Early Intervention Strategies for Alcohol and Depression
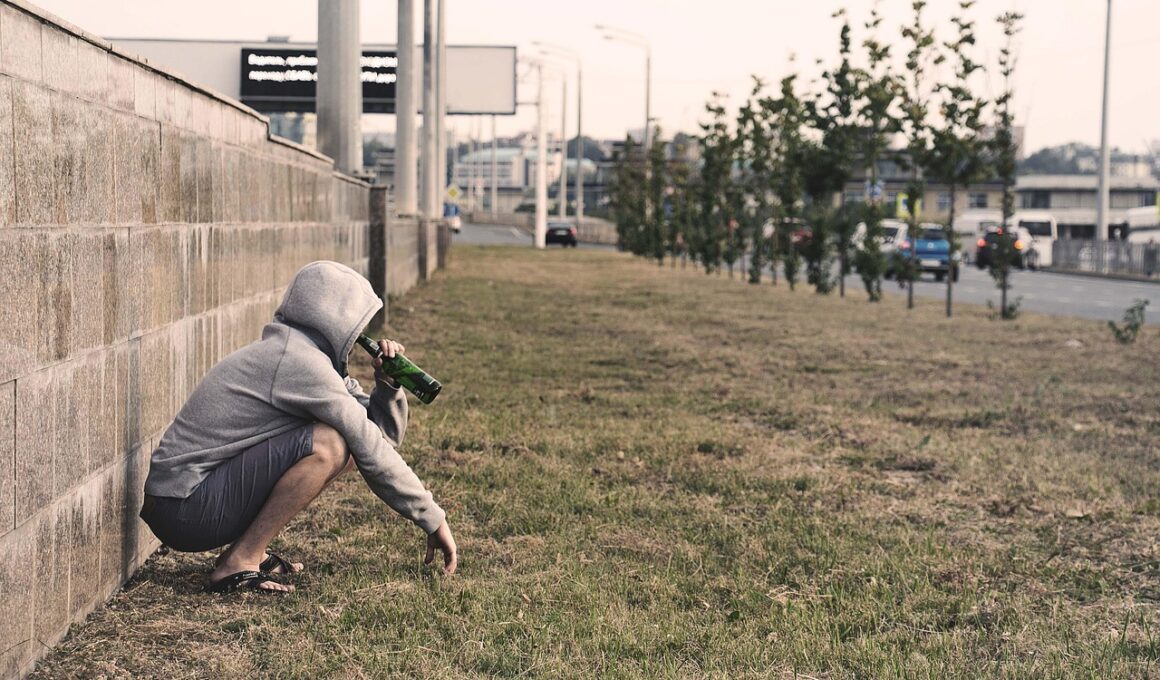
Understanding the intricate relationship between alcohol use and depression is vital for effective treatment. Early intervention strategies play a crucial role in addressing the underlying issues that contribute to this dual diagnosis. One essential strategy is screening and assessment, where healthcare providers evaluate individuals for symptoms of depression alongside alcohol misuse. This dual assessment can lead to a more accurate diagnosis and tailored treatment plans. Incorporating motivational interviewing techniques can help in engaging patients, encouraging them to discuss their alcohol consumption and its potential impact on their mental health. Education and awareness about the risks associated with alcohol use can empower individuals to make informed choices. Group therapy sessions can also provide a supportive environment for individuals struggling with both alcohol and depression. By sharing experiences and coping strategies, participants can foster a sense of belonging and reduce feelings of isolation. Moreover, integrating professional support from mental health specialists can significantly impact recovery outcomes. Overall, proactive measures, including regular screenings and comprehensive care, can facilitate early intervention and promote healthier lifestyles for individuals affected by alcohol and depression.
Another significant aspect of early intervention is the involvement of family and social support networks. Encouraging family participation can enhance treatment effectiveness by fostering a supportive environment for the individual. Family therapy can be beneficial, as it addresses family dynamics and promotes healthier communication patterns among members. This support can be critical in preventing relapse and reinforcing positive behaviors. Additionally, connecting individuals with local support groups can provide the social reinforcement needed for recovery. Groups like Alcoholics Anonymous not only offer peer support but also access to resources that can help navigate the complexities of addiction and mental health issues. Peer support is instrumental in creating lasting change, as shared experiences resonate powerfully with those in similar situations. Health professionals should also consider the use of technology in monitoring and support, utilizing apps that track alcohol consumption and mood patterns. Regular check-ins via teletherapy can offer flexibility and sustained engagement in treatment. Overall, a multifaceted approach integrating family, community, and technology can greatly enhance early intervention strategies, ultimately leading to better health outcomes for those struggling with alcohol and depression.
Strategies for Effective Screening
Implementing effective screening strategies is essential to identify early signs of alcohol misuse and depression. Routine screening tools, such as the AUDIT (Alcohol Use Disorders Identification Test), can help healthcare providers assess patients’ drinking behaviors systematically. Integrating standardized depression screening tools, like the PHQ-9 (Patient Health Questionnaire), allows for a comprehensive view of mental health alongside alcohol consumption patterns. Patients who exhibit risky behaviors can be flagged for immediate intervention, enhancing early detection rates. Moreover, creating a safe and non-judgmental environment encourages patients to be honest about their alcohol use and mental health status. Healthcare providers should receive training on how to conduct these screenings sensitively and effectively. Furthermore, incorporating technology—such as e-screening platforms—can facilitate anonymous assessment, leading to increased participation. Following up with patients who screen positive is critical in developing an effective treatment plan. Effective communication of results can also aid in collaborative care efforts between providers and patients, ensuring that treatment strategies align with the individual’s needs. Overall, embracing a systematic screening approach can significantly improve early intervention capabilities and outcomes for those facing alcohol-related challenges and depression.
