The Role of Fiber in Keto Diets for Diabetes Control
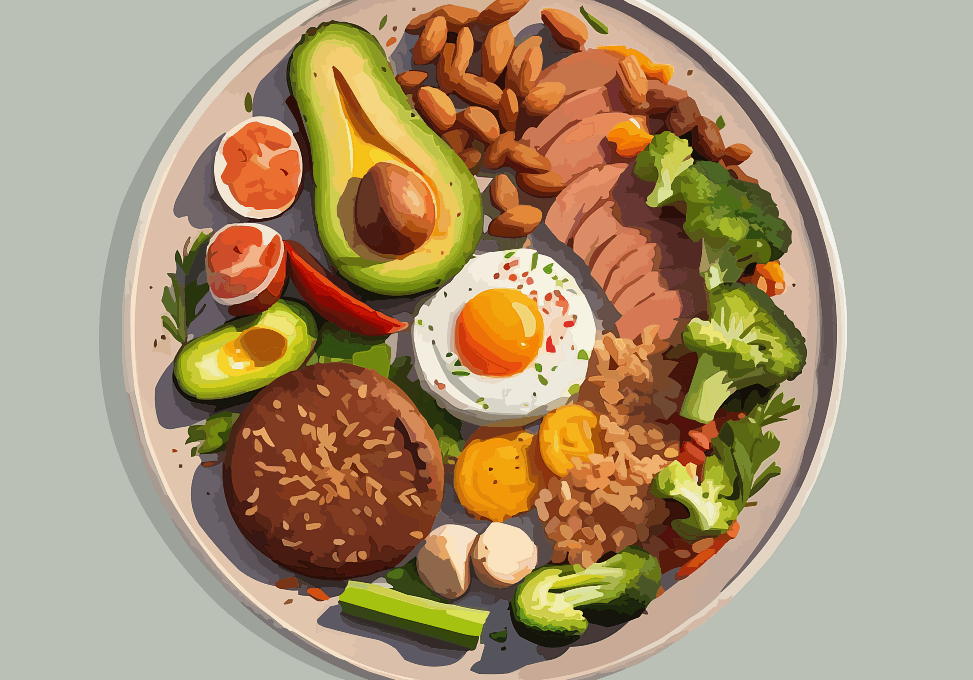
The ketogenic (keto) diet is a high-fat, low-carbohydrate eating plan that has been gaining attention, particularly for diabetes management. With the increase in ketone production in the body, insulin levels can stabilize, allowing for better blood sugar control. However, fiber plays a crucial role in optimizing the benefits of a keto diet for individuals with diabetes. Fiber is essential as it aids digestion and contributes to satiety, making it easier to manage caloric intake. Unlike other carbohydrates, fiber does not dramatically affect insulin levels. This helps in preventing spikes in blood sugar, which can be detrimental to diabetes management. Moreover, there are two types of fiber—soluble and insoluble. Soluble fiber slows down digestion and helps in the absorption of essential nutrients, while insoluble fiber aids in regular bowel movements and digestive health. Including fiber in a keto diet can also improve cardiovascular health, a concern for many individuals with diabetes. Thus, incorporating fiber-rich, low-carb foods is vital to achieve the best outcomes on this dietary path.
Benefits of Fiber in the Keto Diet
One of the many benefits of fiber on the keto diet is promoting healthy gut microbiota. A diverse gut microbiome supports overall health and is associated with better metabolic functions, which is crucial for those managing diabetes. Foods high in fiber, such as vegetables, nuts, and seeds, provide essential nutrients while keeping carb counts low, thus fitting perfectly within the keto framework. Additionally, high-fiber foods can help reduce the overall glycemic load of meals. This means that even if carb intake occasionally increases, the fiber can mitigate the impact on blood sugar levels. Research has indicated that people who consume adequate fiber may experience lower fasting insulin levels, improving insulin sensitivity—a key factor in managing diabetes. Furthermore, some studies suggest that fiber intake may assist in weight management by making individuals feel fuller for extended periods. In summary, the integration of fiber into the keto diet not only aids in digestion and metabolic function but also contributes to more stable blood glucose levels.
A common concern on a ketogenic diet is the potential for nutrient deficiency. This is where fiber comes in, as it can be derived from various low-carb food sources, ensuring individuals get a well-rounded intake of vitamins and minerals. Certain leafy greens, avocados, and even berries are keto-friendly options abundant in fiber. These foods are not only lower in carbs but also packed with vitamins such as C, K, and essential minerals like magnesium. The inclusion of these high-fiber foods ensures that individuals on a keto diet can maintain nutritional balance while achieving the desired level of ketosis. Importantly, dietary fiber can also support heart health, which can be particularly beneficial for those with diabetes, as they have an increased risk of cardiovascular disease. High fiber intake has been linked to lower levels of LDL cholesterol—often referred to as bad cholesterol. This occurs due to the fiber’s ability to bind to cholesterol in the gut, promoting its excretion. Consequently, this aids in reducing overall cholesterol levels, providing yet another strong argument for fiber’s critical role in the keto diet.
