The Gut-Brain Axis: How Your Digestive Health Influences Appetite
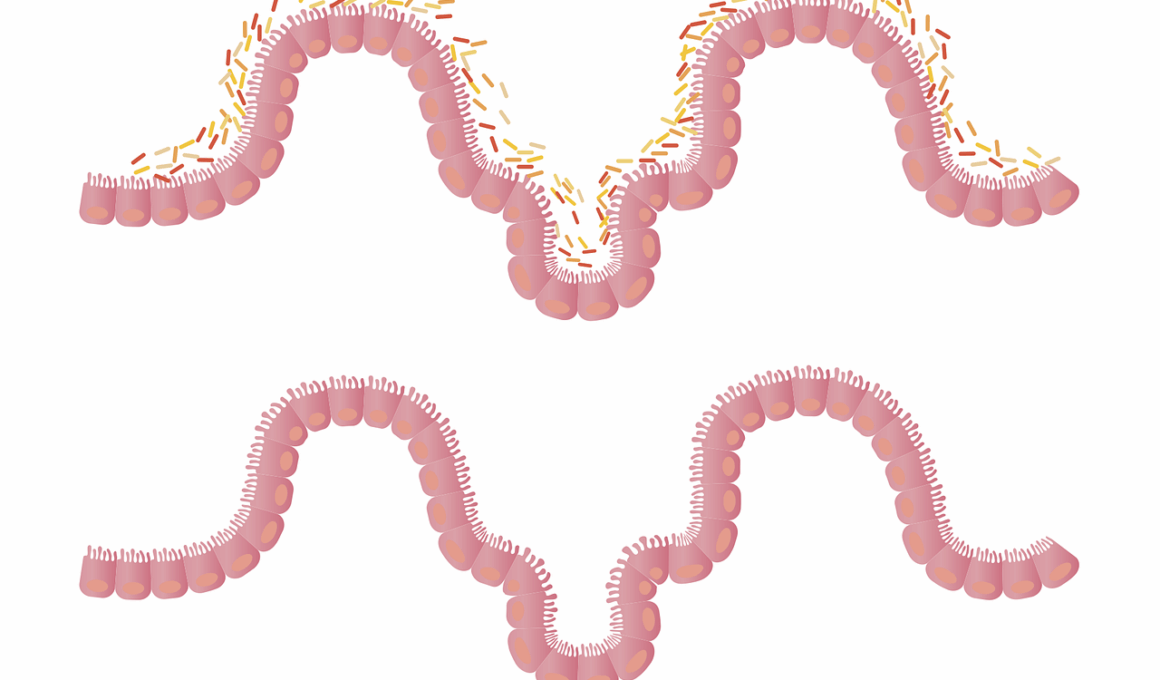
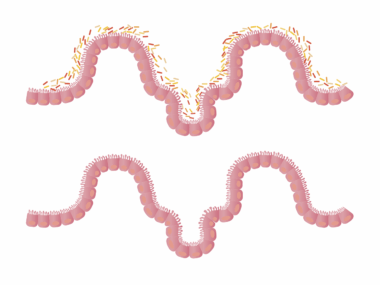
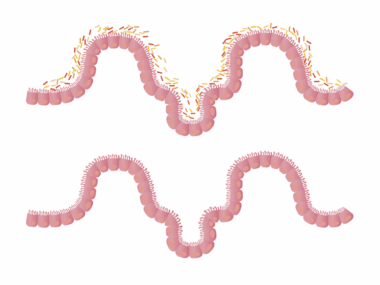
The gut-brain axis illustrates the powerful connection between digestive health and overall well-being. This intricate communication pathway consists of direct and indirect signals exchanged between the gut and the brain. Recent studies emphasize that the gut microbiota, consisting of trillions of microorganisms, can significantly influence neurological functions. These microbes contribute to various brain-gut signaling molecules which affect appetite, mood, and even cravings. When the gut is healthy, it promotes the production of hormones that help regulate hunger and satiety. Additionally, a balanced microbiome can reduce inflammation, impacting the signals sent to the brain. On the contrary, dysbiosis, or an imbalance in gut bacteria, can trigger overeating and unhealthy food choices. It’s essential to prioritize gut health as part of an effective weight loss strategy, thus enabling better appetite regulation. To achieve optimal gut health, incorporating fermented foods, prebiotics, and probiotics can nourish the beneficial bacteria residing in the digestive tract. Balancing these elements can lead to better digestion, improved overall health, and potentially enhance weight management efforts.
The Role of Hormones in Gut Health
Understanding the role of hormones is essential to grasp how gut health affects weight management. Hormones like ghrelin and leptin significantly influence appetite regulation. Ghrelin, known as the hunger hormone, is produced in the stomach and signals the brain to cue hunger. Conversely, leptin, released by fat cells, communicates fullness to the brain. A balanced gut microbiome influences the production and effectiveness of these hormones. A disrupted gut can lead to increased ghrelin levels and decreased leptin sensitivity, ultimately promoting overeating. This hormonal imbalance creates a challenging cycle for individuals striving to lose weight. By adopting a diet rich in fiber and nutrients, individuals can foster a healthy microbiome, thereby supporting the hormone balance necessary for effective appetite control. Furthermore, intermittent fasting and regular exercise can positively impact these hormones, promoting better appetite regulation and weight loss outcomes. Exploring practical strategies such as mindful eating can also significantly enhance awareness surrounding hunger signals and emotional eating. Ultimately, understanding and improving gut health can be a game changer for successful weight management.
