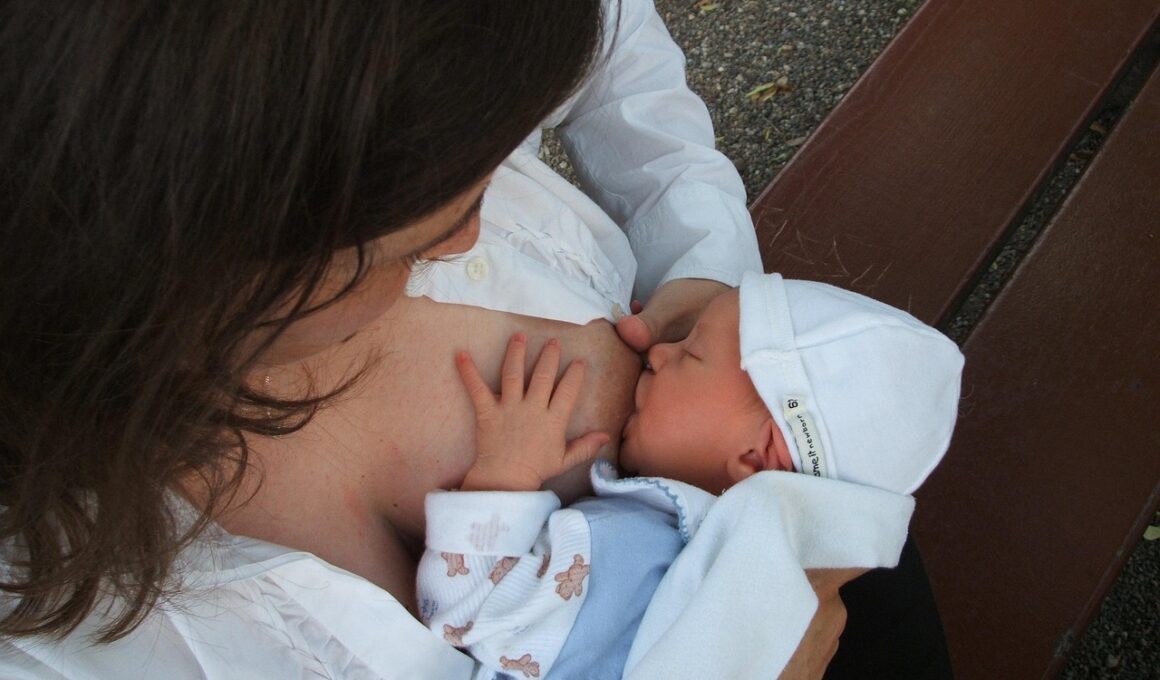
How Breastfeeding Supports Infant Hydration
Breastfeeding plays a crucial role in keeping infants properly hydrated during their early stages of life. Breast milk is composed of approximately 87% water, which provides the necessary hydration that infants require. During the first few months, infants have limited ability to regulate their own body temperature, making hydration from breast milk essential. Additionally, the electrolytes in breast milk are perfectly balanced to meet an infant’s needs, further facilitating hydration. Breastfeeding ensures infants are not only getting hydration but also essential nutrients. In dry or hot climates, breastfeeding becomes even more critical to prevent dehydration. Furthermore, because breastfeeding is bioavailable, the water and nutrients within breast milk are efficiently absorbed by the infant’s body. This efficient absorption supports a healthy digestive system, promoting overall well-being. Mothers should be aware of the signs of dehydration, which include dry mouth, lethargy, and fewer wet diapers. By maintaining breastfeeding, mothers can ensure their infants remain hydrated. Pediatric guidelines recommend exclusive breastfeeding for the first six months, thereby providing infants with tailored hydration and nutrition, leading to better health outcomes as they grow.
Understanding the importance of breastfeeding for hydration can help new mothers make informed decisions. The composition of breast milk varies throughout a feeding, providing different levels of hydration. Initially, the milk is more watery, providing quick hydration, while later milk is richer in nutrients. This unique characteristic means that infants receive adequate fluids at every feeding. Additionally, as babies engage in breastfeeding, they instinctively regulate their intake, feeding more often during hot days or when they are sick. Breast milk also contains antibodies that help protect infants from infections, indirectly supporting hydration needs. In contrast, formula feeding does not possess the same dynamic properties of breast milk. Hydration from formula is influenced by the preparation, and mothers may need to monitor for adequate fluid intake more closely. This potential for variability highlights the advantages of breastfeeding, especially in the context of hydration. Continuous breastfeeding supports not only hydration but also the development of a strong immune system, essential for toddlers venturing into the world. As such, mothers are encouraged to utilize breastfeeding as a primary source of hydration for their infants, ensuring optimal health as their little ones develop.
