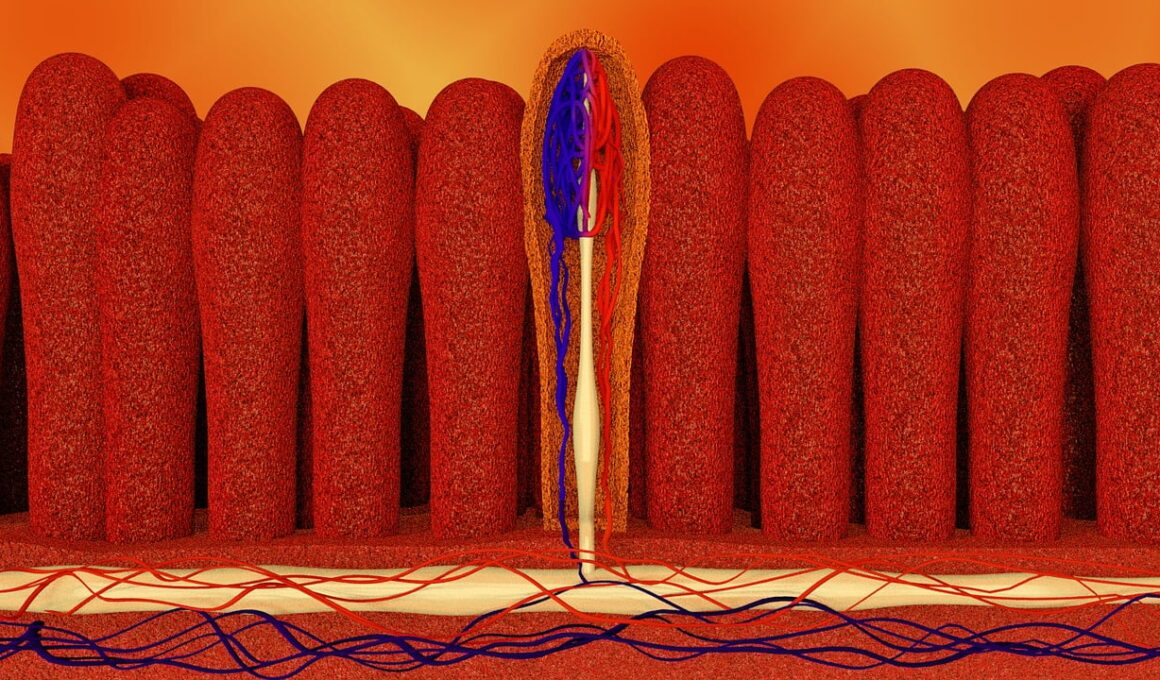
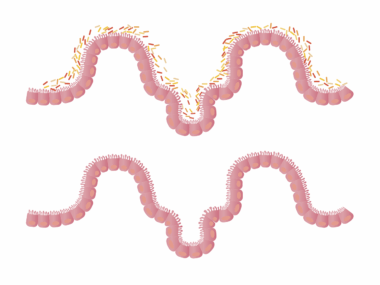
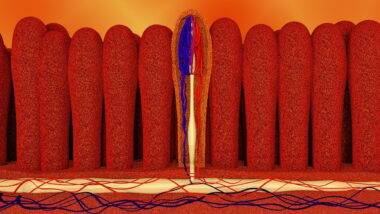
Meal Timing and Its Influence on Small Intestine Function
Understanding meal timing is essential in relation to gut health, particularly how it influences small intestine function. The small intestine plays a crucial role in nutrient absorption, digestion, and overall gastrointestinal health. Disruptive eating patterns can lead to various digestive issues, affecting not just the intestines but the entire digestive system. Meal timing can enhance or impair gut function, depending on when and how we consume food. Studies suggest that consistent meal timing may promote optimal gastrointestinal function, reducing symptoms such as bloating and gas. There is emerging evidence indicating that aligning meal times with the body’s circadian rhythm may further improve gut health. Both the timing and composition of meals can impact gut bacteria, thus influencing digestion. It is important to consider individual habits, including how often people eat and in what time frames. This highlights the connection between meal timing and not only gut function but overall health well-being. Adjusting meal times could be a simple yet effective strategy for those seeking to improve their digestive health.
Research suggests that irregular meal timing contributes to dysbiosis, a microbial imbalance in the gut. Dysbiosis can result from eating at inconsistent hours and may lead to various gastrointestinal problems. For instance, many people tend to skip breakfast or eat late at night, adversely affecting their gut microbiome. Losing synchrony with the body’s internal clock can result in inflammatory conditions, obesity, and even metabolic disorders. Furthermore, studies on intermittent fasting have shown promising results in restoring balance to the microbiome while also promoting a healthier digestive process. Individuals exploring meal timing interventions might notice reduced gastrointestinal distress and improved digestion, especially when they establish a regular eating schedule. This emphasis on routine can promote the healthy growth of beneficial gut bacteria, enhancing nutrient absorption. Exploring the impact of meal timing on gut health may also highlight potential dietary choices that can support better functioning of the entire digestive system. As everyone’s digestive system is unique, personalized meal timing approaches should be encouraged to optimize gut health while also enhancing overall quality of life. Understanding how meal timing informs gut health sets the stage for future research.
