The Role of Omega-3 Fatty Acids in Gut Health
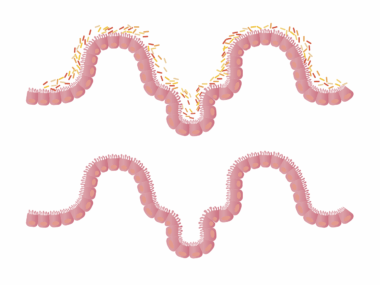
Omega-3 fatty acids are essential fats that significantly contribute to gut health. These polyunsaturated fats are primarily found in foods like fish, flaxseeds, and walnuts. Their potential benefits for gut health are becoming increasingly recognized in the scientific community. Omega-3s help reduce inflammation, which is crucial for maintaining a balanced gut microbiome. An imbalanced microbiome can lead to various digestive disorders such as irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) and inflammatory bowel disease (IBD). Incorporating adequate amounts of omega-3 fatty acids into your diet can help modulate inflammatory responses. Furthermore, these fats support the overall integrity of the gut lining, ensuring it remains healthy and functional. Not only do they alleviate inflammation, but omega-3s also provide nourishment for beneficial gut bacteria. These bacteria flourish when provided with the right nutrients, ultimately contributing to enhanced gut health. Evidence suggests that populations with high omega-3 intake exhibit lower rates of gastrointestinal diseases. Therefore, making mindful dietary choices that include omega-3 sources is essential for optimal gut and overall health.
The gut microbiome consists of trillions of microorganisms that play a pivotal role in digestion. Research indicates that a diverse microbiome is linked to better health outcomes. Omega-3 fatty acids positively influence this microbiome composition. Studies show that they stimulate the growth of beneficial bacteria, which help break down food and absorb nutrients more effectively. This process not only bolsters digestive health but may also impact mood regulation. Emerging evidence links gut health with mental well-being, suggesting an intricate relationship between the gut microbiome and the brain. Furthermore, certain strains of bacteria, thriving due to omega-3s, are known to produce short-chain fatty acids like butyrate. Butyrate serves as an energy source for colon cells and aids in maintaining gut barrier function. A robust gut barrier prevents harmful substances from entering the bloodstream. Therefore, individuals consuming adequate omega-3 fatty acids might experience fewer digestive problems. To promote gut health naturally, it’s beneficial to opt for omega-3-rich foods rather than relying solely on supplements. A balanced diet can work wonders for both gut health and the microbiome.
The Anti-Inflammatory Properties of Omega-3s
Inflammation plays a crucial role in many diseases, including those affecting the gut. Omega-3 fatty acids demonstrate remarkable anti-inflammatory properties. When inflammation occurs, it can lead to various health issues, including chronic pain and digestive disorders. The body converts omega-3s into resolvins and protectins, compounds that act to resolve inflammation. These compounds provide health benefits, particularly for individuals suffering from conditions like inflammatory bowel disease (IBD). Research indicates that patients with IBD often have an imbalance in their omega-3 and omega-6 fatty acids. Increasing omega-3s can help restore this balance, potentially offering relief from symptoms. Furthermore, omega-3 fatty acids improve the mucosal lining of the intestine, enhancing gut health. Clinical studies show that individuals with higher omega-3 intake report improved gut function. Additionally, including omega-3 sources in your diet may protect against IBD flare-ups. Food items such as salmon, chia seeds, and walnuts can help you achieve the necessary omega-3 levels. Remember that consistent dietary habits are essential, as they significantly impact inflammation over time.
The Mediterranean diet is often praised for its numerous health benefits, including enhanced gut health. Rich in omega-3 fatty acids, it emphasizes whole grains, fruits, vegetables, nuts, and fatty fish. This diet model encourages a balanced intake of nutrients. Studies increasingly suggest that adhering to a Mediterranean diet contributes to a healthier gut microbiome. The combination of omega-3s and dietary fiber found in plant-based foods supports beneficial bacteria. The high fiber intake encourages increased bacteria diversity, which is a marker of a healthy microbiome. Additionally, the Mediterranean diet reduces processed food consumption and added sugars, all of which can negatively impact gut health. By adopting this dietary style, not only do you promote better gut health, but you also lower the risk of chronic diseases associated with inflammation. Furthermore, lifestyle choices, such as regular exercise and adequate sleep, play a role in ensuring a healthy gut. Together, these elements may work synergistically to enhance overall well-being. Integrating omega-3-rich foods within the context of a Mediterranean diet is a practical approach to achieving optimal gut health.
