Role of Probiotics in Childhood Gut Microbiome Development
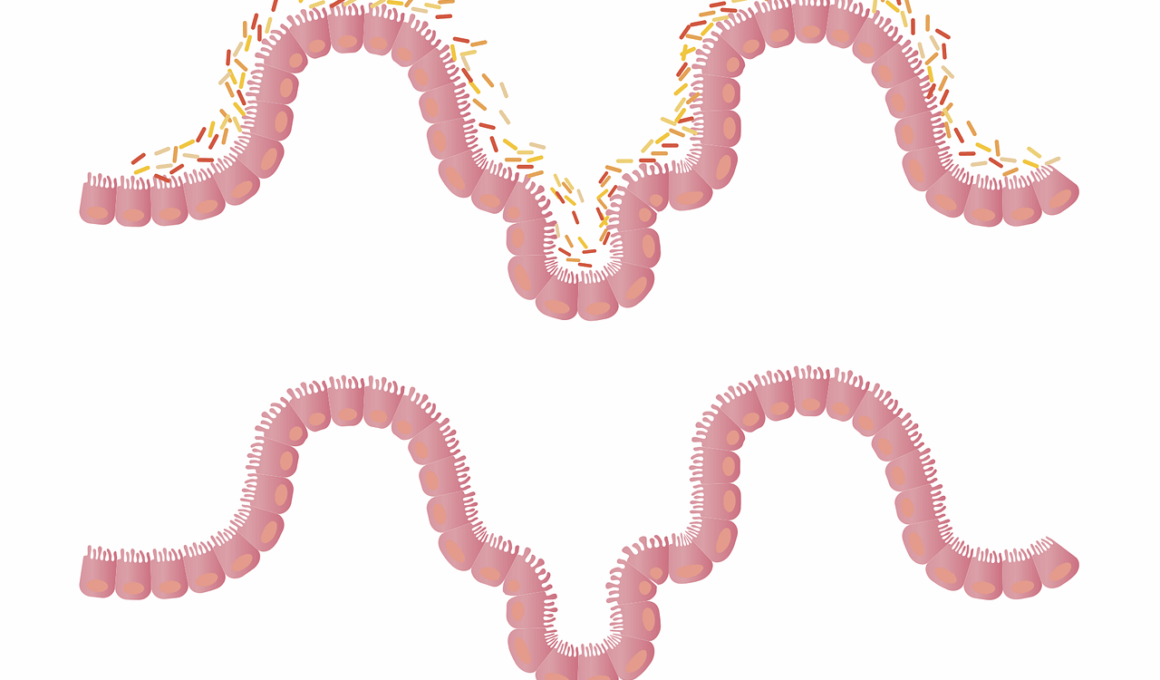
The gut microbiome plays a crucial role in childhood development, impacting many aspects of health. Probiotics are beneficial bacteria that can improve gut health, especially in young children. During the early stages of life, the gut microbiome is rapidly developing, influenced by various factors including diet, mode of delivery, and environment. Research indicates that healthy gut microbiota is essential for optimal immune function and digestion. Probiotics may help establish a balanced microbiome in infants and children, paving the way for better health outcomes. For instance, they can prevent the onset of gastrointestinal disorders and allergies. It’s important for parents to understand how probiotics work, as they can promote the growth of beneficial bacteria in the gut while inhibiting harmful pathogens. Moreover, incorporating probiotics in a child’s diet, through both supplements and fermented foods, can enhance gut flora diversity. They can also aid in nutrient absorption, ensuring that children receive the maximum benefit from their diets. Additionally, many pediatricians recommend specific strains of probiotics to support infant digestion and immunity, as these have been shown to be effective in various studies. Parents should consider these options responsibly and consult healthcare providers.
In recent years, there has been a growing interest in understanding the role of probiotics in boosting a child’s gut microbiome. Research indicates that probiotics can significantly impact the microbial composition in young children. These beneficial bacteria can be introduced both through dietary sources and supplements, providing a dual approach to enhancing gut health. Fermented foods like yogurt, kefir, and sauerkraut are excellent natural sources of probiotics, while supplements can help reach adequate doses more effectively. A balanced gut microbiome can lead to improved digestive function and stronger immunity in children. Furthermore, studies suggest that the timing of probiotic introduction can be important; early exposure during infancy may yield the best outcomes. This timing can help establish a more resilient microbiome that supports lifelong health. Additionally, maintaining a diet rich in prebiotics, such as fiber-rich fruits, vegetables, and whole grains, complements the action of probiotics. By providing a food source for beneficial bacteria, prebiotics help them flourish in the gut. Health professionals may recommend a combination of probiotics and prebiotics to optimize gut microbiome development during childhood, ensuring children grow strong and healthy.
Understanding the Pathways of Gut Development
The process of gut microbiome development begins at birth, where the initial colonization of microbes occurs. Factors such as birth method—vaginal or caesarean—significantly influence early microbiome compositions. Vaginally delivered infants tend to have a microbiome that more closely resembles their mother’s, usually leading to a healthier gut. Conversely, caesarean-born infants may experience altered microbial exposures, increasing the risk for allergies and metabolic disorders later. Environmental factors, including exposure to household pets and siblings, also shape microbiome diversity during infancy and early childhood. Probiotics can play a key role in supporting healthy gut microbial pathways during this crucial period. By providing beneficial bacteria, probiotics can aid in the establishment of a diverse gut microbiome, improving resilience against pathogens while fostering a balanced immune response. Moreover, introducing probiotics during weaning can facilitate a smoother transition to solid foods, assisting in the digestion of new dietary components. Parents should be aware of how these factors interact to influence their child’s health outcomes. Consulting healthcare professionals for tailored advice on probiotic use highlights the importance of a personalized approach to gut health for children.
