Gut Inflammation and Joint Pain: Understanding the Connection
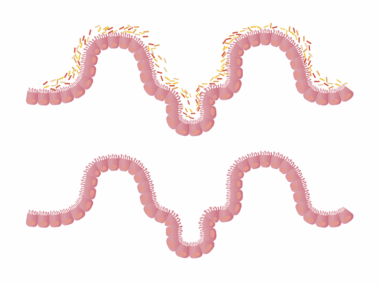
Gut inflammation can manifest in various ways, with symptoms that extend beyond the digestive tract. Many individuals are not aware that inflammatory processes in the gut can lead to joint pain and discomfort. This connection is becoming increasingly recognized in functional medicine, as practitioners focus on identifying underlying causes of Joint pain. Factors such as diet, lifestyle, and gut microbiome health come into play. When the gut is inflamed, harmful bacteria and toxins may leak into the bloodstream, prompting an immune response. This immune response can inadvertently lead to joint inflammation. Additionally, specific food intolerances can exacerbate this situation, making it vital to identify and manage them. Maintaining a healthy gut is essential for overall well-being, and addressing inflammation may ease periodic joint pain. Chronic joint issues could signal the need for dietary adjustments and supplements that promote gut health. Exploring options like probiotics, fermented foods, and anti-inflammatory diets may help soothe the gut, ultimately benefiting the joints. Remember that holistic approaches often yield the best results when dealing with interconnected health issues such as these. Understanding this link sets the stage for impactful healing.
Signs of gut inflammation include various digestive symptoms that may not seem connected to joint pain. Common indicators can encompass bloating, gas, diarrhea, or constipation. However, these digestive disturbances are frequently accompanied by systemic symptoms. For example, fatigue, headaches, and skin conditions are often reported alongside gut issues. Inflammation can lead to an overactive immune response, resulting in the release of inflammatory cytokines that affect different body systems. This cytokine release can subsequently cause pain and inflammation in the joints. Identifying these additional symptoms is crucial for effective diagnosis and treatment of both gut health and joint pain. Hence, healthcare professionals often recommend comprehensive testing to evaluate gut function and the presence of inflammation. Furthermore, understanding how your body responds to certain foods might reveal further insights into gut inflammation. Individuals may also want to consider keeping a food journal for better awareness of symptoms after specific meals, which fosters deeper insights into connections between diet and inflammation. Treatment protocols often evolve to include anti-inflammatory foods that support gut healing. Such preparations optimize recovery and joint health by ensuring a thorough approach addressing inflammation’s multiplicity of effects.
Diet and Its Role in Gut Inflammation
The food we consume holds considerable power over our gut health, influencing inflammation significantly. Consuming processed foods, high in sugar and fat, can lead to imbalances in gut bacteria and promote inflammation. When this occurs, the microbiome may become less diverse and more susceptible to harmful bacteria, worsening gut health. Incorporating nutrient-dense foods such as fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, and whole grains can positively affect gut inflammation. For instance, foods rich in omega-3 fatty acids, like fish and flaxseeds, are known for their anti-inflammatory properties. Additionally, antioxidants found in colorful fruits and vegetables help combat oxidative stress linked to inflammation. Probiotic-rich foods, such as yogurt and sauerkraut, also play a vital role in maintaining a balanced gut microbiome. Such foods help restore beneficial bacteria balance, reducing inflammation. Moreover, it’s crucial to identify and eliminate food sensitivities that may exacerbate gut inflammation. Considerations of gluten or dairy may reveal reactions leading to further discomfort. Customer preferences may vary, requiring personalized approaches to diet, aiming for sustainable wellness that not only improves gut health but also alleviates joint pain effectively.
