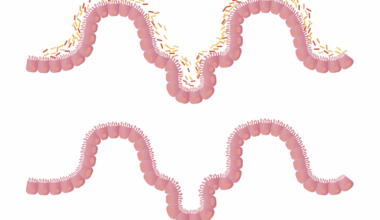
The Link Between Gut Health and Immune Function in Pregnant Women
Gut health is crucial during pregnancy, as it directly impacts immune function and maternal well-being. An optimal gut microbiome supports a balanced immune response, essential for both mother and developing fetus. Research indicates that the gut microbiota alters significantly during pregnancy, influenced by dietary changes and hormonal fluctuations. Pregnant women often experience shifts in gut bacteria that can enhance nutrient absorption and promote immune health. This modulation helps prepare the body for the increased demands on the immune system as the fetus develops in the womb. A diverse gut microbiome is associated with positive pregnancy outcomes, while dysbiosis may lead to complications. Maintaining gut health through diet is vital; there’s evidence that probiotics and prebiotics can positively affect the gut microbiome. Foods rich in fiber, such as fruits and vegetables, are beneficial, forming a well-rounded diet for pregnant women. Adopting healthy lifestyle practices encourages a resilient gut microbiota, playing a significant role in both pregnancy progression and immune function. In conclusion, a focus on gut health is key in ensuring successful and healthy pregnancies, highlighting the critical connection between gut health and immune response.
Healthy gut flora contributes significantly to the overall health of pregnant women. The gut microbiome influences the immune system by microbiota-host interactions that affect inflammation and antibody response. During pregnancy, women are more susceptible to infections, making this aspect vital. A balanced gut microbiome can help reduce inflammation and boost immune defenses, which is particularly important for the health of both mother and baby. Additionally, certain nutrients are crucial for nurturing this delicate balance of gut flora. Micronutrients, such as magnesium and zinc, play a role in immune health, and their presence in food sources can enhance gut microbiota diversity. Furthermore, foods high in omega-3 fatty acids contribute to anti-inflammatory properties that further support gut health during pregnancy. Ensuring adequate hydration is also important, as it aids in maintaining gut mucosa integrity. Pregnant women should consider various factors affecting gut health, such as stress and sleep patterns. Chronic stress can lead to gut dysbiosis, weakening the immune response. Therefore, adopting mindfulness and stress management techniques can positively impact gut health. Overall, nurturing gut health during pregnancy is fundamental to improving immune resilience.
Dietary Influences on Gut Health
Diet is one of the most influential factors in establishing and maintaining a healthy gut microbiome during pregnancy. Consuming a wide variety of natural foods can lead to a balanced and functional gut microbiota. Dietary fiber-rich foods, including whole grains, legumes, fruits, and vegetables, provide nourishment for beneficial bacteria in the gut. Probiotic foods like yogurt, kefir, and fermented vegetables introduce healthy microbes, while prebiotic foods like garlic and onions enhance their growth. Pregnant women must be mindful of their dietary choices, as certain processed foods can contribute to gut imbalance and inflammation. High sugar and fat diets may adversely affect gut health, leading to dysbiosis. Furthermore, adequate hydration is paramount when maintaining fiber in the diet. Drinking sufficient water enhances digestion, nutrient absorption, and supports gut health. Sustainability is key; incorporating seasonal foods can improve gut microbial diversity. An overall balanced diet, rich in plant-based foods, not only supports gut health but also benefits the developing fetus. As such, making informed dietary choices is essential for pregnant women prioritizing their gut microbiome and immune health during their pregnancy journey.
Physical activity is another crucial factor that can positively influence gut health during pregnancy. Engaging in moderate exercise helps regulate hormones that impact gut function, promoting a beneficial microbiome diversity. Exercise not only supports physical well-being but also enhances mental health, reducing stress levels that can negatively affect the gut. Pregnant women should tailor their physical activities based on their comfort and health status. Activities such as walking, swimming, and prenatal yoga are excellent options to maintain fitness while being gentle on the body. These activities encourage blood circulation, which supports the digestive system and boosts nutrient delivery to the fetus. Furthermore, exercising can stimulate intestinal motility, reducing discomfort and constipation, common issues during pregnancy. It’s essential to listen to the body and respect its limits, adopting a personalized approach to fitness. Additionally, consulting a healthcare professional before starting any routine is recommended. Incorporating physical activity into daily life can serve as a parallel strategy alongside dietary adjustments to enhance gut health. Overall, maintaining regular exercise during pregnancy not only fosters a healthy gut microbiome but also contributes to overall well-being for both mother and baby.
