How Fiber Helps Maintain Gut Integrity and Function
Dietary fiber plays a critical role in maintaining gut health, offering several benefits that support overall digestion. It comes in two forms: soluble and insoluble fiber. Soluble fiber dissolves in water, forming a gel-like substance that helps regulate blood sugar and cholesterol levels. On the other hand, insoluble fiber adds bulk to the stool, helping it pass more easily through the digestive tract. Both types are essential for healthy gut function because they feed beneficial gut bacteria, which contribute to digestive stability and health. Including a variety of fiber-rich foods in your diet naturally enhances gut integrity. Some excellent sources of dietary fiber include fruits, vegetables, whole grains, legumes, nuts, and seeds. These foods improve bowel regularity, prevent constipation, and reduce the risk of gastrointestinal disorders while also promoting a healthy weight. A balanced, fiber-rich diet provides lasting benefits, improving nutrient absorption and reducing the chance of diseases. It is essential to meet the recommended daily intake of fiber, which ranges from 25 grams for women to 38 grams for men. Eating fiber should be approached gradually to avoid digestive discomfort.
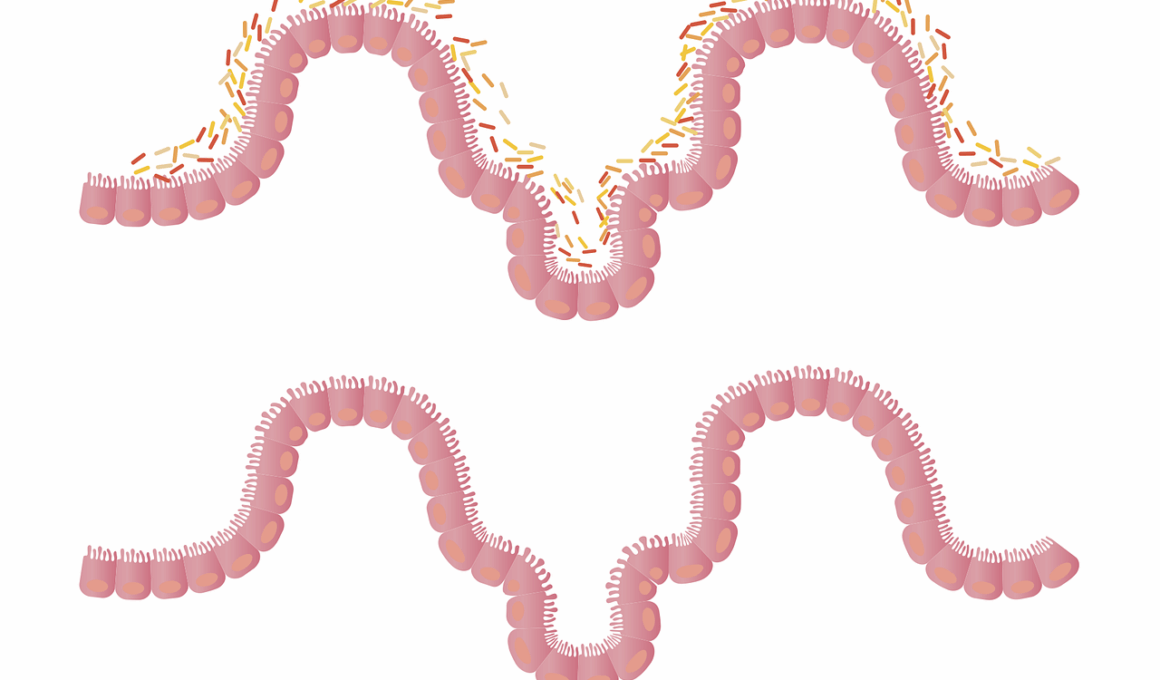
In addition to improving gut health, dietary fiber has other significant benefits that contribute to maintaining gut integrity. A high-fiber diet promotes the production of short-chain fatty acids (SCFAs) during fermentation in the colon. SCFAs, such as butyrate, are vital for maintaining the integrity of the intestinal lining and serve as an energy source for colon cells. This contributes to a stronger gut barrier, which helps prevent the entry of harmful bacteria and toxins into the bloodstream. Moreover, a robust gut barrier is crucial for reducing inflammation and lowering the risk of chronic diseases like diabetes and obesity. Various fiber sources, including oats, beans, and fruits, can positively impact SCFA production, directly linking fiber intake to gut health. Regular consumption of dietary fiber not only bolsters gut integrity but also helps modulate the immune response, ensuring that the gut remains resilient against pathogens. Emphasizing a diverse intake of fiber-rich foods is vital to support the development and maintenance of a healthy gut microbiome, ultimately providing benefits that extend beyond digestion to overall health.
The Role of Soluble Fiber
Soluble fiber significantly contributes to digestive health by supporting gut integrity and proper function. It dissolves in water to form a gel-like substance, which slows digestion and enhances nutrient absorption. This complex process allows the body to better utilize the vitamins and minerals from the food consumed. The slower absorption rates help control blood sugar levels, reducing the risk of spikes that can lead to insulin resistance. Additionally, soluble fiber is instrumental in managing cholesterol levels, ultimately contributing to cardiovascular health. Foods rich in soluble fiber include oats, legumes, apples, and citrus fruits, which can be easily incorporated into meals and snacks. Incorporating these foods into daily diets helps foster the growth of beneficial bacteria in the gut, which relies on soluble fiber for sustenance. However, it is essential to gradually increase fiber intake to allow the digestive system to adjust. The benefits of soluble fiber extend to enhanced satiety, helping control appetite and leading to more successful weight management. Understanding the importance of soluble fiber in the diet is crucial for maintaining overall gut function and integrity.