In the quest to alleviate gut inflammation, lifestyle modifications can prove beneficial. Regular physical activity promotes healthy digestion and can help mitigate inflammatory processes. Exercise enhances circulation, supports immune function, and can reduce stress levels, all contributing to improved gut health. Additionally, stress management is vital, as psychological stress is tied to gut-brain interactions and gut health. Techniques such as meditation, yoga, and deep-breathing exercises can significantly benefit both the gut and joints. Moreover, ample hydration is essential to maintain an effective digestive process, as water aids in nutrient absorption and helps manage inflammation. Practicing mindful eating can also play a role; slowing down and appreciating each bite may alleviate digestive disturbances. Adequate sleep is another critical element of lifestyle choices impacting gut health. Sleep deprivation can worsen inflammation and the risk of chronic conditions affecting joint health. Implementing these changes gradually may yield more sustainable results. Ultimately, integrating simple yet effective practices can lead to significant improvements in overall health, showing that gut healing truly benefits joint health. Awareness and commitment to lifestyle changes foster long-term wellness for patients suffering from gut-related discomfort.
Supplements for Gut Health
In addition to dietary changes, various supplements can aid in reducing gut inflammation and improving overall joint health. Probiotics are increasingly recognized for their effectiveness in supporting the microbiome and preventing dysbiosis, which can lead to inflammation. Different strains of probiotics address different health issues, making it essential to select those targeting inflammation specifically. Research has shown that specific probiotic strains can reduce inflammatory markers, ultimately benefiting joint health. Omega-3 fatty acids represent another class of supplements widely studied for their anti-inflammatory properties. They can be sourced from fish oil, algae-based options, or flaxseed oil. Each source helps combat chronic inflammation found in both gut and joint pain. Additionally, curcumin, derived from turmeric, has exhibited strong anti-inflammatory effects. This potent phytochemical can enhance gut health while reducing joint pain. Furthermore, vitamins and minerals, such as vitamin D and zinc, support immune function and gut integrity. Ensuring that your body has adequate nutrients can further optimize gut health and potentially reduce pain across the body. Some individuals might benefit from combining these supplements with dietary changes for maximum effectiveness in addressing gut inflammation and joint pain.
It is essential to recognize the significance of monitoring gut health in individuals experiencing joint pain. While the connection might not be readily apparent, it often reflects systemic inflammation beyond the gut. Patients frequently reported improvements in joint pain after addressing their underlying gut issues. Undertaking comprehensive assessment strategies helps illuminate this intimate relationship, often prompting changes in management strategies. Such assessments could involve evaluating gut flora, digestive symptoms, and joint inflammation markers. Establishing this relationship might encourage the implementation of holistic treatment plans that encompass both areas. Furthermore, collaboration between healthcare providers, such as nutritionists and rheumatologists, can lead to more effective management of symptoms. This teamwork improves health outcomes and enhances patients’ lives, creating a pathway toward a healthier gut and reduced joint pain. Continuous education in gut health remains crucial in clinical settings, providing healthcare professionals with understanding and tools necessary to assist patients effectively. Ensuring patients comprehend the body’s interconnected systems fosters proactive health management and overall satisfaction. Empowering individuals with knowledge about gut health provides them with resources and support that facilitate healing, leading to more fulfilling lives free from the burden of undiagnosed pain.
Conclusion
In conclusion, understanding the relationship between gut inflammation and joint pain opens new doors for effective healing and symptom management. By addressing gut health holistically, individuals can often find relief from chronic joint discomfort. Identifying dietary triggers, practicing healthy lifestyle habits, and utilizing supportive supplements can lead to remarkable improvements. Additionally, awareness of symptoms associated with gut inflammation can pave the way for more accurate diagnoses. Each person’s journey toward better health can significantly benefit from such awareness and proactive care. As research continues to uncover the connections between gut health and overall wellness, innovative approaches may arise, offering hope and relief for those affected. The integration of functional medicine principles is a growing field of study that emphasizes individualized treatment plans based on personal health histories and responses. Future developments in this realm hold promise for improved outcomes for individuals struggling with joint pain linked to gut inflammation. Promoting ongoing research and education empowers individuals to take control of their health journeys. Ultimately, a comprehensive understanding of gut health represents a critical aspect of holistic well-being, bridging the gap between nutrition, health, and quality of life.
Reinforcing these practices into daily life will yield lasting benefits, promoting gut health while reducing joint pain symptoms significantly.