The Role of Circadian Rhythms
The relationship between meal timing and the body’s circadian rhythms cannot be overlooked when discussing gut health. The body’s biological clock influences when we should eat and when our digestive system functions optimally. Circadian rhythms regulate numerous physiological processes, including hormone release, digestion, and gut motility. Disrupting this rhythm can lead to various health challenges, such as obesity and metabolic syndrome. Eating in alignment with these rhythms, particularly during daylight hours, may enhance nutrient absorption and reduce the risk of gastrointestinal diseases. Studies indicate that consuming food late in the evening may lead to poorer digestion and less effective nutrient absorption. Emphasizing a meal pattern that respects these circadian rhythms encourages our bodies to perform essential functions efficiently. People who follow regular meal times aligned with daily light-dark cycles experience improved metabolic flexibility and gut health. Adjusting mealtimes to enhance alignment with natural light and dark cycles promotes a more balanced gut microbiome. This serves as a crucial reminder of the broader implications of meal timing on health.
Meal timing is not just about the schedule of eating but also flexible enough to accommodate individual lifestyle choices. For instance, shift workers, who face significant challenges in meal timing due to their irregular schedules, might benefit from tailored dietary interventions. These individuals are at increased risk for various health conditions, primarily due to misalignment between their work hours and the body’s natural rhythms. By employing strategic meal timing strategies, such as meal prepping or intermittent fasting, they can mitigate some negative effects. It is essential to focus on whole foods while ensuring that meals are nutrient-dense, irrespective of the timing. Adopting healthy choices can support digestive health, especially when habitual meal times reinforce gut function. Moderate amounts of fiber, healthy fats, and protein can further help maintain steady energy levels throughout the day and avoid undue digestive strain. Consequently, meal timing adaptations must consider individual preferences and lifestyle. Through proper planning, individuals can set their digestive system up for success, enhancing their overall well-being amidst unconventional daily routines.
Food Composition and Timing
The composition of the meals we consume is just as vital as when we eat them. A well-balanced diet, rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins, can optimize gut function. When combined with strategic meal timing, the health benefits multiply. For instance, having a protein-rich breakfast may promote satiety, with sustained energy levels extending throughout the day. Foods high in fiber support regular bowel movements and contribute positively to gut health, especially when fiber intake is timed effectively with meals. Pairing complex carbohydrates and proteins with healthy fats can stabilize energy levels and prevent rapid spikes in blood sugar, promoting sustained digestive health. When considering meal timing, people should also strive to consume antioxidants and phytonutrients, which support gut health and fight inflammation. Prioritizing specific food groups during certain times of the day can help maintain optimal digestive function while simultaneously fostering a balanced microbiome. Finally, remember that hydration is essential; drinking water helps digestion and nutrient absorption. Therefore, how we balance food composition with timing plays a vital role in our gut health journey.
The influence of meal timing on small intestine function also intersects with emotional and environmental factors. Stress and environmental cues can disrupt our usual eating patterns, leading to feelings of nausea or discomfort. Additionally, societal norms may promote certain eating times, such as late-night snacking or large meals. However, individuals who navigate through these disruptions should seek alternatives or practice mindful eating. Mindfulness in meals can facilitate proper digestion by focusing on the process rather than distractions like screens. Implementing practices such as gratitude before meals can shift focus towards appreciating food, positively impacting gut function. As people begin to understand the psychological implications of food and timing, adjusting their habits can favor overall better health. Engaging in regular physical activity may also support healthier meal timings, facilitating regulation of appetite and digestion. Recognizing the multifaceted relationship between emotional health and digestive function can empower people to make healthier choices. Ultimately, by addressing psychological and environmental factors, individuals can take charge of their gut health through conscientious meal timing.
Conclusion: Optimizing Gut Health
In summary, meal timing significantly influences small intestine function and overall gut health. Establishing regular patterns in eating not only aligns with biological rhythms but also can lead to a thriving gut microbiome. Consideration for meal composition and individual lifestyle choices plays an integral role in promoting digestive health. By emphasizing the timing of meals, people can support nutrient absorption and foster a balanced gut environment. Moreover, mindfulness about external factors affecting meal habits will prepare individuals to make thoughtful choices in their dietary routines. Exploring personalized meal timing interventions may guide those seeking to improve their gut health through simple but effective strategies. As science uncovers more about meal timing’s role, individuals may find new ways to tailor their diets. With increased awareness, optimizing meal timing could lead to transformative changes in health and well-being. When individuals prioritize both the time and the content of their meals, they set themselves up for long-term health and vitality. Continuous education about the digestion-gut health connection will drive public interest toward making enlightened dietary choices that resonate with today’s busy lifestyles.
Focusing on these key aspects of meal timing will help individuals form better habits around food intake, fostering a healthier gut.