Gut health significantly impacts emotional well-being and appetite through various mechanisms. The gut is often referred to as the “second brain” due to the vast network of neurons found within its lining. This extensive nervous system communicates with the brain via the vagus nerve, affecting mood and emotions. When gut bacteria are imbalanced, it can potentially lead to mood disorders such as anxiety or depression. These emotional states can trigger processes leading to unhealthy eating patterns and weight gain. A healthy gut microbiome can promote the production of neurotransmitters like serotonin, which plays a role in mood regulation. To maintain this balance, it is crucial to adopt a wholesome diet. Foods rich in omega-3 fatty acids, antioxidants, and vitamins contribute to promoting a flourishing gut microbiota. Regular physical activity also aids in sustaining gut health and reducing stress, further enhancing emotional and mental stability. Moreover, practicing mindfulness techniques such as meditation can help people reconnect with their body’s hunger signals, which may lead to improved decision-making regarding food and eating habits. Overall, maintaining emotional well-being is integral for effective weight management.
Impact of Diet on Gut Microbiome
The type of diet consumed plays a crucial role in shaping the gut microbiome. A diet rich in processed foods, sugar, and unhealthy fats can lead to an imbalance of gut bacteria, called dysbiosis. This imbalance can provoke bloating, constipation, and increased hunger signals. In contrast, a diet emphasizing whole foods, vegetables, fruits, and healthy fats nourishes beneficial bacteria, promoting gut health. Fiber is particularly important, as it serves as a prebiotic, feeding good bacteria and helping them thrive. Consuming a variety of fiber-rich foods can create a diverse microbiome, which has been linked to improved appetite regulation. Probiotic-rich foods like yogurt and fermented vegetables also contribute positively to gut health. Additionally, limiting sugar intake and incorporating anti-inflammatory foods can help reduce excess weight and improve gut function. Hydration should not be overlooked, as water is essential for digestion and maintaining a balanced microbiome. By prioritizing a nutritious diet that fosters a flourishing gut environment, individuals may experience increased energy, improved mood, and more effective appetite control, ultimately supporting weight loss strategies.
Emotions and stress levels can have a profound impact on digestive health, further linking gut health to weight management. Emotional eating often leads individuals to seek comfort in high-calorie, low-nutrient foods. This behavior can perpetuate a cycle of weight gain and poor gut health. Stress triggers the release of cortisol, a hormone that can lead to increased appetite and cravings for unhealthy foods. Managing stress is essential for maintaining a healthy gut microbiome and optimal digestion. Techniques such as yoga, deep breathing, and regular physical activity can aid in lowering stress levels. Cultivating awareness around emotional eating habits is also crucial for making healthier choices and understanding hunger signals. Keeping a food diary can enable individuals to identify emotional triggers, allowing for more conscious decisions about food intake. Practicing mindfulness during meals can create a deeper connection to one’s body and its signals. By addressing stress management and emotional health, individuals can support their gut health and appetite regulation, leading to a more effective weight loss strategy that focuses not just on calories but also on emotional well-being.
Benefits of Probiotics for Weight Loss
Research supports the introduction of probiotics as a beneficial component for gut health and weight loss. Probiotics are live microorganisms that confer health benefits when consumed in adequate amounts. They play a pivotal role in maintaining gut microbiota balance and enhancing digestion. By restoring beneficial bacteria, probiotics can help combat dysbiosis, which is linked to obesity and weight gain. Regular consumption of probiotic-rich foods or supplements can enhance metabolic rates, promoting fat loss. Studies suggest that specific strains, including Lactobacillus and Bifidobacterium, can significantly reduce body weight and fat mass. Additionally, probiotics may help regulate appetite hormones, making it easier to resist cravings. A healthy microbiome exerts an influence on fat storage and energy balance, further supporting weight loss efforts. Incorporating fermented foods such as kefir, kimchi, and sauerkraut into your diet can provide a natural source of probiotics. Furthermore, combining probiotics with prebiotics can maximize their effects, ensuring the beneficial bacteria thrive. Embracing probiotics as part of an overall dietary approach can provide additional support for those looking to lose weight and maintain digestive health.
Monitoring one’s gut health consistently can develop a tailored approach to weight loss. Identifying personal food sensitivities, allergies, or habits can significantly enhance overall well-being and weight management. It’s essential to embrace a trial-and-error method, as every individual responds differently to various foods. Keeping track of how specific foods impact both gut health and satiety can offer valuable insights. Regular check-ins with a healthcare professional or nutritionist can help navigate these changes effectively. Additionally, supporting a positive gut environment involves considering lifestyle factors. Adequate sleep and hydration are vital, as both contribute to optimal digestion, minimize stress, and support hormonal balance. Engaging in regular exercise can further bolster gut health and improve appetite control. Making sustainable dietary and lifestyle adjustments brings long-term success. Finally, staying informed about the latest research on gut health can guide strategies for managing weight. Seeking resources such as reliable blogs, podcasts, or organized workshops foster a sense of community and shared experience. Thus, empowering individuals to make informed decisions to support their gut health and effective weight management.