The Connection Between Gut Health and Mental Wellbeing
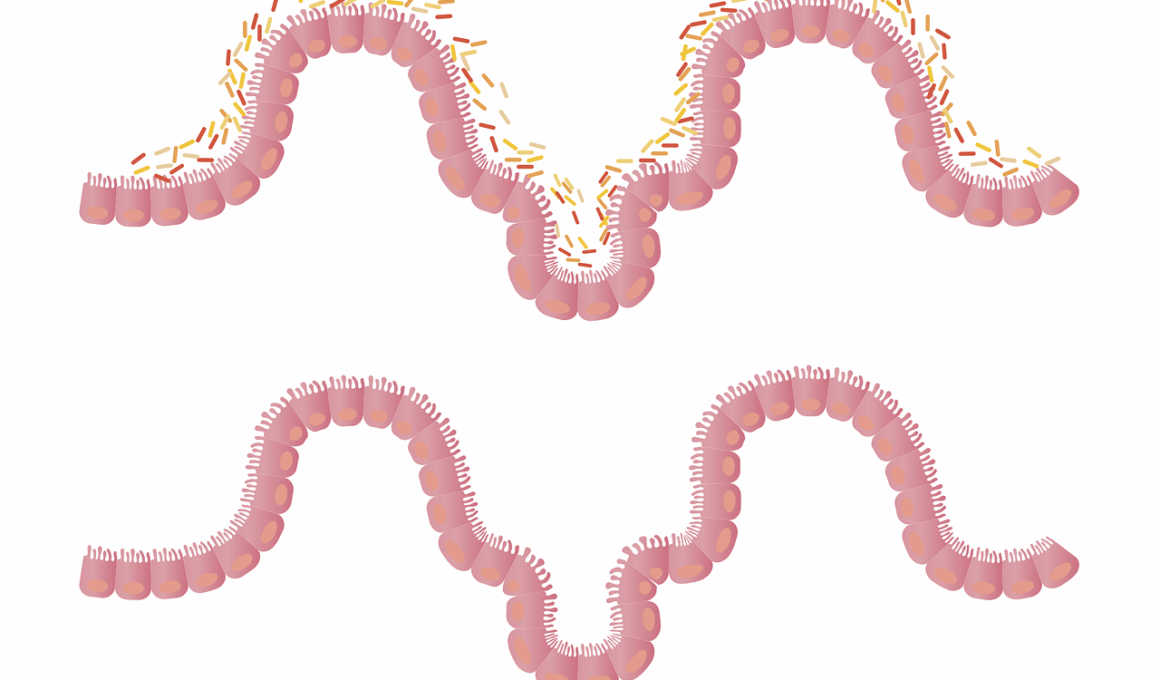
Gut health plays a significant role in overall wellbeing, particularly in its surprising connection to mental health. Many individuals may not realize that the gut, often referred to as the “second brain,” is home to trillions of microorganisms known as the gut microbiome. This complex system interacts closely with our brain through the gut-brain axis, a bidirectional communication pathway that links gastrointestinal function to emotional and cognitive processes. Poor gut health can lead to imbalances in gut bacteria, which may trigger mood disorders such as anxiety and depression. Research indicates that a diverse and healthy microbiome can positively influence mood and improve mental clarity. Foods rich in probiotics, such as yogurt and fermented vegetables, can help maintain gut balance, fostering better mood regulation. Maintaining a healthy diet, rich in fiber and nutrients, can significantly impact gut microbiome diversity. Therefore, taking care of gut health is not just essential for physical health, but also plays a crucial role in enhancing mental wellbeing, making it important for individuals to recognize the vital interplay between diet, gut health, and mental state.
Common gut disorders often emerge as a result of poor gut health, affecting not only physical but also mental wellbeing. Disorders such as irritable bowel syndrome (IBS), inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), and gut dysbiosis can lead to significant physical discomfort and stress. These conditions can create a cyclical relationship in which gut issues exacerbate anxiety and depression, while mental health struggles further complicate digestive problems. For instance, individuals suffering from IBS may experience heightened stress levels, which consequently worsen their gut symptoms. On the other hand, research has shown that improving gut health through diet and probiotics can alleviate some mental health struggles. Incorporating dietary changes designed to benefit digestion can positively affect emotional wellbeing. Eating a balanced diet with an emphasis on whole foods, fiber, and probiotic-rich items can significantly improve gut function and mental clarity. It’s crucial for individuals experiencing gut disorders to seek treatment and support, both for their physical symptoms and their overall mental wellbeing, addressing the interconnectedness of these issues in a holistic manner.
