The Relationship Between Gut Health and Allergies
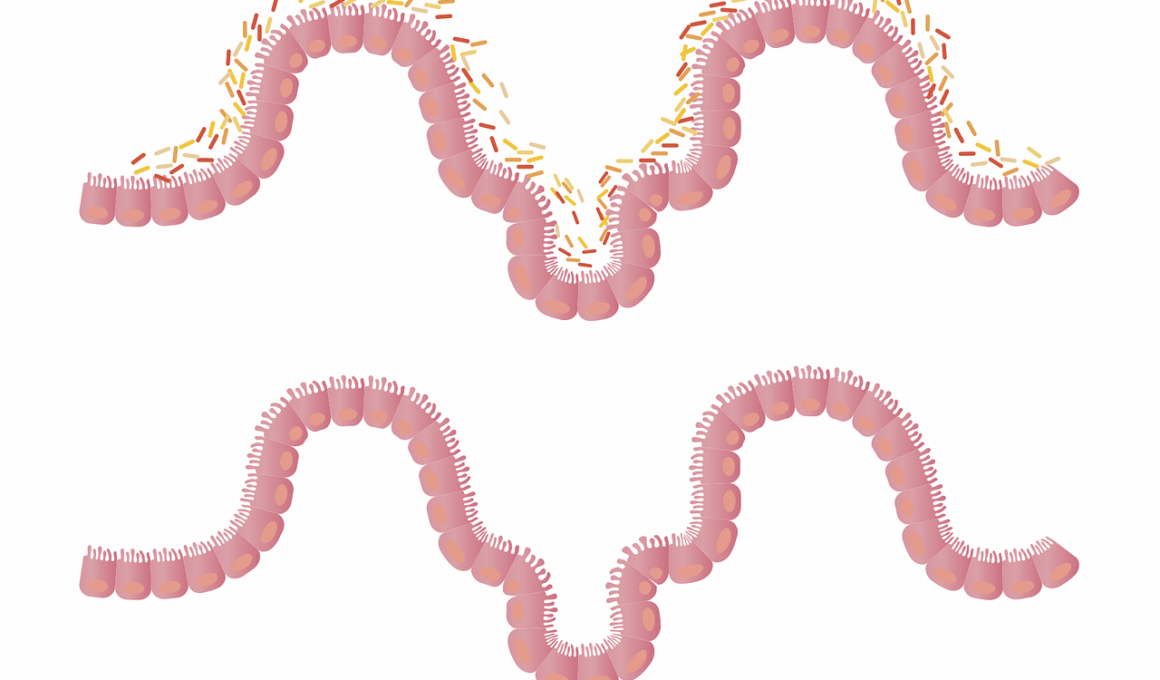
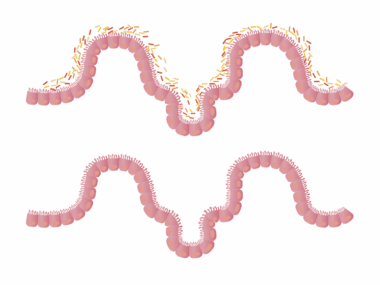
The connection between gut health and allergies is a vibrant area of research. Increasing evidence suggests that the gut microbiota plays a regulatory role in the immune system, which can subsequently impact the onset of allergic reactions. The gut is home to trillions of microorganisms that can influence local and systemic immunity. Dysbiosis, or an imbalance in gut bacteria, can lead to increased intestinal permeability, termed “leaky gut,” which may facilitate the entry of allergens into the bloodstream. This leads to heightened immune responses. Additionally, specific gut bacteria types have been associated with either promoting or inhibiting allergy development. Diet significantly impacts gut health, as a diverse diet rich in fiber can foster beneficial bacteria. Furthermore, early-life exposures, such as breastfeeding and living in rural environments, may offer some protection against allergies by nourishing the gut microbiota. Individuals with allergies often exhibit altered gut microbiomes, indicating a potential target for therapeutic intervention. Probiotics and dietary changes are being explored as methods to restore balance to the microbiota. Further understanding of this relationship may lead to more effective prevention and management of allergic diseases.
Considering the prevalence of allergic conditions in modern society, it is important to explore how gut health can influence these situations. Chronic allergies, including asthma, hay fever, and allergic dermatitis, are common and often debilitating. Research shows that alterations in gut flora can affect inflammation levels, which may worsen allergy symptoms. In contrast, a well-balanced gut microbiome may help mitigate inflammatory responses. Probiotics are gaining attention as possible adjunct therapies for allergies. They aim to restore balance in the gut microbiome and have been shown to reduce the incidence of certain allergic conditions when taken preemptively. Fermented foods like yogurt, kefir, and sauerkraut are excellent sources of probiotics and can be easily included in the diet. Investigating infant nutrition and its role on gut development is also crucial, as it can set the stage for later health. Additionally, encouraging gut-friendly habits like reducing processed foods while increasing fiber intake can have lasting benefits. Understanding the interplay between gut health and allergies can empower individuals in managing their health better. An integrative approach focusing on diet, lifestyle, and targeted interventions may provide a roadmap for improved allergy management.
