Antioxidants and Gut Microbiome Health in Autoimmune Disease Management
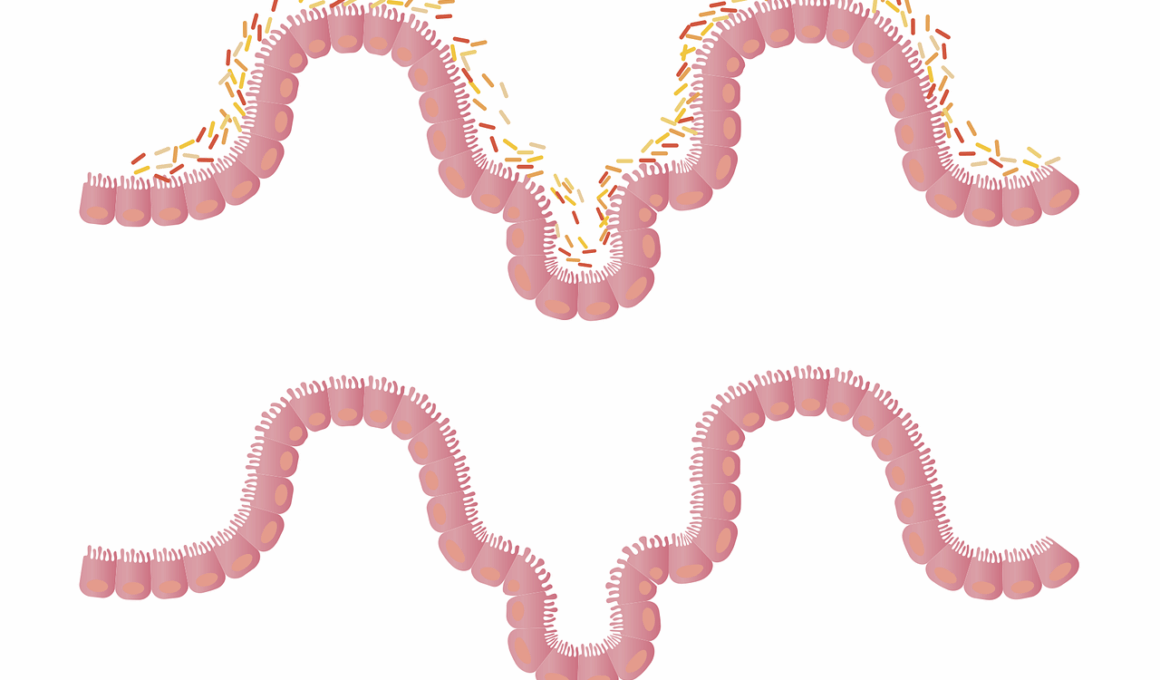
The gut microbiome plays a pivotal role in our overall health, particularly in the context of autoimmune diseases. Research indicates that the diversity and composition of gut bacteria can significantly impact the immune system’s function. A healthy microbiome may help in regulating inflammation and autoimmunity. Autophagy, the body’s process of breaking down and recycling damaged cells, can be influenced by gut microbes, thus highlighting their importance in sustaining bodily functions. One essential strategy to enhance gut health involves consuming antioxidant-rich foods. Antioxidants, such as vitamins C and E, can help combat oxidative stress, fostering a balanced gut environment. This balance allows beneficial bacteria to thrive while suppressing harmful pathogens. Consequently, various studies suggest that patients with autoimmune diseases may benefit from strategies that promote a healthy gut microbiome. Maintaining this balance through diet can aid in immune modulation. Certain probiotics, for instance, may also confer positive effects on gut health, further supporting immune responses aimed at reducing inflammation. Thus, bolstering the gut microbiome through antioxidants presents a promising avenue for improved outcomes in managing autoimmune diseases.
Numerous studies link oxidative stress and inflammation with the exacerbation of autoimmune conditions. High levels of free radicals can disrupt cellular functions and contribute to inflammatory processes. Antioxidants neutralize these free radicals, helping to mitigate potential damage. As such, integrating antioxidant-rich foods such as berries, nuts, and leafy greens into the diet becomes crucial. These foods not only provide essential nutrients but also foster a thriving gut microbiome. Experimenting with foods, such as fermented items like yogurt and kimchi, can further diversify gut bacteria, enhancing health benefits. A study conducted on patients with rheumatoid arthritis showed improvements when participants consumed antioxidants regularly. The outcomes indicated that these nutrients assisted in reducing inflammatory markers relevant to the disease. Moreover, herbal antioxidants like turmeric and green tea have gained attention for their potential in immune modulation. Additionally, maintaining hydration and consuming prebiotic foods can nourish beneficial gut bacteria. Through these dietary interventions, individuals can make strides towards better gut health, ultimately aiming to provide a conducive environment for fighting autoimmune ailments. Therefore, it’s essential to explore holistic approaches to optimize gut microbiome health.
How Gut Microbiome Affects Autoimmune Diseases
Scientific literature indicates a clear connection between gut microbiome composition and autoimmune diseases. A diverse microbiome can influence the immune system’s behavior, playing a critical role in maintaining homeostasis. Disruption or dysbiosis, characterized by a reduced diversity of gut flora, has been observed in several autoimmune conditions. Such imbalances can trigger abnormal immune responses. As an illustration, studies show that patients with conditions like multiple sclerosis may exhibit significant differences in gut microbial populations when compared to healthy individuals. Consequently, understanding the mechanisms by which gut bacteria influence autoimmunity can pave the way for innovative treatment strategies. Emerging research identifies specific bacterial strains that could be administered as probiotics to restore balance in dysbiotic microbiomes. Furthermore, these beneficial bacteria can produce short-chain fatty acids (SCFAs), which possess anti-inflammatory properties, fostering an improved gut environment. Preserving a healthy gut enables the immune system to communicate effectively without overreacting, making it a vital aspect of autoimmune disease management. Hence, cultivating favorable gut microbiota through dietary methods is not just beneficial but necessary for mitigating autoimmune conditions.