Importance of Omega-3 Sources in Diet
When considering omega-3 fatty acids, it’s important to classify them into three primary types: ALA, EPA, and DHA. ALA, or alpha-linolenic acid, is primarily found in plant sources like flaxseed and chia seeds. EPA and DHA, on the other hand, are largely derived from fish, particularly fatty fish like salmon and mackerel. Understanding the sources of these omega-3s can aid in dietary planning. Vegetarians and vegans can focus on ALA sources to ensure adequate intake. However, EPA and DHA are more readily utilized by the body and are fundamental for optimal health. It’s crucial to balance these omega-3 fatty acids with omega-6 fatty acids, commonly found in vegetable oils. The ratio of omega-3 to omega-6 is essential for managing inflammation. Diets excessively high in omega-6 can lead to inflammatory issues. Therefore, including a variety of omega-3-rich foods in daily meals is key. Food preparation methods also matter; for instance, grilling or baking fish retains healthy fats better than frying. Understanding these dietary actions can enhance gut and overall health significantly.
If you’re looking to enhance your gut microbiome health, consider omega-3 supplementation through fish oil or algae-based products. These supplements can provide concentrated doses of EPA and DHA, the two most beneficial forms of omega-3s. Individuals with specific dietary restrictions or those who find it challenging to consume enough omega-3-rich foods may benefit from these options. However, consulting with a healthcare professional before starting any supplement is wise. They can help determine the correct dosage and ensure it aligns with your individual health needs. While supplements can complement dietary intake, they should not replace whole foods. Whole food sources provide additional nutrients essential for overall health. It’s helpful to monitor how your body responds to these supplements. Some individuals may experience digestive discomfort when initially incorporating fish oil. Gradual introduction can help improve tolerance. Alongside supplementation, maintaining a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, along with drinking water, is vital. Ultimately, combining omega-3 supplementation with healthy eating practices can help achieve optimal gut health.
Conclusion: Embrace Omega-3 for Gut Health
Ultimately, prioritizing omega-3 fatty acids in your diet is a significant step towards improving gut health. The body’s needs for these essential fats cannot be overstated, especially in a world filled with processed foods. Maintaining a proper balance between omega-3 and omega-6 fatty acids fosters an environment conducive to a healthy microbiome. Moreover, omega-3s offer powerful anti-inflammatory benefits that can alleviate various gut-related issues. By incorporating foods rich in these healthy fats, you support beneficial gut bacteria, leading to improved digestion and overall well-being. Don’t forget that lifestyle factors, such as stress management, adequate sleep, and regular exercise, also contribute to gut health. Embracing a holistic approach to wellness can lead to sustainable results. As we better understand the important role of omega-3s, empowering ourselves with knowledge can revolutionize our health choices. Begin with small changes, such as introducing fatty fish or plant-based omega-3 sources in your meals. Over time, these adjustments will significantly impact your gut health, setting the stage for vibrant well-being.
In summary, omega-3 fatty acids are invaluable allies in the quest for optimal gut health. Their numerous benefits range from fueling healthy gut bacteria to combating inflammation and enhancing the gut lining’s integrity. Understanding the significance of omega-3s is crucial for making informed dietary choices. Whether through whole foods or supplements, incorporating these essential fats can promote a flourishing gut microbiome. Awareness of this relationship empowers individuals to take charge of their health. Consider how omega-3-rich meals can replace less nutritious options in your daily diet. It’s a simple yet powerful change toward better gut health. A healthy gut supports not only the digestive system but the immune system, brain function, and even mood. Therefore, prioritize omega-3 intake as part of a balanced, nourishing diet to help optimize your overall well-being. The journey towards gut health is ongoing and requires dedication, but the benefits are profound. In a world where gut health is paramount, omega-3 fatty acids should remain at the forefront of dietary considerations. Commit today to making omega-3s a regular part of your meals, and watch how your health flourishes over time.