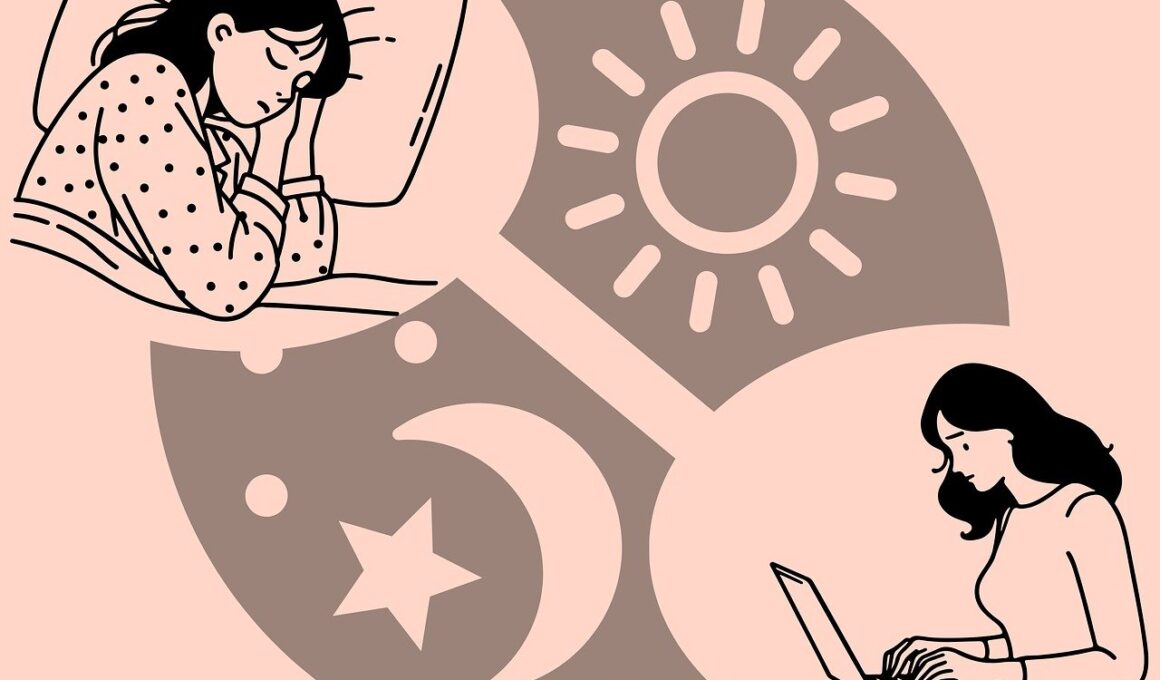
Circadian Rhythms and Their Impact on Athletic Performance
Circadian rhythms are natural cycles regulated by the internal body clock, influencing various physiological processes. These rhythms are crucial for athletes as they directly affect sleep, performance, recovery, and overall health. Primarily, they dictate sleep-wake cycles, ensuring that the body receives restorative sleep during the night. Without proper alignment of these rhythms, athletes may experience impaired cognitive functions and slower reaction times. The disruption of circadian rhythms has been linked to decreased endurance and increased fatigue during training and events. Athletes must prioritize maintaining consistent sleep schedules that align with their individual biological clocks. External factors like light exposure, meal timings, and exercise can further influence these rhythms, making it vital for athletes to manage their environments. Adopting strategies such as exposure to natural light during training can help realign internal clocks. Furthermore, implementing specific schedules for workouts and nutrition can significantly enhance athletic performance by promoting optimal sleep patterns. Overall, understanding and optimizing circadian rhythms can give athletes a competitive edge in their training and performance. Establishing a routine that harmonizes with these natural cycles can amplify recovery, enhance focus, and ultimately improve athletic output.
The connection between circadian rhythms and athletic performance is well-documented. Research indicates that training at specific times can yield better results, as the body is naturally more alert and energetic. For example, studies suggest higher strength output occurs in the late afternoon. Moreover, flexibility and muscle readiness often peak in the same period, which encourages athletes to train at optimal times. Conversely, performing strenuous workouts during low-energy periods, such as early mornings or late evenings, can lead to subpar results. The impact extends beyond just the time of day; consistent sleep patterns play a pivotal role as well. Disruptions due to travel, night games, or irregular sleep can hinder recovery and adaptation. Sleep deprivation negatively affects reaction times, decision-making skills, and endurance; thus, athletes must be vigilant about their sleep hygiene. Additionally, like any biomechanical system, individual differences matter—some athletes are naturally predisposed to being “morning” or “evening” types. Understanding one’s chronotype can guide when to best engage in various training sessions, allowing for maximum performance benefits. Lastly, these rhythms are impacted by seasonal changes, suggesting that year-round planning should consider these cycles for optimal outcomes in competitive environments.
The Role of Light in Regulating Circadian Rhythms
Light exposure is a significant regulating factor of circadian rhythms, affecting melatonin production in the body. Melatonin is a hormone that signals the body when it is time to sleep, playing a crucial role in promoting restorative sleep patterns. For athletes, exposure to natural light during the day enhances alertness and performance while suppressing melatonin levels, thereby encouraging daytime activity. On the contrary, exposure to artificial light, particularly blue light from screens, at night can disrupt the body’s natural response, delaying the onset of melatonin release. Consequently, it is recommended that athletes minimize screen time before bed and engage in relaxation techniques that promote melatonin production. Implementing strategies, such as using dimmed lights in the evening, can create an environment conducive to better sleep. Moreover, athletes may also benefit from light therapy remedies to correct disrupted circadian cycles, especially during extensive travel or when facing shifts in time zones. Harnessing ambient light effectively aids performance by informing the body when to be active and when to rest. Ultimately, athletes who leverage appropriate light exposure can enhance overall performance through better adaptation of their natural circadian rhythms.
