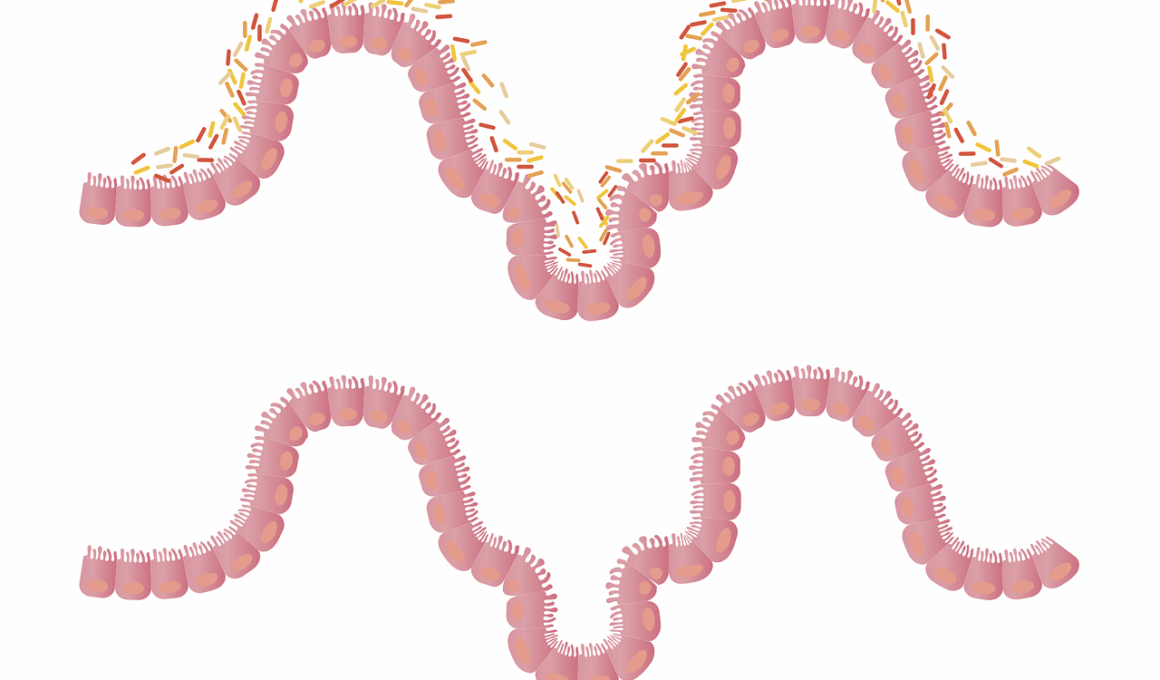
Meal Timing and Its Role in Gut Inflammation Control
Gut health is increasingly considered essential for overall wellness, with gut microbiome balance playing a vital role. Standard meal timing can significantly affect the gut microbiome, which, in turn, influences inflammation levels. Disruptions to this timing, such as irregular meal patterns, can negatively impact gut health. It’s crucial to understand how the timing of food intake reshapes the gut microbiota. Research indicates that irregular meal timing can lead to dysbiosis, an imbalance that may promote gut inflammation. By optimizing meal timing, individuals can help maintain a healthy microbiome and mitigate inflammatory responses. Some studies suggest that consuming most calories during the day aligns better with our body’s circadian rhythms. For optimal health, it might be beneficial to limit caloric intake to specific windows, enhancing metabolic efficiency and gut health. Additionally, various studies show that late-night eating correlates with increased inflammation markers in the body. Being mindful about timing when we eat can drastically alter microbial composition and health outcomes, highlighting the importance of meal timing in managing inflammation effectively.
Emerging evidence suggests that the gut microbiome is not static; it’s influenced by numerous factors, including meal timing. During the daylight hours, our metabolism is naturally more active, which also affects the gut microbiota. Mice studies have demonstrated that feeding aligns with circadian rhythms results in improved gut health and reduced inflammation. Similarly, research in humans supports the idea that favorable meal timing leads to positive shifts in gut microbiota composition. Incorporating time-restricted eating (TRE) may enhance microbiome diversity. TRE involves eating within a specific time frame each day, which aims to synchronize food intake with the body’s natural metabolic cycle. This approach can help stabilize blood sugar levels and regulate fat metabolism. By shifting the focus to meal timing, individuals may experience significant health benefits. Eating regularly at similar times increases the body’s ability to anticipate nutrient arrival, optimizing digestive processes and microbial responses. Ultimately, when we eat matters just as much as what we eat, emphasizing the dynamic relationship between meal timing and gut health in reducing inflammation.
Impact of Meal Timing on Inflammation
In chronic inflammatory conditions, optimal meal timing can provide crucial support for gut health. Research reveals that certain meal patterns can help reduce markers of inflammation. For instance, late-night eating is associated with heightened inflammatory responses, possibly due to lower digestive efficiency at night. Shifting food intake to earlier times can optimize gut microbiota diversity, which plays a protective role against inflammation. A balanced microbiome secretes beneficial metabolites, aiding in reducing inflammatory damage. Studies suggest that specific timings, like consuming larger meals earlier in the day, can correlate with lower inflammation levels. By adopting early eating schedules, individuals can support their microbiome’s ecology, aligning more closely with their natural circadian rhythms. Further, fasting or delaying breakfast may enhance microbiome composition, fostering better health outcomes. Taking care of meal timing is not merely about caloric intake; it’s a comprehensive approach to nurturing gut health and managing inflammation. The relationship between meal timing and gut inflammation underscores the need for mindful eating habits, which can lead to substantial improvements in overall well-being over time.