Insoluble fiber, another crucial form of dietary fiber, provides numerous benefits for digestive health and gut integrity. Unlike soluble fiber, it does not dissolve in water, adding bulk to the stool and facilitating regular bowel movements. This property helps prevent constipation and promotes a healthy digestive system, which is vital for overall health. A healthy digestive tract minimizes the risk of developing conditions such as diverticulosis and irritable bowel syndrome (IBS). Foods high in insoluble fiber include whole grains, nuts, seeds, and many vegetables like broccoli and carrots. These foods contribute to the physical structure of the stool, promoting efficient elimination from the body. Additionally, insoluble fiber supports the growth of diverse gut microbiota, which fosters a balanced and healthy gut environment. A diet rich in both soluble and insoluble fibers can lead to more profound health benefits, including reduced inflammation and improved immune function. As such, it is essential to incorporate adequate amounts of both types of fiber to support overall digestive health and maintain gut integrity. Regular intake of insoluble fiber complements soluble fiber, creating a well-rounded approach to fiber consumption.
Gut Microbiome and Fiber
The gut microbiome consists of trillions of microorganisms that play a vital role in digestion, immune function, and overall health. Dietary fiber is a key player in supporting the growth and maintenance of the gut microbiome. Fiber acts as a prebiotic, feeding beneficial bacteria in the gut and promoting their proliferation. This, in turn, contributes to a diverse microbiome, which is crucial for optimal gut function and integrity. When the microbiome is well-balanced, it enhances the body’s ability to digest food efficiently and absorb nutrients effectively. Furthermore, a healthy gut microbiome helps regulate metabolism, reducing the risk of obesity and metabolic syndrome. Certain fiber types, such as inulin found in chicory root, are particularly effective at stimulating the growth of beneficial bacteria. Regular consumption of fiber supports a flourishing gut microbiome, which has far-reaching effects on overall health. A diverse and balanced microbiome can improve mental health, combat inflammation, and protect against gastrointestinal disorders. Incorporating various fiber-rich foods into one’s diet naturally supports the health of the gut microbiome, leading to tangible benefits over time.
Maintaining gut integrity does not solely rely on fiber intake; hydration plays an equally crucial role. Fiber works best when adequately hydrated, as it absorbs water and facilitates a smoother flow through the digestive system. This combination of fiber and hydration promotes regular bowel movements and optimizes the overall digestive process. Drinking enough water throughout the day is essential for supporting the bulk-forming properties of both soluble and insoluble fiber. Dehydration can lead to constipation, negating the benefits of fiber and causing digestive discomfort. Therefore, it is recommended to consume plenty of fluids, particularly when increasing fiber intake. The synergy of fiber and hydration enhances gut integrity by ensuring that the digestive system functions optimally. Additionally, adequate hydration can help in the formation of SCFAs from fiber fermentation, further showcasing the interconnectedness of these dietary factors. A simple approach can be taken – often relying on water intake, herbal teas, and high-water-content fruits and vegetables. This ensures a well-functioning digestive system, promoting gut integrity while maximizing fiber’s many benefits for digestion and health.
Conclusion
In conclusion, dietary fiber is vital for maintaining gut integrity and optimal digestion. Both soluble and insoluble fibers play unique roles in the digestive process, promoting the health of the gut microbiome and reinforcing the intestinal lining. Regular consumption of various fiber-rich foods improves bowel regularity, nutrient absorption, and overall gut health. Additionally, fiber intake interacts synergistically with hydration to ensure that digestive functions operate smoothly. The benefits of a high-fiber diet extend beyond digestion, encompassing improvements in metabolic health, immune function, and inflammation reduction. To harness these benefits, it is essential to focus on incorporating adequate amounts of both types of fiber into daily meals, while also staying properly hydrated. This comprehensive approach can lead to profound long-term health advantages, making dietary fiber an indispensable component of a balanced diet. Whether through fruits, vegetables, legumes, or whole grains, the incorporation of fiber-rich foods fosters a thriving gut environment. Ultimately, achieving a well-rounded diet that prioritizes fiber intake contributes to health, vitality, and improved quality of life.
Understanding the critical importance of dietary fiber is essential for anyone looking to enhance their overall health and well-being. Making informed dietary choices not only supports gut integrity but also provides a range of other health benefits that contribute to long-term wellness. By prioritizing fiber and understanding its role in digestion and overall body function, individuals can take proactive steps to improve health outcomes. Whether seeking solutions for digestive discomfort or aiming to maintain optimum gut health, a focus on dietary fiber brings rich rewards. Educating oneself on fiber sources and incorporating diverse foods into daily meals is crucial in achieving these objectives. Embracing a fiber-rich lifestyle empowers individuals to optimize their digestion, support their gut microbiome, and promote overall wellness, paving the way for a healthier future. Research continues to highlight the connection between dietary fiber, gut health, and chronic disease prevention, highlighting the need for increased awareness and integration into daily diets. Choose to make dietary fiber a priority; the gut will thank you for it!