The Connection Between Gut Health and Autoimmune Disease
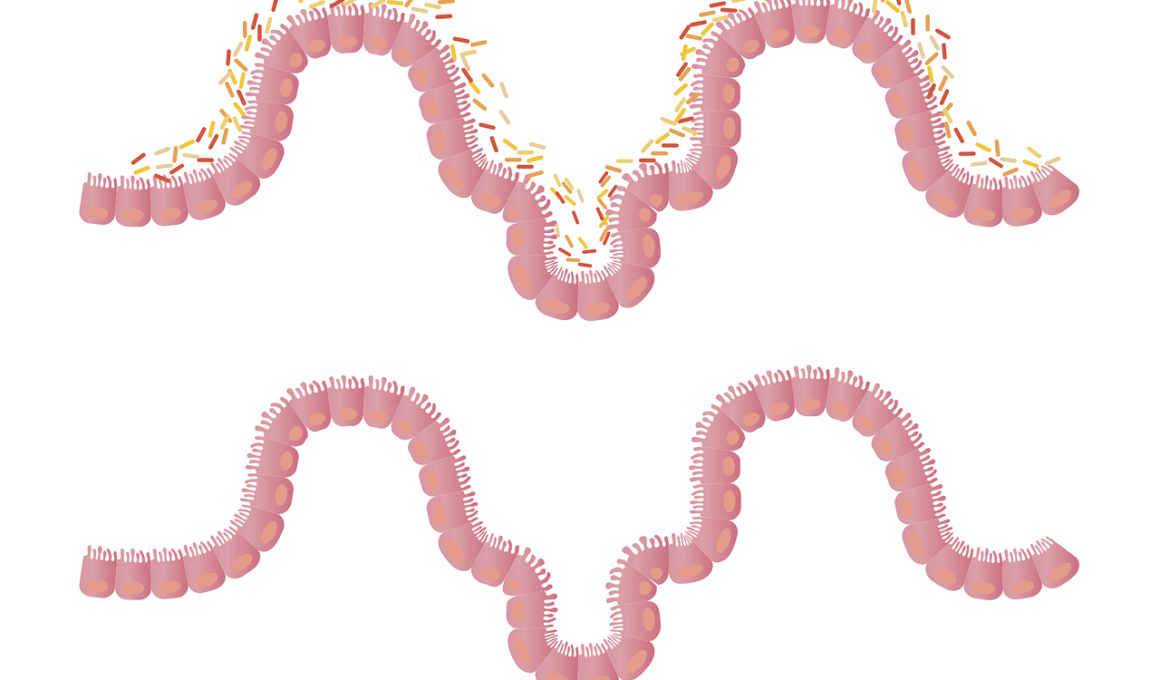
Autoimmune diseases have become increasingly prevalent in recent years, leading to concerns about underlying causes. Research indicates that gut health plays a crucial role in the development and management of autoimmune conditions. The gut houses trillions of microbes, often referred to as the gut microbiome. An imbalance in this microbiome can lead to inflammation and immune dysfunction. Maintaining a healthy gut flora can promote better digestion, nutrient absorption, and overall well-being. A balanced microbiome can help regulate immune responses and prevent the onset of autoimmune diseases. Diet can significantly influence gut health, making it essential for individuals with autoimmune conditions to focus on their nutritional choices. Adopting a diet rich in whole foods, fiber, and fermented products is essential for nurturing gut bacteria. These foods support beneficial bacteria, enhancing gut barrier function and preventing leaky gut syndrome, which has been implicated in autoimmune diseases. Furthermore, reducing processed foods and sugar can lower inflammation, another pivotal factor in managing autoimmune conditions. Considering the strong connection between gut health and autoimmune diseases, dietary adjustments may provide effective management options.
At the core of understanding autoimmune diseases and their connection to gut health lies the concept of leaky gut syndrome. This condition occurs when the intestinal lining becomes compromised, allowing toxins and undigested food particles to enter the bloodstream. The immune system recognizes these substances as foreign, triggering an autoimmune response. Numerous studies link leaky gut syndrome to various autoimmune diseases, highlighting the impact of gut permeability on immune function. By addressing leaky gut syndrome, individuals may find relief from autoimmune symptoms. To mitigate this condition, a targeted diet can be beneficial. Incorporating gut-healing foods, like bone broth, collagen peptides, and probiotics, may strengthen the intestinal barrier. Nutrients such as zinc, glutamine, and omega-3 fatty acids can help repair the gut lining, ultimately improving gut health and immune response. Additionally, eliminating potential triggers — such as gluten, dairy, and sugar — may provide further support. Monitoring symptoms can assist individuals in determining which foods affect their health adversely. The relationship between diet, gut health, and autoimmune diseases is complex yet essential for achieving optimal health.