Nutrition also ties closely to circadian rhythms and can substantially influence an athlete’s performance. It is essential for athletes to time their meals effectively, as eating at irregular hours can disrupt metabolism and circadian cycles. Research findings suggest a close relationship between meal timing and athletic performance, indicating that aligning food intake with these natural rhythms can lead to better energy levels and recovery. For example, consuming carbohydrates can replenish depleted glycogen stores effectively when eaten post-workout during the body’s peak insulin sensitivity period. Additionally, an athlete’s nutritional strategies should incorporate elements of circadian biology; factors such as meal composition, frequency, and timing can significantly alter metabolic rates. Furthermore, nutrients have varying effects based on circadian positions, meaning certain nutrients may have enhanced benefits dependent on the time of day consumed. For instance, protein synthesis can be more efficient at specific times after training sessions. Overall, creating a clear nutrition plan that corresponds with circadian rhythms can help facilitate better recovery, provide necessary energy, and cater to optimizing sustained performance over time. Athletes are encouraged to monitor how their eating habits impact their physical and mental states and adjust accordingly for maximum benefit.
Implications of Travel and Time Zone Changes
When athletes travel, especially across multiple time zones, their circadian rhythms can become severely disrupted. This phenomenon is known as jet lag and can impede performance, making it challenging for athletes to compete at their best levels. The body can take several days to recalibrate and adjust to new time zones, which may lead to decreased alertness, fatigue, and potentially heightened injury risks. Therefore, understanding strategies to mitigate jet lag is crucial for athletes. One effective approach includes gradual adjustment to the new time zone before departing, helping the body acclimatize more seamlessly. This may involve adjusting sleep and meal schedules a few days prior to traveling. Furthermore, athletes can leverage sunlight exposure at their new destinations to facilitate quicker adaptation. Strategic napping and hydration are key components in combating the effects of jet lag; careful timing of these practices can aid in quicker recovery of circadian rhythms. Also important is the use of melatonin supplementation when traveling long distances to help signal appropriate sleep-wake cycles. Consequently, traveling athletes must develop an individualized plan to manage their internal clocks effectively. By incorporating these approaches, they can enhance their overall performance quality when competing internationally and handle travel-related fatigue more effectively.
Coaches and trainers play a vital role in managing athletes’ circadian rhythms effectively. It is essential for them to understand the importance of optimal sleep patterns, nutrition timing, and light exposure on performance. Moreover, they should aid athletes in developing habits that promote natural rhythm alignment throughout the training cycle and during competition. Properly structured training schedules must be mindful of an athlete’s circadian cues to maximize performance outcomes. Team training sessions should be scheduled to correspond with peak performance times, after determining the team’s collective chronotypes. Additionally, prioritizing recovery time and ensuring proper sleep hygiene is crucial for athletes’ overall well-being and performance consistency. Coaches may also incorporate education on the science behind circadian rhythms, allowing athletes to grasp the significance of maintaining these natural rhythms for their competitive advantage. Ultimately, the emphasis on circadian rhythm management should become a central tenet in training programs, seamlessly integrating these practices with physical conditioning and skill development. As scientific evidence continues to emerge, the importance of these rhythms will likely grow, positioning coaches to leverage this knowledge for enhanced team performance and individual athlete success. The impact on training and results can be profound when these considerations are adequately addressed.
Conclusion: Embracing Circadian Rhythm Science
Embracing the science of circadian rhythms holds immense potential for enhancing athletic performance across all disciplines. Athletes are encouraged to proactively integrate knowledge of their natural rhythms into their training regimens to reap the most benefits. From optimizing sleep patterns to aligning nutrition and hydration strategically, these changes can lead to substantial improvements in energy, focus, and recovery. Moreover, coaches and sports professionals must work hand-in-hand with athletes to foster an environment that respects these rhythms, helping them make necessary adjustments during training and competition to mitigate performance risks. As the relationship between circadian rhythms and athletic performance gains more recognition, individualized approaches will become increasingly sought after. The realization of the critical impact of time on biological functioning can foster a deeper understanding of training adaptations and injury prevention. Therefore, research and education should focus not only on physical conditioning but on this underlying biological framework. By comprehensively addressing these factors, athletes will position themselves for optimal results. Ultimately, the journey towards peak performance is as much about understanding the body’s internal clock as it is about physical prowess, strategy, and effort.
Future investigations into the role of circadian rhythms in sports science will likely unveil even more nuances and strategies for optimizing performance. Researchers are gradually uncovering the multi-dimensional ways that time affects physiological processes, providing valuable insights into how best to synchronize training and recovery. Continued examination of sleep quality and its impact on athletic output will emphasize individualized sleep strategies as essential components of performance regimens. Additionally, the exploration of specific dietary patterns aligned with circadian rhythms may yield discoveries that cater to enhanced energy levels and reduced fatigue during competition. Athletes should view these studies as vital tools to gain a competitive edge in an increasingly demanding sports environment. Implementing technology such as wearable devices can also provide athletes with real-time data on their sleep and recovery, allowing for informed adjustments to improve training outcomes. As sports professionals increasingly embrace circadian science, they will refine preparation tactics, leading to sustained high-level performance. This evolution signifies a shift towards a more holistic understanding of health, performance, and recovery tailored to the individual athlete’s biological clock. As research progresses, the exponential potential of harmonizing with circadian rhythms will continue to redefine the future of athletic excellence.