Diet and Its Role in Gut Health
Diet is fundamentally crucial in influencing gut health and, by extension, allergy susceptibility. Foods high in fiber and nutrients support diverse microbiota, fostering a healthy gut environment. A diet rich in fruits, vegetables, legumes, and whole grains offers prebiotics that stimulate beneficial bacteria growth. On the contrary, processed foods high in sugars and unhealthy fats can lead to an imbalance in gut flora, potentially exacerbating allergic reactions. Gluten and dairy, common allergens, are often eliminated by those with allergies to assess their impact on symptoms. However, indiscriminate removal of these food groups without proper guidance may lead to nutrient deficiencies. Exploring potential food intolerances through systematic dietary approaches can yield insight into individual allergies. Moreover, consistent hydration supports gut function and helps maintain mucus membranes in the gastrointestinal tract. Personalized diets are a cutting-edge area of investigation, focusing on individual microbiota responses to certain foods. Future studies in this area hold promise for tailored dietary recommendations which could significantly lower allergy incidence. Ultimately, adopting a balanced and informed dietary approach may lead to enhanced gut health and mitigation of allergy symptoms.
Beyond dietary considerations, the relationship between environment and gut health cannot be overlooked, particularly concerning allergies. Modern living conditions, including urbanization and sanitization, have dramatically altered our gut microbiome, which could impact immune responses to allergens. Early-life exposure to diverse microbial environments, such as rural living or exposure to pets, can enhance gut health by promoting a richer microbiota, thereby potentially offering protection against allergies. Furthermore, antibiotics, often used in childhood, can disrupt gut microbiome development. Excessive use of antibiotics correlates with rising allergy rates worldwide, as these medications can eliminate beneficial bacteria. Working towards a more balanced microbial exposure, particularly during infancy, is vital for fostering strong immune responses later in life. Natural strategies, such as implementing varied diets and minimizing unnecessary antibiotic use, can help in nurturing a healthy microbiome. These efforts may promote resilience against allergy development. Thus, recognizing lifestyle and environmental influences on gut health empowers individuals to make informed decisions. The interaction between our environment, lifestyle, and gut health is complex but critical to understanding allergy dynamics in today’s world.
The Role of Probiotics in Allergy Management
Probiotics are live microorganisms that confer health benefits, particularly concerning gut health. They are often recommended as a part of a strategy to manage allergies effectively. Specific strains of probiotics have been shown to enhance gut barrier function, thereby mitigating the chances of allergens crossing into the bloodstream. Some research indicates that targeted probiotic supplementation during pregnancy or early life may help significantly in lowering allergy risk in children. Identifying which strains to employ is crucial, as not all probiotics offer the same benefits. Strains like Lactobacillus and Bifidobacterium have demonstrated promising results in alleviating symptoms of allergic rhinitis and eczema. Incorporating probiotic-rich foods such as kimchi, kombucha, and miso into the diet can enhance overall gut health while providing beneficial bacteria. Sustained consumption can lead to lasting changes in the gut microbiome, assisting in the reduction of allergies. However, it is essential to consult healthcare professionals when considering probiotics, especially in children or those with existing allergies. The emerging understanding around gut health reveals exciting potential for probiotics in shaping allergy responses and health outcomes.
Another invaluable aspect of holistic health involves integrating lifestyle factors that influence both gut health and allergies. Stress management is often an overlooked yet significant factor in maintaining good gut health. Stress can negatively impact gut microbiota composition, leading to heightened allergy sensitivity. Techniques such as mindfulness, meditation, and yoga can benefit mental well-being, thus promoting better gut functions. Regular physical activity is also vital for gut health, as exercise helps increase gastrointestinal motility and positively influences the microbiome diversity. Furthermore, maintaining a balanced sleep schedule supports the body’s recovery mechanisms, including those affecting gut health. Chronic sleep deprivation can disrupt hormonal imbalances that influence gut microbiota. Creative approaches such as gardening or spending time in nature can bolster psychological resilience and foster a more diverse microbial exposure. Therefore, recognizing the interconnectedness of these elements—diet, environmental exposure, stress, and lifestyle—can empower individuals toward proactive health approaches. These lifestyle adjustments, coupled with informed dietary choices, create a solid foundation for enhanced gut health that may reduce the risk of allergic conditions considerably.
Looking Ahead: Future of Gut Health Research
As research continues to evolve, the future of gut health and its connection to allergies presents exciting possibilities. Identifying the specific interactions between our gut microbiome and immune responses could lead to personalized preventive measures and treatments for allergies. Ongoing studies are exploring advanced sequencing technology aimed at mapping the complex interactions within the gut microbiota. This could reveal novel insights into how gut bacteria communicate with the immune system, opening new doors for therapeutic interventions. Furthermore, future research may uncover how environmental factors interact with our microbial inhabitants to drive health outcomes. The integration of machine learning techniques could expedite the discovery process of effective probiotics and specific dietary recommendations tailored to individual microbiomes. Efforts to increase public awareness about maintaining gut health and its implications for allergies will be crucial for preventative strategies. Embracing a proactive approach, making informed lifestyle choices, and continuing research discussions can establish a community that prioritizes gut health. Overall, the unfolding landscape of gut health research is promising, with the potential to transform the way we understand and manage allergies effectively.