Stress, Gut Dysbiosis, and Nutritional Interventions
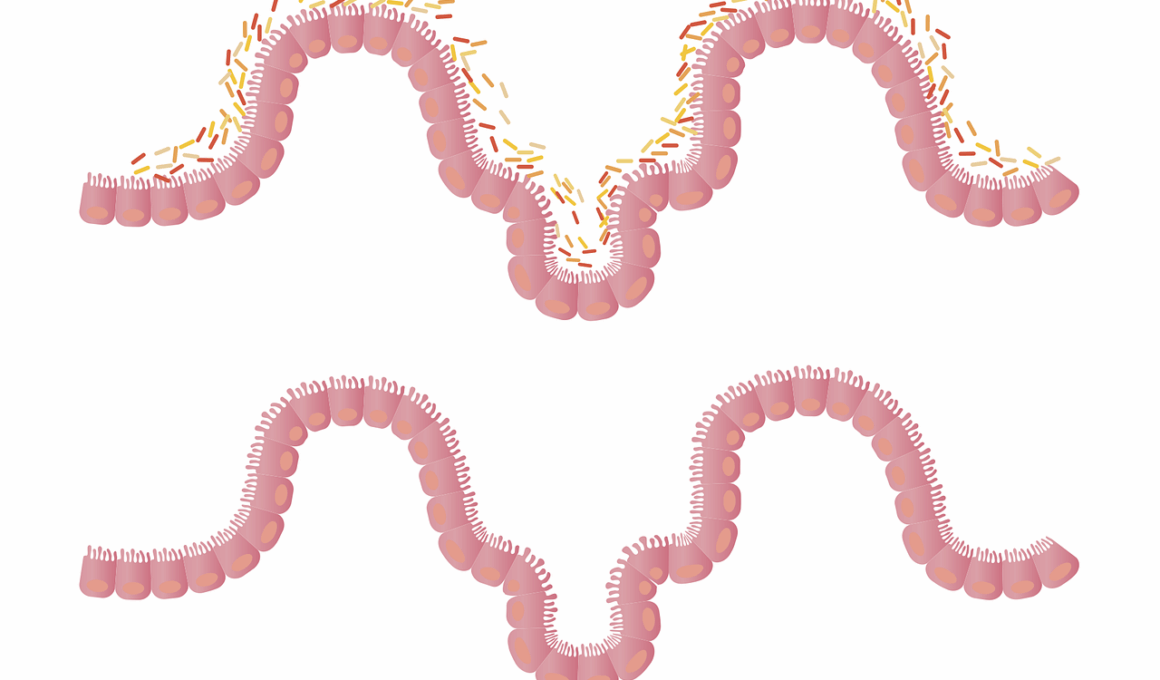
Stress is a significant factor influencing gut health, contributing to conditions like gut dysbiosis. Gut dysbiosis refers to an imbalance in the gut microbiome, which can negatively affect digestion, immune function, and overall health. This imbalance can arise from various factors, including chronic stress, poor diet, and lifestyle choices. Stress activates the body’s fight-or-flight response, releasing hormones like cortisol that can alter the gut environment. As a result, beneficial bacteria may decrease, while harmful bacteria can proliferate. The diversity and composition of the gut microbiome are essential for maintaining a healthy gut environment. A diverse microbiome fosters better digestion and enhances immune responses. Therefore, understanding the link between stress and gut health is crucial for developing effective nutritional interventions. Restoring balance in the gut microbiome can lead to improved overall health and well-being. Incorporating stress-reducing practices, such as yoga, meditation, and deep breathing exercises, alongside a balanced diet rich in probiotics and prebiotics, may help mitigate the adverse effects of stress on gut health. In the next sections, we explore nutritional strategies to combat gut dysbiosis.
Understanding Gut Dysbiosis
Gut dysbiosis can manifest in various ways, causing symptoms that range from digestive disturbances to immune dysfunction. It often results from unhealthy lifestyle choices, including poor dietary habits. Diets high in processed foods, sugars, and unhealthy fats contribute to an imbalance in the gut microbiome. Furthermore, stress exacerbates this imbalance, affecting the gut-brain axis. When stress levels rise, the gut’s permeability can increase, allowing harmful substances to enter the bloodstream. This phenomenon, often referred to as ‘leaky gut,’ can lead to inflammation and various health issues. Additionally, insufficient intake of essential nutrients can diminish the gut’s ability to maintain microbial diversity. Foods rich in fiber, such as fruits, vegetables, and whole grains, support beneficial bacteria by providing necessary nutrients. Fermented foods, including yogurt, kefir, and sauerkraut, introduce probiotics, which are live beneficial bacteria. To correct gut dysbiosis, individuals should adopt dietary changes that promote microbiome health and resilience to stress. Personalized nutrition plans focusing on whole foods can significantly improve gut health and overall well-being.