The Role of Anti-Inflammatory Foods
In managing autoimmune diseases, anti-inflammatory foods can play a critical role in achieving a balanced immune response. Incorporating certain foods into the diet can help reduce systemic inflammation, which may be heightened in individuals with autoimmune conditions. Foods rich in antioxidants, such as berries, leafy greens, and nuts, can help counter inflammation and support overall health. Omega-3 fatty acids, found in fatty fish like salmon and flaxseeds, also contribute to lowering inflammation and may reduce the severity of autoimmune symptoms. Moreover, spices like turmeric and ginger possess anti-inflammatory properties that can enhance gut health. Incorporating these foods into daily meals can contribute significantly to overall well-being. Individuals should also consider the timing of their meals, as intermittent fasting may provide additional inflammatory benefits, allowing the gut to rest and reset. An anti-inflammatory diet typically focuses on whole, unprocessed foods while avoiding refined sugars and unhealthy fats. This dietary approach can create a positive effect on gut health, potentially assisting in the recovery and management of autoimmune diseases through effective nutritional strategies.
Another key factor in the relationship between gut health and autoimmune diseases is the impact of stress on the gastrointestinal system. Chronic stress can exacerbate gut permeability and inflammation, leading to an increase in autoimmune symptoms. The connection between the gut and the brain, known as the gut-brain axis, highlights the importance of addressing stress and mental well-being. To support gut health, individuals with autoimmune diseases should adopt stress management techniques such as mindfulness, meditation, and regular exercise. These practices can help reduce stress levels, promoting a healthier gut environment. Additionally, developing a strong social support system can also alleviate stress and enhance emotional health. Engaging in hobbies and maintaining a balanced lifestyle can ultimately improve gut health and contribute to managing autoimmune disorders effectively. Practicing relaxation techniques can help restore balance to the immune system while promoting the healing of the gut lining. This holistic approach to managing autoimmune diseases can lead to improved quality of life, emphasizing the need for individuals to prioritize mental health in their treatment plans.
Probiotics and Their Benefits
Probiotics are beneficial bacteria that can provide significant advantages for gut health, especially in individuals suffering from autoimmune diseases. Integrating probiotics into the diet can help restore a healthy gut microbiome, improving immunity and overall health. Fermented foods such as yogurt, kefir, sauerkraut, and kimchi are excellent sources of probiotics, supporting digestive health and enhancing the immune system. These beneficial microorganisms can help combat harmful bacteria and inflammation, thereby promoting a balanced immune response. For individuals unable to obtain sufficient probiotics from food sources, supplements can be considered but should be tailored to individual needs. Choosing specific strains, such as Lactobacillus or Bifidobacterium, may provide beneficial effects based on personal health circumstances. It’s essential to consult a healthcare provider before introducing any new supplements into the diet. As research continues to unfold, understanding how probiotics can positively influence gut health in autoimmune disease management will be pivotal. Continued exploration into the link between gut microbiome diversity and autoimmune disease outcomes will help individuals make informed dietary choices to improve their health in the long run.
In addition to dietary adjustments, incorporating fiber into the diet can be instrumental in promoting gut health and managing autoimmune diseases. Fiber-rich foods, such as fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and legumes, support healthy gut bacteria and facilitate proper digestion. The consumption of soluble fiber can enhance the production of short-chain fatty acids (SCFAs), which play a critical role in reducing inflammation and strengthening the gut lining. SCFAs help regulate immune responses and can alleviate symptoms related to autoimmune diseases. It is vital to gradually increase fiber intake, as sudden changes can cause digestive discomfort. Hydration is equally critical when increasing fiber consumption, as water supports healthy digestion and helps prevent constipation. Individuals should aim for a balanced diet that incorporates a wide variety of fiber sources to promote gut microbiome diversity. Consulting with healthcare professionals or dietitians can provide tailored dietary recommendations based on personal health status and goals. Emphasizing fiber-rich foods can significantly enhance gut health, creating a supportive environment for individuals striving to manage autoimmune conditions effectively.
Conclusion: The Importance of Gut Health
In conclusion, the connection between gut health and autoimmune disease is multifaceted and highlights the importance of a well-balanced diet in managing these conditions. Individuals diagnosed with autoimmune diseases can experience varying degrees of symptoms related to gut health, underscoring the need for personalized dietary approaches. By focusing on anti-inflammatory foods, probiotics, fiber, and stress reduction, individuals can create a supportive environment for gut health and immune function. Adopting these lifestyle changes may help alleviate symptoms and enhance the quality of life for many living with autoimmune disorders. Collaborating with healthcare professionals to formulate a suitable action plan can empower individuals to take control of their health. This knowledge not only fosters hope but encourages informed nutritional choices for individuals facing autoimmune challenges. Understanding the significance of gut health allows individuals to navigate dietary adjustments more effectively and address their autoimmune symptoms holistically. The journey toward improving gut health entails patience and commitment but can ultimately lead to profound positive changes in an individual’s well-being.
Adopting dietary changes requires dedication and awareness of gut health’s pivotal role in autoimmune disease management. Through careful selection of foods and lifestyle alterations, people can promote gut healing and improve immune function. This holistic approach underscores the intricate relationship between the gut, diet, and autoimmune disorders, making it essential for informed decision-making about nutrition. The future of autoimmune disease treatment will likely continue to embrace nutritional perspectives and individualized care as central themes in supportive health.