Another advantage of breastfeeding for hydration is its convenience. New parents often find that breastfeeding allows for on-demand feeding, which is vital for infants requiring consistent hydration. This demand-driven approach ensures babies can consume breast milk whenever they need, whether due to thirst or hunger cues. Parents do not have to worry about preparing bottles or measuring formula; the mother’s body produces milk tailored to meet the baby’s current needs. This ease of accessing nutrition is particularly beneficial during travel or outings, where maintaining hydration may become challenging. Furthermore, breastfeeding promotes bonding between the mother and infant. This close contact encourages alertness to the infant’s needs, enabling the mother to recognize signs indicating the need for hydration. If a baby seems fussier than usual, it may indicate a requirement for more fluids. As infants grow, the relationship between breastfeeding and hydration evolves, leading to the gradual introduction of solid foods. These foods should complement breastfeeding, with the mother ensuring that her infant remains adequately hydrated until transitioning to a diverse diet. Understanding these dynamics is essential for all caregivers managing infant nutrition and hydration.
The Role of Temperature in Hydration
Temperature plays an essential role in managing infant hydration through breastfeeding. During warmer months or when temperatures rise, babies may need to feed more frequently. Breast milk helps regulate body temperature, allowing babies to stay cool. Even with heat, breast milk uniquely accommodates an infant’s hydration needs without requiring additional water or fluids. Mothers can help by ensuring they are well-hydrated themselves, which promotes increased breast milk production. Hydration is vital, especially when infants exhibit signs of increased thirst, such as increased fussiness or a desire to nurse more frequently. On the contrary, during colder months, mothers should still continue breastfeeding, as breast milk nourishes and hydrates without the infant needing supplementary water. Seasonal variations can impact an infant’s feeding pattern; thus, remaining attuned to those changes can yield better hydration levels. Ultimately, continuous breastfeeding adapts to these environmental factors, offering tailored solutions for infant hydration seamlessly. Understanding how temperature affects both the mother’s milk production and the infant’s feeding behavior allows caregivers to keep hydration levels optimal throughout the changing seasons.
Beyond hydration, breastfeeding aids in the overall growth and development of infants. The first few days after birth, colostrum is produced, which is packed with nutrients and important antibodies. This early milk is crucial not just for hydration but also as an immune boost that helps shield infants from illness. Enhanced hydration from breastfeeding safeguards infants against dehydration-related illnesses, such as diarrhea. Infants receiving adequate hydration through breast milk are likely to experience fewer health issues, contributing to their long-term well-being. A well-hydrated infant is less prone to irritability and lethargy, factors that can stem from dehydration. Additionally, a healthy hydration level supports healthy cognitive development, setting a solid foundation for learning as they grow older. Parents who choose breastfeeding contribute positively toward preventing dehydration-related complications. It is important for caregivers to understand how breastfeeding intersects with overall health, creating an environment where infants can thrive. As babies progress through milestones, ensuring they are hydrated primarily through breast milk can have lasting benefits into their childhood and beyond.
Breastfeeding in Various Situations
In special circumstances, such as illness, breastfeeding can be vital for maintaining hydration. If an infant is sick, their body may need extra fluids to help recover. Breast milk not only hydrates but also provides antibodies to support their fight against illness. For instance, during bouts of fever or other infections, breastfeeding is the most effective way to ensure an infant stays hydrated. In addition, mothers can directly assess their infant’s needs through frequent feeds, adapting their approach as necessary. The closeness achieved through breastfeeding aids in promoting comfort to the littlest ones, allowing for better hydration management. Amid illness, not only does breast milk nourish the infant, but it also offers peace and warmth during recovery. The unique bacterial hydrating properties of breast milk simultaneously enhance the benefits. Awareness of breastfeeding’s ability to meet hydration needs in these moments highlights its significance as a life-sustaining source. Families should embrace breastfeeding as a central part of caring for an ill infant, ensuring hydration is both effectively met and emotionally supported during difficult times.
In conclusion, breastfeeding remains the optimal method for providing hydration to infants. The unique composition of breast milk not only ensures adequate fluid intake but also supports infants’ overall health, growth, and development. From regulating temperature to maintaining hydration during illness, breast milk adapts to meet an infant’s evolving needs. As children grow, ensuring hydration through continued breastfeeding, alongside introducing solid foods, further emphasizes the role nutrients play in health. Finally, educating parents about the importance of hydration can lead to better health outcomes for their children. Pediatricians and healthcare providers should advocate for exclusive breastfeeding during the first six months, with ongoing support beyond that. Parents and caregivers are encouraged to remain mindful of hydration needs, ensuring a continuous flow of nourishment throughout the early formative years. Thus, breastfeeding, defined by its adequate supply of hydration, stands as a critical component in healthy infant diets, fostering a generation of well-hydrated children. Celebrating the natural benefits of breastfeeding creates a supportive environment where infants can thrive, providing all necessary hydration to cultivate their growth and health.
In summary, maintaining hydration through breastfeeding is essential for infants, ensuring they receive necessary nutrients and fluids for their growth and well-being. The significant benefits of breastfeeding contribute directly to a child’s healthy development, making it a key factor in pediatric wellness. Knowledge and awareness concerning hydration requirements will have lasting impacts on children, promoting their overall health.