The integration of pharmacotherapy is another pivotal strategy in managing co-occurring alcohol use and depression. Medications, such as selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs), are often effective in treating depressive symptoms while also addressing alcohol dependency. Furthermore, the use of naltrexone may help individuals curb cravings for alcohol, thereby easing the path to recovery. Collaborating closely with psychiatric professionals ensures that individuals receive the right medications tailored to their unique needs. Continuous monitoring of medication effects and side effects is crucial during treatment. Patients should be educated on the importance of adhering to prescribed medication regimens, which can significantly impact their recovery journey. Therapeutic alliances can be strengthened through regular follow-ups, thus promoting adherence and open communication regarding medication efficacy. This dual approach can lead to improved mental health, allowing individuals to engage more fully in other therapeutic activities. Moreover, addressing barriers to medication access, such as costs and availability, should be a primary goal for healthcare systems. A comprehensive treatment plan that integrates both medication management and psychosocial strategies can substantially enhance recovery outcomes for individuals dealing with alcohol use issues and depression.
Role of Lifestyle Modifications
Implementing lifestyle modifications represents an essential component of early intervention strategies for alcohol and depression management. Encouraging individuals to adopt healthy habits can significantly improve their mental well-being and reduce alcohol cravings. Regular physical activity, for instance, has been shown to alleviate symptoms of depression, enhance mood, and provide a constructive outlet for stress. Additionally, incorporating nutritional education into treatment can help patients understand the impact of diet on mental health. A balanced diet rich in nutrients can boost serotonin levels and may contribute to emotional stability. Mindfulness practices, such as yoga and meditation, can assist in managing stress and enhancing overall mental health as well. Early intervention programs should prioritize these lifestyle changes alongside traditional therapeutic approaches, creating a holistic treatment program tailored to the individual’s needs. Support groups can also emphasize the importance of healthy lifestyle choices, offering shared resources and success stories as motivation. Providing patients with tools and strategies for making lasting lifestyle changes will empower them to take charge of their recovery journey. Ultimately, fostering a lifestyle that promotes mental and physical health can lead to improved outcomes for those affected by alcohol use and depression.
Incorporating technology into treatment strategies is also essential for early intervention in alcohol and depression. Mobile health applications can aid individuals in tracking their emotions, alcohol consumption, and triggers, allowing for better self-monitoring and reflection. These applications often include resources, reminders, and coping skills, creating an invaluable tool for engagement in recovery. Telehealth services provide flexible therapy options, reducing barriers to access associated with traditional therapy settings. Individuals in remote or underserved areas can benefit significantly from convenient and affordable access to mental health support. Virtual support groups can also allow individuals to connect with peers and share their experiences, fostering community and encouragement. As technology continues to evolve, the integration of artificial intelligence in personalized treatment plans may present new possibilities for tailored therapeutic interventions. Ensuring that health professionals are trained to utilize these technological tools will enhance their capacity to deliver effective early interventions. While technology offers new avenues for support, it is crucial to maintain a balance with face-to-face interactions and traditional therapeutic practices. This blended approach can lead to impactful, comprehensive treatment for those struggling with alcohol-related challenges and depression.
Long-Term Support and Maintenance
Providing long-term support is fundamental in ensuring sustained recovery from alcohol use and depression. Early intervention should not conclude with the initial treatment phase; ongoing support mechanisms are essential for preventing relapse and maintaining mental health stability. Aftercare programs, which often include regular follow-ups and continued engagement with support groups, facilitate a smoother transition from intense treatment to everyday living. These programs should extend beyond therapy sessions, incorporating lifestyle adjustments, coping strategies, and social support to foster resilience against triggers. Regular assessments and check-ins help individuals monitor their progress and address challenges proactively. Encouraging individuals to establish a support network, including friends, family, and peers who understand their journey, can provide invaluable assistance during the recovery process. Building strong relationships and social connections is crucial for combating loneliness and isolation often experienced during recovery. Education on the potential signs of relapse is also important; individuals should be equipped with skills to recognize warning signs early. Through a combination of community support, professional guidance, and self-awareness, long-term support can significantly enhance recovery outcomes, ensuring individuals lead fulfilling lives free from addiction and depression.
Integrating cultural competence into early intervention strategies can also enhance effectiveness for diverse populations. Understanding cultural backgrounds, beliefs, and values can inform treatment approaches and improve patient-provider relationships. Tailoring interventions to reflect cultural considerations can lead to higher engagement and better outcomes. Additionally, involving community leaders or support networks in treatment delivery can bolster trust and communication. Culturally specific education resources can address stigma and normalize discussions around alcohol use and depression within communities. Involving family systems, which are often central in various cultures, enhances the healing process and builds a more robust support network. Navigating cultural nuances requires training and sensitivity from healthcare professionals to address potential disparities in treatment access and engagement. Collaboration with local organizations that focus on mental health and addiction can facilitate culturally competent care. Ensuring all individuals receive equitable treatment is vital for promoting social justice in health outcomes. Overall, incorporating cultural competence alongside existing early intervention strategies creates a more inclusive and effective framework for addressing alcohol use and depression across demographics. Ultimately, personalized and culturally sensitive care leads to sustainable recovery and improved community well-being.