Impact of Stress on Gut Microbiome
Pregnancy can be a period of immense emotional change and stress, which can negatively impact gut health. Stress can significantly disrupt the balance of gut microbiota, leading to issues such as irritability and digestive discomfort. Chronic stress has been implicated in several studies showing its correlation with changes in microbial composition. Healthy microbiota play a vital role in regulating mood and stress levels through the gut-brain axis. Thus, managing stress effectively during this period is crucial. It’s important for pregnant women to adopt relaxation techniques such as meditation, deep-breathing exercises, or gentle yoga to combat stress. These activities are known to improve mental well-being and positively affect gut health. Furthermore, establishing a support system with family, friends, or counseling services can create a nurturing environment. Seeking professional guidance on mental health can also be beneficial. Quality sleep is a key aspect of stress management and can greatly affect gut health. A well-rested body can better regulate hormones, reduce anxiety, and thereby promote a healthier gut microbiome. Overall, stress management during pregnancy is essential for maintaining a healthy gut and, subsequently, a strong immune response.
Incorporating supplements may also play a role in supporting gut health during pregnancy. Probiotics, specifically formulated for pregnant women, can help restore gut balance and provide essential bacteria beneficial for immunity. Research suggests that taking probiotics during pregnancy may reduce the risk of gestational diabetes and associated complications, supporting both maternal and fetal health. Some studies even indicate that probiotic intake can positively influence mood and anxiety levels, reinforcing the connection between gut health and overall well-being. Before starting any supplementation, pregnant women should consult their healthcare provider to ensure safety and appropriateness. Prebiotic supplements may also be considered, as they act as food for probiotics, fostering a healthy environment for these beneficial microorganisms. Additionally, omega-3 fatty acids, often derived from fish oil supplements, contribute to anti-inflammatory actions, supporting gut health. Ensuring a comprehensive approach combining a varied diet, exercise, stress management, and appropriate supplementation can create synergy in promoting gut health. Ultimately, maintaining a well-balanced gut microbiome plays a vital role in the immune function, potentially contributing to healthier pregnancy outcomes. Prioritizing these aspects paves the way for both maternal and infant health.
Conclusion: Nurturing Gut Health for a Healthy Pregnancy
In summary, nurturing gut health during pregnancy is essential for optimal immune function and overall maternal health. The intricate relationship between the gut microbiome and immune system highlights the need for pregnant women to prioritize a balanced diet, hydration, exercise, and stress management. Each element plays a vital role in maintaining a healthy microbiome that supports both the mother and developing fetus. In addition to lifestyle choices, informed supplementation may provide added support to enhance gut health and foster a resilient immune response. Understanding the benefits of gut health can empower expectant mothers to make informed decisions that lead to successful pregnancies. Community and professional support can facilitate better choices, fostering environments conducive to health. Ongoing research continues to unravel the complexities of the gut and its influence, shedding light on strategies that may enhance well-being during this critical period. Each pregnancy is unique, and embracing a personalized approach can lead to the best outcomes. Ultimately, empowering pregnant women with knowledge about gut health may pave the path for a smoother transition into motherhood, resulting in healthier lives for both mother and child.
In conclusion, the intricate connection between gut health and immune function cannot be understated during pregnancy. A comprehensive strategy that includes a focus on diet, physical activity, mental health, and supplementation lays the foundation for optimal health outcomes. By prioritizing gut health and embracing practices that support a balanced microbiome, pregnant women can effectively bolster their immune defenses and provide a healthier environment for their developing child. Each positive choice contributes to a holistic approach in nurturing not only maternal health but also the health of future generations, making the overall pregnancy experience more fulfilling and health-oriented.