Exploring the Gut-Brain Connection
The connection between gut health and brain function has become a promising area of research. Scientists are exploring how the gut microbiome affects neurotransmitter production, the chemicals responsible for transmitting signals in the brain. About 90% of serotonin, a key neurotransmitter that influences mood, is produced in the gut. Therefore, disturbances in gut health can potentially lead to changes in serotonin levels, impacting emotional states. Various studies suggest that a diet rich in omega-3 fatty acids, fibers, and fermented foods can boost gut microbiota diversity, contributing positively to mental health. For example, fatty fish, like salmon, which are high in omega-3s, have been shown to improve cognitive function and reduce symptoms of depression. It is valuable for individuals to recognize the foods that nourish their gut might also protect against psychological distress. Consequently, implementing dietary changes can enhance both gut and mental health, showcasing the need for integrated approaches in treating mental health disorders. Understanding this intricate relationship can help individuals make healthier lifestyle choices that support overall wellness.
Stress and anxiety can worsen digestive problems, creating a loop that is hard to escape. When the body undergoes stress, it can influence gut motility and secretion, which may contribute to gastrointestinal issues. This leads to a greater sense of discomfort and anxiety, showcasing how mental states can influence gut function. In turn, exacerbated gut disorders can reinforce stress responses, leading to further psychological effects. Many individuals may experience symptoms such as bloating, diarrhea, or constipation during periods of high stress. Addressing mental health through various techniques like mindfulness, yoga, and cognitive-behavioral therapy can aid in alleviating these symptoms. These therapies promote relaxation and help disengage from the stressor, allowing the gut to function more optimally. It’s crucial for those experiencing symptoms of anxiety or stress-related gut disorders to practice stress management and seek professional thorough evaluation. By doing so, they can engage in effective coping strategies to mitigate the negative impacts stress can have on both their gut health and their mental wellbeing.
The Role of Diet in Gut and Mental Health
A balanced diet is foundational for good gut health, which ultimately supports mental health. Specific types of food can foster a diverse gut microbiome, benefiting mental processes. Antioxidant-rich foods such as leafy greens, berries, nuts, and seeds support inflammation reduction, which is vital for both gut and brain health. Conversely, highly processed foods high in sugar and unhealthy fats can disrupt gut bacteria balance. When the gut microbiome is unbalanced, it can lead to systemic inflammation that affects mood regulation. Knowledge about which foods promote gut health can empower individuals to make informed choices. Incorporating prebiotics, found in foods like garlic, onions, and bananas, further nourishes beneficial gut bacteria. As such, developing consistent dietary habits focused on whole, natural foods can lead to significant improvements in both physical digestion and mental performance. Encouraging these dietary changes within a regimen not only aids physical health but can support emotional resilience, highlighting why individuals should consider dietary choices alongside other wellness practices.
Finally, understanding the connection between gut health and mental wellbeing is vital for developing effective treatment methodologies. As research evolves, it reveals the complex relationship involving dietary influences, gut bacteria, and mental health conditions. Health practitioners should adopt a multi-faceted approach that considers diet, lifestyle, and mental health when treating patients. This approach can help encompass not only physical ailments but also emotional and cognitive aspects that patients may experience, supporting holistic care. Education and awareness initiatives that promote awareness about this relationship can empower individuals to take control of their wellness journey. Lifestyle changes, such as incorporating regular physical activity, investing in mental health care, and establishing social connections can bring improvements in both gut and mental health. Support groups that recognize these links may provide therapeutic benefits by offering shared knowledge and experiences. Ultimately, embracing this knowledge can lead to a more fulfilling and healthier life, showcasing the importance of maintaining both gut health and mental wellbeing for everyone.