Incorporating Fiber into Keto Meal Plans
When planning meals on a ketogenic diet, identifying fiber sources can boost overall nutritional content significantly. From salads loaded with spinach, kale, or arugula to incorporating chia seeds in smoothies or yogurt, the opportunities for fiber are plentiful. Additionally, snacking on raw vegetables such as cucumbers or celery sticks topped with healthy fats like guacamole can offer fiber benefits without the carb load. Furthermore, flaxseeds can be a wonderful addition to baking keto-friendly bread or muffins, ensuring that fiber intake remains adequate. Exploring various keto recipes? Look for ones that emphasize vegetables and seeds to maximize fiber while keeping carbs minimal. Mushroom-based dishes or zucchini noodles are creative alternatives to traditional pasta that still maintain a high-fiber profile. For those looking to sweeten their keto recipes, consider low-carb fruits like raspberries or blackberries, which contain fibers while remaining compliant with a ketogenic diet. These adjustments can lead to delicious meals that are both satisfying and health-promoting.
While the importance of fiber is evident, some may struggle to increase their intake on a ketogenic diet due to its restrictive nature. Learning which foods offer the best fiber-to-carb ratios becomes essential. It’s also wise to gradually introduce fiber into meals to avoid digestive discomfort that may arise from a sudden increase in intake. Staying hydrated is equally important as it helps improve fiber’s role in digestion. Drinking sufficient fluids helps the fiber work effectively—reducing the risks of constipation. It’s beneficial to be mindful of the need for hydration, especially for individuals with diabetes. Fiber supplementation through low-carb fibers available in shakes or bars can also be an alternative. Not all fibers are created equal, and choosing high-quality sources, such as psyllium husk, can be beneficial. In conclusion, focusing on fiber-rich foods within the keto diet and supplementing where necessary can play a critical role in managing diabetes effectively. Individuals must remain committed to gradually increasing their fiber intake to reap the full range of benefits.
Monitoring Fiber Intake
Monitoring fiber intake can be a helpful strategy in maximizing the advantages of a keto diet, especially for individuals with diabetes. Keeping a food diary or using tracking apps can allow users to see the fiber content in foods consumed daily. These tools can also help ensure carb limits remain within range while encouraging fiber-rich food choices. Another strategy is to focus on high-volume, nutrient-dense foods—fulfilling meals that will provide plenty of fiber without spiking blood glucose levels. Awareness of portion sizes without compromising fiber intake helps individuals maintain control over their dietary goals. For instance, understanding the net carbs in low-carb fruits can aid better decision-making while on a keto plan. Moreover, it is essential for individuals to listen to their bodies. If experiencing discomfort, it may be worth reevaluating fiber sources and adjusting their approach. Regular consultations with healthcare providers are also wise, as they can offer personalized advice on incorporating fiber effectively in keto diets tailored for diabetes management.
In summary, fiber emerges as a vital component of the ketogenic diet, especially for individuals managing diabetes. The benefits of fiber extend beyond digestive health to include improved blood glucose control, feelings of fullness, and enhanced cardiovascular health. To derive maximum benefits, individuals should focus on strategically incorporating high-fiber foods and monitoring their intake. The inclusion of various low-carb, fiber-rich foods—like leafy greens, nuts, seeds, and select berries—can contribute to overall well-being. There’s no doubt that the keto lifestyle must evolve to accommodate fiber needs effectively, to avoid potential nutritional deficiencies. However, this transition may come with initial challenges; those new to keto must remain patient and willing to experiment. Consultation with nutritionists or dieticians specializing in dietary plans can provide invaluable support. By balancing fat intake and fiber consumption, it is possible to enjoy the full potential of a keto diet while safeguarding against the complications often posed by diabetes. All in all, a fiber-rich keto diet is not just feasible; it is an important key to managing diabetes.
In summary, fiber emerges as a vital component of the ketogenic diet, especially for individuals managing diabetes. The benefits of fiber extend beyond digestive health to include improved blood glucose control, feelings of fullness, and enhanced cardiovascular health. To derive maximum benefits, individuals should focus on strategically incorporating high-fiber foods and monitoring their intake. The inclusion of various low-carb, fiber-rich foods—like leafy greens, nuts, seeds, and select berries—can contribute to overall well-being. There’s no doubt that the keto lifestyle must evolve to accommodate fiber needs effectively, to avoid potential nutritional deficiencies. However, this transition may come with initial challenges; those new to keto must remain patient and willing to experiment. Consultation with nutritionists or dieticians specializing in dietary plans can provide invaluable support. By balancing fat intake and fiber consumption, it is possible to enjoy the full potential of a keto diet while safeguarding against the complications often posed by diabetes. All in all, a fiber-rich keto diet is not just feasible; it is an important key to managing diabetes.