As children grow, dietary habits significantly influence the composition of the gut microbiome. High sugar and processed foods may disrupt microbiome balance, leading to dysbiosis, a state linked with obesity and chronic diseases. On the other hand, a nutrient-rich diet encourages diverse gut flora. Probiotics emerge as a foundational element in promoting this healthy dietary pattern. The inclusion of probiotics in a child’s diet can be a fun and educational experience, introducing them to various fermented foods. Ingredients like yogurt smoothies can make incorporation of beneficial bacteria enjoyable. Moreover, understanding how specific strains of probiotics function can empower parents. For allergies, strains such as Lactobacillus rhamnosus have shown promising results in preventing allergic sensitization in high-risk infants. Additionally, probiotics can reduce the duration and severity of gastrointestinal infections, an essential consideration for parents. Collaboration with pediatricians is crucial to determining appropriate strains and dosages, ensuring safety and efficacy. Therefore, the benefits of probiotics during childhood are multifaceted, extending beyond gut health alone and contributing to overall well-being and development. Educating families about these options aids in cultivating lifelong healthy eating habits and recognizing the importance of gut health.
Recommendations for Probiotic Use in Children
When considering probiotics for children, parents should prioritize quality assurances and evidence-based choices. It is vital to select supplements with strains that have been studied and proven effective for the specific health benefits desired. Not all probiotics are equal, and distinguishing between them can be daunting. Moreover, understanding the correct dosage is essential; guidelines often vary based on age and individual health needs. Introducing probiotics gradually is advisable, monitoring for any allergic reactions or adjustments. Dairy-based probiotics might not be suitable for lactose-intolerant children, so exploring non-dairy options is necessary. Additionally, combining probiotics with a well-balanced diet enriched with prebiotics can amplify benefits. Foods high in prebiotics like bananas, garlic, and onions not only support probiotics but also enhance digestive health. Parents should work closely with healthcare professionals to develop personalized probiotic plans that consider their child’s unique health scenarios. Keeping a dialogue about gut health open within families reinforces the importance of digestive wellness from a young age. By creating awareness and practical steps for improvement, a nurturing approach to gut health during childhood can foster healthier individuals in adulthood.
In conclusion, the role of probiotics in childhood gut microbiome development cannot be overstated. Probiotics can lay the foundation for a healthy gut, essential for overall growth and development. They not only support gut health but also encourage a robust immune system, paving the way for lifelong wellness. The immersion of beneficial bacteria ensures that children can effectively utilize nutrients from their diets, thereby influencing their energy levels and cognitive function. Furthermore, as research into gut health continues to expand, the future looks promising for identifying even more benefits associated with probiotics. Parents are encouraged to stay informed about new advancements in probiotics and their implications for children’s health. Collaborative discussions with pediatric professionals will aid in navigating probiotic options tailored to individual needs. Ultimately, the nurturing of a healthy microbiome must begin early, incorporating practical dietary changes, probiotic supplementation, and lifestyle choices to optimize outcomes. This dedication to gut health now will ripple into the future, contributing to more resilient children better prepared for life’s challenges. Understanding the critical nature of the gut microbiome is vital, and promoting health-focused strategies will be foundational for healthier societies.
Future Considerations for Probiotic Research
The field of probiotic research is continually evolving, with various avenues yet to explore. Future studies focusing on the long-term impacts of early probiotic consumption on childhood health are essential. Understanding how different strains of probiotics interact with various diets and environments can yield insights, possibly leading to more tailored recommendations for specific dietary patterns. There is a growing interest in how probiotics also influence mood, cognition, and overall psychological well-being in children, possibly linking gut health and mental health; further studies in this area could reveal profound connections. Investigating different routes and timings for probiotic administration could optimize gut colonization, revealing what works best for diverse populations of children. As our understanding of the microbiome expands, it will become critical to educate parents and caregivers on safe and effective practices for probiotic use. This ongoing research will also help dispel misconceptions and provide clear guidelines. In parallel, increasing access to probiotic-rich foods, especially in underprivileged communities, must be a priority. Simultaneously, relevant policies should encourage public awareness campaigns promoting the benefits of a healthy gut microbiome during childhood. This collaboration aims to bolster future generations’ health by optimizing their developmental pathways.
In summary, probiotics play an instrumental role in establishing a healthy gut microbiome during childhood. While the research continues to deepen, the current knowledge suggests that probiotics significantly enhance gut health, immune defense, and overall well-being. Educational initiatives and proper consultation with healthcare professionals will provide families the tools to make informed decisions regarding probiotic use. Engaging with children about the importance of gut health, including practical applications through fun dietary choices and understanding gut microbiome influences, can cultivate lasting habits. As the world becomes increasingly aware of the importance of digestive health, fostering environments that support healthy gut microbiota is essential. Probiotics offer an exciting path forward, allowing children to thrive physically and emotionally. Therefore, greater emphasis needs to be placed on integrating probiotics into children’s diets, combined with prebiotics, to maximize health benefits. Future discoveries in probiotics, their effectiveness, and their interactions with the gut will undoubtedly shape health practices in years to come. Continued advocacy for research alongside educational efforts can ensure that the best practices for childhood gut health are widely shared. The future of probiotic applications in childhood health is hopeful, promising vibrant lives for future generations.