While antioxidants play a critical role in supporting gut health, it is essential to identify synergistic relationships between different dietary components. For instance, combining probiotics with fiber-rich foods can enhance their effectiveness. Foods like legumes, whole grains, and bananas act as prebiotics, feeding healthy gut bacteria and promoting resilience. Such comprehensive dietary strategies can further maximize the potential benefits of antioxidants. Enhanced gut flora from these combined approaches can lead to improved digestion, nutrient absorption, and comfort. Furthermore, anti-inflammatory diets, such as the Mediterranean or plant-based diets, emphasize whole and unprocessed foods rich in antioxidants, beneficial fats, and fiber. These patterns have shown promise in alleviating symptoms for many autoimmune diseases. Ensuring sufficient macronutrients also supports the microbial environment. It is crucial for individuals to maintain a balanced intake of proteins, carbohydrates, and fats while focusing on antioxidants. Each element contributes uniquely to gut health and overall well-being. Exploring these dietary patterns allows for making informed choices that align with health goals—especially for those managing autoimmune diseases. Therefore, embracing a holistic approach to nutrition can profoundly enhance gut microbiome stability.
The Role of Diet in Autoimmune Disease Management
A well-planned diet serves as a cornerstone in managing autoimmune conditions effectively. Especially, the Mediterranean diet has shown benefits in reducing inflammation and supporting gut microbiome diversity. This diet promotes a rich selection of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and healthy fats, which are abundant sources of antioxidants. Research advocates for the inclusion of omega-3 fatty acids found in fish and flaxseeds, recognized for their anti-inflammatory properties. Regular consumption of nutrient-dense foods aids in establishing a robust gut microbiome. Moreover, avoiding highly processed foods, refined sugars, and excessive saturated fats remains vital for individuals with autoimmune diseases. Such items have been linked to negative outcomes in gut health and increased inflammation. Integrating a variety of colorful plant foods enriches the diet with phytonutrients, which further boosts antioxidant levels while improving overall health. Adopting mindful eating practices, such as cooking at home and meal planning, can critically support personalization in dietary routines. Individuals and healthcare providers should acknowledge the intricate relationship between diet and autoimmune health, recognizing that engaging in informed dietary choices can significantly impact overall well-being.
Maintaining an active lifestyle can also complement dietary changes in managing autoimmune diseases. Regular physical activity is linked to improved gut health and increased microbial diversity. This diversification can, in turn, lead to enhanced immune responses, promoting resilience against autoimmune symptoms. Engaging in aerobic exercises, strength training, and flexibility workouts can offer numerous benefits. Individuals should consult healthcare professionals to create a tailored exercise plan that considers personal ability and health status. Ensuring adequate rest and reducing stress through practices such as yoga or meditation can also positively influence gut health. Chronic stress can disturb the gut microbiome balance, heightening vulnerability to autoimmune conditions. Initiating supportive mental health practices is essential for comprehensive autoimmune management. Alongside dietary attention, incorporating healthy lifestyle changes fosters a strong foundation for gut optimization. Lastly, staying hydrated is another straightforward yet impactful practice. Proper hydration aids in digestion and nutrient absorption while helping maintain mucosal barriers in the gut. These multi-faceted approaches—diet, exercise, and stress management—become integral to a holistic strategy for managing autoimmune diseases effectively. Thus, cultivating these habits can lead to lasting improvements in gut health.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the interplay between antioxidants, gut microbiome health, and autoimmune disease management underscores the importance of a holistic approach to wellness. Ensuring an antioxidant-rich diet, incorporating probiotics, and maintaining diversity in gut flora are crucial steps in promoting gut health. Additionally, adopting anti-inflammatory dietary patterns can significantly enhance clinical outcomes for individuals battling autoimmune diseases. It remains essential to personalize nutrition plans and include physical activity to reinforce these changes. Striving for a balanced diet while remaining aware of individual differences enables more tailored approaches. Research continues to unveil the complexities of gut health and its influence on autoimmune disorders, paving the way for future therapeutic innovations. Consequently, practitioners and healthcare providers must foster awareness of this vital connection. Ultimately, a well-rounded lifestyle that embraces healthy eating, exercise, and stress reduction offers tremendous potential to improve life quality and diminish disease symptoms. Combining these factors helps harness the gut’s power, leading to healthier outcomes. As we further our understanding of the gut microbiome, we may uncover even more precise strategies for autoimmune disease management in the near future. Therefore, continuing education and exploration in this field remain central to progress.
In summary, the journey towards better gut microbiome health involves embracing diverse food choices, enhancing physical activity, and prioritizing mental wellness to optimize autoimmune disease management. Overall well-being hinges on the dynamic relationship between diet, lifestyle, and gut health. By focusing on antioxidants and maintaining a variety of gut flora, individuals can foster resilience and improve their autoimmune conditions over time. Increased attention to these aspects creates a comprehensive approach to health, empowering individuals in their management journey. The learnings gathered underscore the intricate connections within our bodies, promoting positive changes over time as we embrace these health strategies.