Additionally, it’s crucial to consider the type of macronutrients consumed during particular meal times. Specific foods can either exacerbate or alleviate inflammation based on when they are eaten. Diets rich in fiber, antioxidants, and omega-3 fatty acids are known to help mitigate inflammation. Pairing these foods with strategic meal timing maximizes their benefits, aligning dietary intake with the body’s natural rhythms. Foods high in refined sugars and unhealthy fats, especially if ingested late at night, can disrupt gut hemostasis and promote inflammation. Identifying optimal timing for nutrient-dense foods can significantly enhance gut microbiome health. Moreover, meals should ideally be consumed in sync with biological cues, ensuring the body can adequately process and utilize nutrients. Furthermore, incorporating diversity in food choices during designated eating windows fosters a resilient microbiome. This varied diet can support different bacterial species, contributing to a more balanced microbiota, directly impacting inflammatory processes. Overall, understanding meal composition in conjunction with timing can empower individuals in managing gut inflammation, paving the way for improved health outcomes.
Strategies for Effective Meal Timing
Implementing effective meal timing requires conscious effort and planning. Individuals can start by establishing a consistent eating schedule, creating timing rituals around meals. Focus on setting regular meal times, aiming for meals earlier in the day and avoiding late-night eating. Incorporating larger breakfasts may be advantageous, as it primes the metabolism for the day. Meals should ideally be completed within a suitable timeframe, fostering a period of fasting overnight to allow gut repair and rejuvenation. Attention must also be given to snacking habits, discouraging continuous grazing that disrupts metabolic cycles. Limiting eating to a window of eight to ten hours can optimize gut microbiota health. Emphasizing whole, nutrient-dense foods, and wholly avoiding processed snacks during eating windows is paramount. Individuals may also track their food intake and gut-related symptoms to understand how timing and food choices interact. Regular reflection and adjustments based on experiences can cultivate long-lasting habits. Additionally, consulting with a healthcare professional can provide tailored meal timing strategies suited to individual needs and health goals.
Furthermore, mindful eating practices can significantly enhance the benefits gained from strategic meal timing. By focusing on the sensory experience associated with meals—savoring each bite, observing hunger cues, and appreciating flavors—individuals can develop a healthier relationship with food. This mindfulness not only aids digestion but also reinforces satiety signals which are vital for maintaining a balanced diet. Eating mindfully ensures that meal timing complements not just physical health but also psychological well-being. Stress and disturbances due to the hurried nature of modern eating habits can exacerbate inflammation, creating a vicious cycle. Incorporating relaxation techniques into meal times, such as breathing exercises, may mitigate these stressors. Additionally, sharing meals with loved ones fosters social connections, making dining a more positive experience. Engaging in conversations while eating can slow down the process and create greater awareness of meals. Ultimately, the combination of mindful consumption with well-timed meals can harmonize bodily responses, providing extensive benefits for controlling gut inflammation and promoting a healthy microbiome.
Conclusion: Embracing Meal Timing for Gut Health
To conclude, recognizing the importance of meal timing in relation to gut inflammation is vital for achieving overall health. The intricate interaction between meal timing and gut microbiota cannot be overlooked. Irregular eating patterns can lead to detrimental health outcomes manifested through chronic inflammation. By adopting structured meal timings, individuals can guide their bodies toward a state of balance, reducing inflammation, and nurturing gut health. Fostering a meal environment that prioritizes nutrient-dense, anti-inflammatory foods during optimal time windows enhances the benefits. This understanding fosters a proactive approach, emphasizing that not merely what individuals eat, but when they eat matters. Integrating mindful eating practices further strengthens this relationship, amplifying the potential benefits of a robust gut microbiome. As research continues to unveil the nuances of diet and timing, individuals have the opportunity to adopt healthier habits that deeply affect their well-being. In a rapidly evolving world filled with dietary choices, focusing on meal timing could emerge as a simple yet effective tool in managing inflammation and embracing a healthier lifestyle.
Ultimately, allowing the body to align its eating behaviors with natural rhythms can be transformative. Engaging with these principles can initiate a journey toward enhanced gut health, ultimately leading to reduced inflammation and lasting wellness. In this pursuit, individuals are encouraged to dig deeper into their unique responses to meal timing and how it influences health outcomes. The synergy between meal timing and the gut microbiome offers invaluable insights for anyone seeking an improved quality of life. Exploring ways to implement these strategies can lead to profound shifts in health. Consistency and awareness are key; small changes often yield significant results. Embracing meal timing as a fundamental component of nutrition provides a roadmap for establishing balance and harmony within the body. With the support of scientific research, individuals can make informed decisions about their eating patterns, fostering opportunities for a thriving gut environment. In a world where gut health is paramount, meal timing stands out as a simple yet effective strategy worth incorporating, ensuring sustainable health for years to come.