Probiotics have gained considerable attention for their role in restoring gut health, particularly during times of stress. They are live bacteria that confer health benefits when consumed in adequate amounts. Research suggests that probiotics can help restore the balance of the gut microbiome by increasing the population of beneficial bacteria. They can also enhance the gut’s barrier function, reduce inflammation, and even improve mood. Some specific strains, such as Lactobacillus and Bifidobacterium, have been shown to positively influence gut health and mitigate the effects of stress. Moreover, probiotics may modulate the gut-brain axis, influencing brain function and behavior. In addition to probiotics, prebiotics, which are non-digestible fibers that nourish beneficial gut bacteria, play a vital role in maintaining gut health. Foods rich in prebiotics include garlic, onions, bananas, and asparagus. Incorporating both probiotics and prebiotics into one’s diet is essential for restoring gut health, especially in situations of chronic stress. Overall, further research is needed to define specific probiotics effective in various situations, but their potential is significant and promising.
Dietary Strategies for Stress Management
Managing stress is crucial for maintaining a healthy gut microbiome, and dietary strategies play a key role in this process. Consuming a well-balanced diet that includes a variety of nutrient-dense foods can provide the body with the necessary tools to combat stress and support gut health. Incorporating whole foods, such as fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, and healthy fats, can help reduce inflammation and promote well-being. Omega-3 fatty acids, found in fish, flaxseeds, and walnuts, are particularly beneficial in managing stress levels. Furthermore, magnesium-rich foods like leafy greens, nuts, and seeds can help improve stress resilience. Hydration also plays a vital role in maintaining a healthy gut function. Drinking adequate water throughout the day supports digestion, nutrient absorption, and the elimination of waste. Regular meal patterns and mindful eating practices can help regulate blood sugar levels and reduce stress. By prioritizing nutrient-rich foods and hydration, individuals can enhance their ability to cope with stress while promoting a healthy gut microbiome. Emphasizing these dietary strategies can significantly impact managing stress and gut health.
Moreover, lifestyle changes are essential for reducing stress and supporting gut health. Regular exercise is one of the most effective stress management tools. Physical activity promotes endorphin release, enhancing mood while also benefitting gut health. Even moderate activities, such as walking or yoga, can help alleviate stress. Additionally, establishing a consistent sleep schedule is crucial for overall well-being. Sleep deprivation can negatively affect the microbiome, leading to increased stress levels and dysbiosis. Mental health is also integral to gut health; practices such as mindfulness and meditation promote relaxation and emotional resilience. Connecting with nature can also serve as a powerful stress reliever; studies show that spending time outdoors can enhance mood and reduce anxiety. Social connections and support systems are equally important; fostering positive relationships can buffer stress effects. Integrating these lifestyle changes with dietary interventions creates a holistic approach to improving gut health and managing stress. Individuals should aim to create a supportive environment that prioritizes well-being. Overall, the synergy between diet and lifestyle interventions plays a significant role in promoting a healthier gut microbiome.
Supplementing for Gut Health
In addition to dietary and lifestyle changes, supplements may play a beneficial role in enhancing gut health. Supplements such as probiotics can provide targeted benefits, especially when dietary sources are insufficient. High-quality probiotic supplements may help restore gut balance, particularly during periods of stress or dietary upheaval. Additionally, certain vitamins and minerals such as vitamin D, zinc, and B vitamins are vital for maintaining gut health. These nutrients can modulate the immune response, reduce inflammation, and support the integrity of the gut barrier. Omega-3 fatty acid supplements can provide additional anti-inflammatory benefits, further supporting both mental and gut health. However, individuals should consult with healthcare professionals before starting any supplementation. Personalized advice based on individual health needs ensures that supplements chosen align with dietary goals. It is essential to focus on whole food sources of these nutrients while considering supplements as an adjunct strategy. Integrating healthy foods with supplements can provide a synergistic effect that promotes a balanced gut microbiome. Further research continues to clarify the best practices for supplementing gut health, but current evidence is encouraging.
In conclusion, understanding the interplay between stress, gut dysbiosis, and nutritional interventions is crucial for maintaining a healthy gut microbiome. Chronic stress can negatively impact gut health, leading to dysbiosis and various health issues. Implementing dietary strategies focused on whole foods, prebiotics, and probiotics is essential for restoring balance. Furthermore, lifestyle practices like regular exercise, adequate sleep, and stress management techniques can significantly benefit gut health. Supplements can also provide additional support, especially during challenging periods. By adopting a holistic approach that encompasses both dietary and lifestyle changes, individuals can enhance their resilience to stress and promote a healthy gut microbiome. Future research in this field will continue to shed light on effective strategies for improving gut health and addressing stress-related dysbiosis. Ultimately, fostering a healthy gut microbiome plays a vital role in overall well-being and quality of life. Attention to diet, stress management, and lifestyle choices is key to achieving optimal health outcomes. Emphasizing these principles can help individuals lead healthier lives and unlock the benefits of a balanced gut.