Leaky Gut and Weight Gain: Is There a Connection?
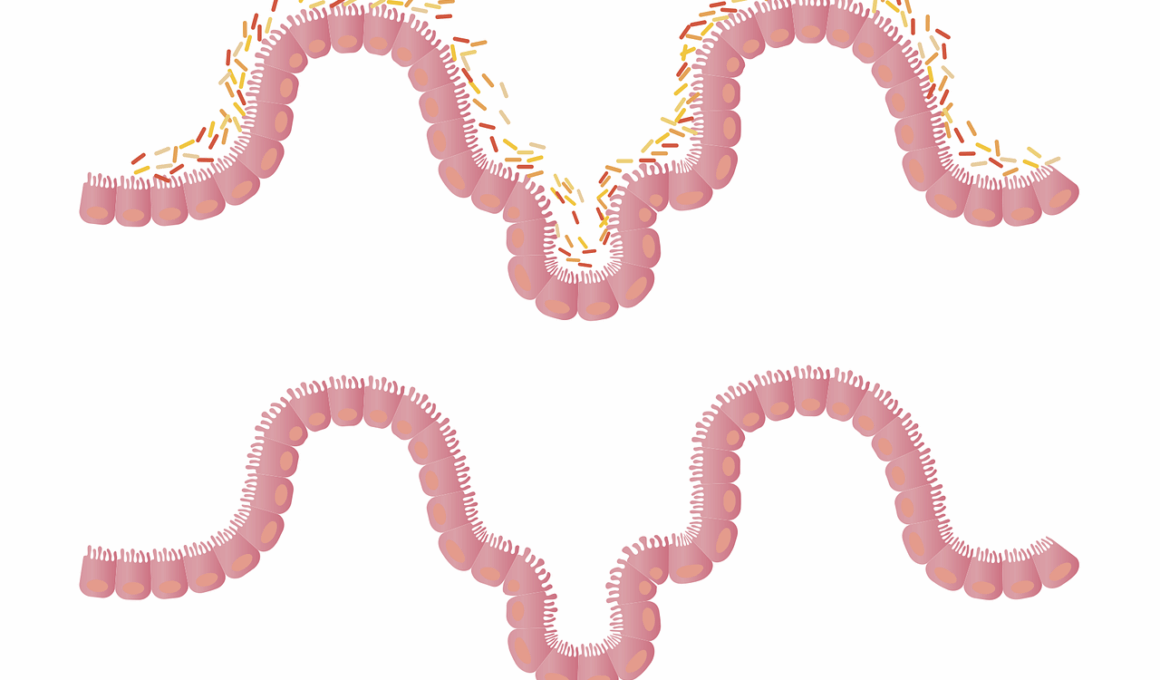
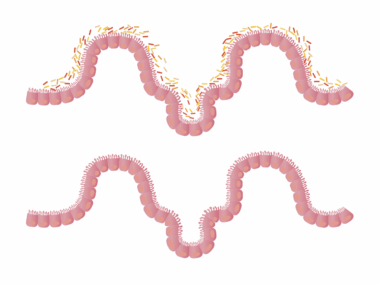
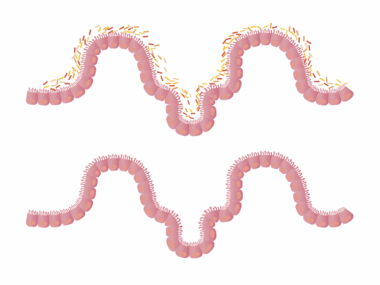
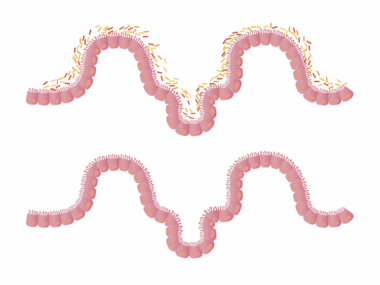
Leaky gut syndrome, characterized by increased intestinal permeability, has attracted significant attention in recent years, primarily concerning its links to weight gain. This condition allows toxins and undigested food particles to enter the bloodstream, triggering inflammation and immune responses. Consequently, individuals with leaky gut may experience a variety of health issues, including weight fluctuations. Research suggests that inflammation can lead to hormonal imbalances, particularly with insulin and cortisol, both of which play vital roles in weight management. Furthermore, when the gut microbiome is compromised, it may struggle to regulate hunger hormones effectively, resulting in increased appetite. In particular, studies have indicated that certain pathogenic bacteria associated with leaky gut can influence calorie absorption, further contributing to weight gain. It is important to differentiate between common weight gain caused by overeating and the more complex scenarios connected to gut health. Understanding how leaky gut influences body weight is essential for developing effective treatment strategies. Ultimately, restoring gut health through dietary changes and appropriate supplements may aid in weight management and overall well-being.
Understanding Leaky Gut Syndrome
Leaky gut syndrome emerges from various lifestyle factors, including poor diet, chronic stress, and environmental toxins. Highly processed foods, rich in sugars and unhealthy fats, can damage the gut lining, contributing to inflammation and permeability. Moreover, excessive alcohol consumption and certain medications, like non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), may exacerbate the condition. Individuals often experience symptoms such as bloating, gas, cramps, and food sensitivities. Leaky gut doesn’t solely impact digestion; it can also have widespread effects on emotional health, energy levels, and the immune system. Scientific evidence suggests that chronic inflammation from a leaky gut can lead to systemic diseases, including obesity and diabetes. As these conditions are intricately linked to hormone disruptions, they may complicate efforts to maintain a healthy weight. While there is a growing body of research on leaky gut, it remains controversial due to ongoing debates in medical circles regarding its specific existence and effects. Nonetheless, individuals experiencing symptoms may benefit from working with healthcare providers to address their gut health and associated weight concerns.
