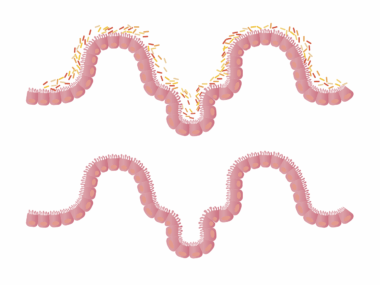
The Impact of Smoking on Gut Microbiome and Healing
Smoking is a behavior that not only harms the lungs but also significantly affects the gut microbiome. When we smoke, various harmful substances enter the body, disrupting the delicate balance of our gut bacteria. This imbalance may lead to various gastrointestinal issues, including inflammation and various digestive disorders. Smokers may experience a decreased abundance of beneficial bacteria, such as lactobacilli and bifidobacteria, which play a crucial role in gut health. In addition, smoking is associated with an increase in pathogenic bacteria, which contributes to gut dysbiosis. Studies have shown that individuals who smoke are at a higher risk for developing irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) and other gut-related problems. Moreover, quitting smoking can lead to potential improvements in gut health, highlighting the role of lifestyle choices in maintaining a healthy microbiome. Overall, the impact of smoking on the gut microbiome is multifaceted and detrimental, necessitating serious consideration for smokers regarding their gut health and general well-being.
Gut healing protocols are essential for restoring gut health after damage caused by smoking or other factors. A comprehensive approach can involve dietary changes, supplementation, and lifestyle modifications. For instance, increasing the intake of fermented foods like yogurt and kimchi, known for being rich in probiotics, can help restore beneficial bacteria. Additionally, incorporating prebiotics found in foods such as bananas and asparagus supports the growth of healthy gut microbiota. Supplements like omega-3 fatty acids and glutamine can also contribute to gut healing. Furthermore, reducing processed foods and refined sugars can have a positive impact on gut health. Lifestyle changes, including regular exercise and stress management, are vital for promoting a balanced gut microbiome. Sleep is another critical factor, as it can influence gut health significantly. By embracing these gut healing protocols, individuals can mitigate the adverse effects of smoking and enhance their overall gut health, paving the way for a healthier lifestyle.
Understanding Gut Dysbiosis
Gut dysbiosis refers to an imbalance in the gut microbiome, often characterized by a decrease in diversity and a change in composition. Smoking can directly contribute to this disbalance, making it crucial to understand its implications. A healthy gut typically contains a wide variety of bacteria that work synergistically to promote proper digestion and immune function. However, smoking introduces toxins that can suppress beneficial bacterial growth and promote dysbiotic conditions. As a result, smokers often report various digestive issues, including bloating, gas, and constipation. Interestingly, studies suggest that dysbiosis can extend beyond immediate gastrointestinal symptoms, influencing mental health and overall well-being. The relationship between gut bacteria and mood, often referred to as the gut-brain axis, shows that imbalances may be linked to anxiety and depression. Addressing gut dysbiosis through targeted dietary changes and lifestyle modifications is critical for those who smoke or have smoked in the past. By restoring gut health, one can significantly improve how the body processes food and removes toxins, ultimately benefiting overall health.
To repair damage caused by smoking, specific nutrients play pivotal roles in gut healing protocols. Incorporating vitamins such as vitamin C and vitamin E, both of which have antioxidant properties, can help combat oxidative stress inflicted by smoking. Omega-3 fatty acids, found in fatty fish like salmon and walnuts, can reduce inflammation and promote the healing of gut tissues. Furthermore, minerals such as zinc are crucial for maintaining mucosal integrity, ensuring the gut barrier functions effectively. Additionally, certain herbal supplements like aloe vera or slippery elm have been used to soothe gastrointestinal irritation and promote healing. A holistic approach that includes hydration, adequate fiber intake, and nutrient-dense meals is also beneficial. Staying well-hydrated helps maintain optimal digestion and nutrient absorption, vital components of gut healing. Through understanding the essential nutrients and their roles in healing protocols, individuals can better equip themselves to recover from the adverse effects of smoking.
The Role of Probiotics in Gut Recovery
Probiotics have gained attention as crucial players in gut recovery, especially for individuals affected by smoking. These beneficial microbes help restore the balance of the gut microbiome, counteracting the detrimental effects of harmful bacteria. Probiotic strains such as Lactobacillus and Bifidobacterium can significantly improve gut health by enhancing the body’s natural defenses and promoting digestion. They may also help in alleviating symptoms associated with dysbiosis, such as bloating and irregular bowel movements. Incorporating probiotic-rich foods into one’s diet can be easily achieved through yogurts, fermented vegetables, and supplements. Moreover, research indicates that probiotics may influence immunity, providing additional health benefits beyond gut health. While some individuals may opt for probiotic supplements, obtaining these beneficial bacteria from whole foods is regarded as the most natural approach. It’s essential to consult a healthcare professional to determine the best probiotics tailored to individual needs, as different strains offer various health benefits. By prioritizing probiotics in gut recovery efforts, individuals embrace a proactive step towards better gut health.
In addition to diet and probiotics, managing stress levels is critical for gut healing. The gut-brain connection illustrates how emotional well-being directly influences gut health. Stress can lead to gastrointestinal issues, emphasizing the need for relaxation techniques like meditation and yoga. Engaging in physical activity regularly not only alleviates stress but also promotes healthy digestion and can enhance gut bacteria diversity. Practices such as mindfulness can foster a positive mindset, contributing to better overall health outcomes. Incorporating adequate sleep into one’s routine is equally impactful; sleep deprivation has been associated with alterations in gut microbiota composition. Establishing restorative sleep patterns can help restore the balance necessary for optimal gut health. Furthermore, community support and sharing experiences with others facing similar gut health challenges can lead to encouragement and motivation. When individuals take a proactive approach to manage their stress and overall lifestyle, they greatly enhance their chances of healing their gut. By integrating these strategies, one can successfully navigate the process of gut recovery after the damaging effects of smoking.
Conclusion and Future Directions
In conclusion, the impact of smoking on gut microbiome health is profound and multifaceted. The adverse effects on gut bacteria can lead to dysbiosis and numerous digestive problems. To counteract these effects, implementing gut healing protocols is beneficial. This includes dietary adjustments, introducing probiotics, managing stress, and prioritizing restorative practices. Each aspect contributes uniquely to promoting a balanced gut microbiome, paving the way for overall health improvements. Emerging research continually highlights the importance of these strategies and their effectiveness in restoring gut health. As understanding of the gut microbiome evolves, future directions may include personalized nutrition plans based on individual gut profiles. Collaborating with healthcare specialists can illuminate tailored approaches that match personal needs, improving outcomes for individuals impacted by smoking. Furthermore, ongoing education about the connection between lifestyle and gut health is essential to empower individuals to make informed choices. In summary, addressing the impact of smoking on gut health and implementing comprehensive healing protocols is pivotal for anyone looking to enhance their overall wellness.
The Science of Gut Healing