Diet plays a pivotal role in either promoting or alleviating leaky gut syndrome. Foods rich in fiber, healthy fats, and essential nutrients support gut healing and overall health. Fermented foods, such as yogurt, kefir, sauerkraut, and kimchi, are excellent sources of probiotics that help restore the gut microbiome. Additionally, incorporating bone broth and collagen-rich foods can strengthen the intestinal lining. Eliminating inflammatory foods, including gluten, dairy, and refined sugars, is often advised for individuals with leaky gut. Implementing an elimination diet initially helps identify specific triggers while allowing time for gut healing. Moreover, maintaining proper hydration is equally important for gut health. Staying well-hydrated supports digestive processes and aids in nutrient absorption. Supplements like L-glutamine, zinc, and probiotics may help reinforce the intestinal barrier and reduce inflammation. However, it is essential to consult with a healthcare professional before introducing supplements, as individual needs can vary significantly. Ultimately, a nutrient-dense, gut-friendly diet can significantly impact both leaky gut and overall body weight, making it essential for those looking to manage their health.
Link Between Weight Gain and Leaky Gut
Recent studies have established a stronger connection between leaky gut and weight gain, leading to a reevaluation of dietary approaches for weight management. The presence of metabolic endotoxemia, resulting from leaky gut, has been identified as a contributing factor to obesity. When harmful bacteria penetrate the gut lining, they release lipopolysaccharides (LPS) into the bloodstream, promoting systemic inflammation. This inflammatory response may lead to insulin resistance, making it harder for the body to regulate blood sugar levels and maintain a healthy weight. In fact, individuals with higher LPS levels tend to exhibit higher body mass indices (BMIs). The interplay between the gut, brain, and metabolism highlights how gut health can influence satiety signals and cravings, leading to excessive calorie intake. Furthermore, altered gut microbiota may inhibit the body’s ability to burn fat, adding a layer of complexity to weight loss efforts. Therefore, understanding the relationship between leaky gut and weight gain is crucial for developing effective dietary strategies. Addressing gut health can become a fundamental piece of the puzzle for achieving and maintaining healthy weight.
Incorporating lifestyle changes can significantly help in managing leaky gut and associated weight gain. Regular physical activity aids in reducing systemic inflammation, improving insulin sensitivity, and maintaining a healthy weight. Engaging in moderate exercise like walking, yoga, or strength training for at least 150 minutes per week can bring multiple benefits to gut health. Stress management techniques, such as mindfulness, meditation, and deep breathing exercises, play vital roles in reducing stress-induced gut issues. Stress can adversely affect the gut microbiome and increase intestinal permeability, exacerbating leaky gut symptoms. Improving sleep quality is equally essential, as inadequate rest can influence hormone levels and exacerbate weight gain issues. Aim for 7-9 hours of quality sleep each night to support gut healing processes. Furthermore, establishing a routine that promotes regularity, including consistent meal timings, can improve digestive function. Working with professionals, such as nutritionists and health coaches, can provide personalized guidance and support in the journey of healing and maintaining gut health. By addressing these lifestyle factors, individuals can facilitate better management options for both leaky gut and weight gain.
Conclusion: Healing the Gut
Healing the gut is a journey that requires time, patience, and commitment. Individuals must recognize that persistent weight gain associated with leaky gut often requires a multifaceted approach. The combination of dietary changes, lifestyle modification, and possibly medical intervention creates the necessary foundation for improvement. It is essential to adopt a holistic view, focusing on factors that contribute to leaky gut beyond food choices. Staying informed about gut health developments enables individuals to make educated choices and seek advice that aligns with their particular needs. Engaging with support groups or communities experiencing similar health challenges can provide valuable motivation and encouragement throughout this process. As individuals embark on their healing journey, they should embrace gradual changes that feel sustainable rather than quick fixes. With dedication, many can restore gut health, which may significantly impact overall health and manage weight issues effectively. Partnering with healthcare providers for personalized strategies and monitoring progress helps uphold accountability. Ultimately, achieving optimal gut health results in improved well-being and a higher quality of life for individuals.
People often gravitate towards certain gut-supporting strategies without entirely understanding their influence on weight. Integrating more awareness around gut health in mainstream discussions illuminates the physiological connections between diet, the microbiome, and body weight. The interdependencies between internal and external factors necessitates an integrated approach to health and wellness. This approach empowers individuals to make informed decisions about their choices and health behaviors. Continued research into the links among leaky gut, inflammation, and weight gain will expand knowledge and provide deeper insights. Furthermore, healthcare professionals must stay updated with emerging findings specific to gut health while promoting tailored treatment plans for patients. Practicing self-care that nurtures gut health fosters an environment for healing that goes beyond weight management and encompasses overall wellness. To address chronic conditions effectively, recognizing the complexity of human physiology further supports the need for personalized interventions. Individuals aiming for better gut health and weight management can benefit tremendously from becoming proactive in their wellness journeys. Overall, this proactive mindset can lead to greater success and satisfaction in achieving their health goals.