The Gut-Brain Axis: How Meal Timing Plays a Role
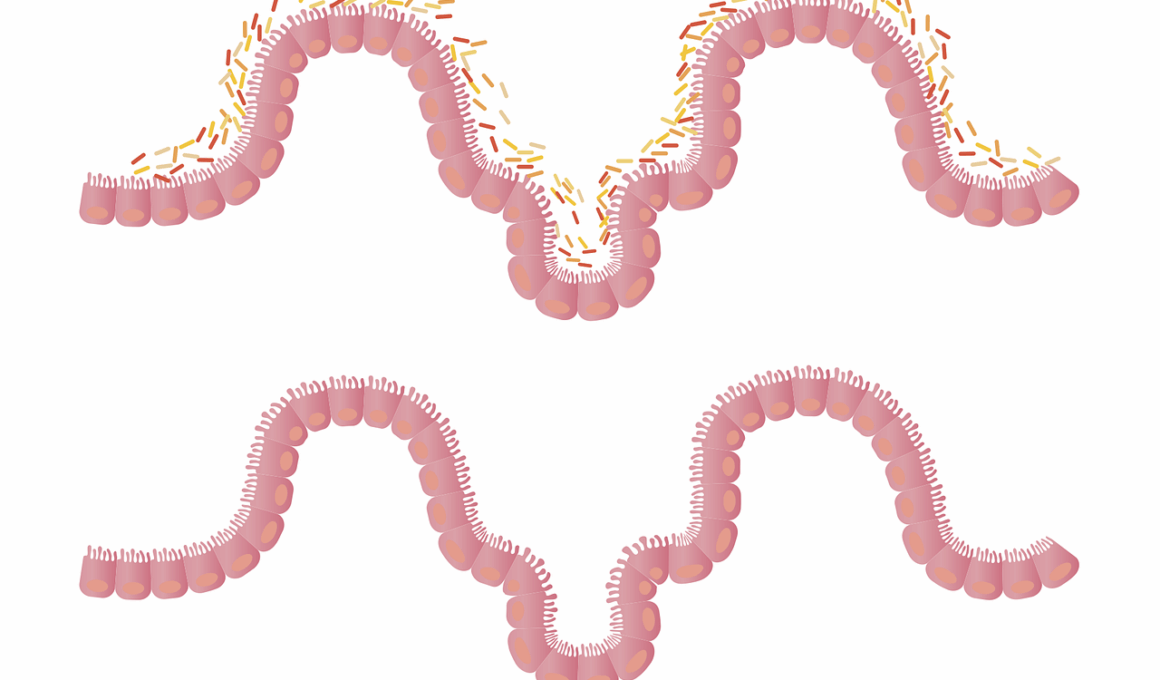
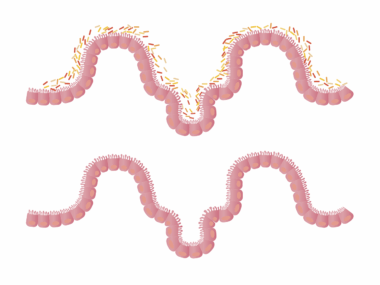
The gut-brain axis is a complex communication network between the gastrointestinal tract and the brain. This connection suggests that what we eat and when we eat can significantly affect our mental health and overall well-being. Understanding the gut-brain relationship requires a look at how meal timing influences gut function. Research shows that meal timing impacts circadian rhythms, which play a crucial role in regulating digestive processes. Consuming meals at irregular intervals can disrupt these rhythms and lead to gastrointestinal issues such as bloating, indigestion, and irritability. Moreover, the gut microbiome, which consists of trillions of microorganisms, also responds to meal timing. It can change its composition and activity based on when food is introduced. When we eat in sync with our body’s natural rhythms, we can improve digestion and nutrient absorption. Thus, paying attention to meal timing may help optimize gut health. To summarize, optimizing meal patterns can influence the gut-brain axis and support overall health. Experimenting with consistent meal timing may provide better digestion and emotional balance.
The influence of meal timing on gut health is supported by various scientific studies. These studies explore how regular eating patterns contribute to a healthier gut microbiome. For example, consuming meals at the same time every day can foster a stable environment for beneficial gut bacteria to thrive. On the contrary, inconsistent meal timings can promote the growth of harmful bacteria, leading to digestive disorders. Furthermore, the connection between gut bacteria and mental health underscores the importance of gut health in overall well-being. Dysbiosis, an imbalance in gut bacteria, has been linked to conditions like anxiety and depression. Consequently, maintaining a regular eating schedule can help in balancing these bacteria. Adopting time-restricted eating, where food intake is limited to certain hours, has shown promise in improving gut health. Such patterns may enhance metabolic processes and reduce inflammation, benefiting both gut function and brain health. Moreover, the timing of meals can affect hormonal signals in the body, particularly those regulating hunger and satiety. Hormonal balance plays a pivotal role in our relationship with food, making it essential to consider when we eat.
Meal Timing Strategies for Gut Health
Adopting specific meal timing strategies can significantly enhance gut health and function. One essential strategy is practicing regular meal intervals throughout the day. This can include having three main meals, spaced evenly, along with healthy snacks as needed. Monitoring meal sizes is equally important, as oversized portions can overload the digestive system and hinder gut function. Another effective strategy is implementing time-restricted eating. This method involves limiting the eating window, thus allowing the gut time to rest and repair during fasting periods. Such an approach can improve digestion and metabolic health while minimizing gut-related discomforts. Additionally, consuming meals rich in dietary fibers at consistent times boosts gut microbiome health effectively. Foods such as fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and legumes help nourish beneficial gut bacteria, enhancing their activity. It’s also beneficial to pay attention to hydration, ensuring fluid intake supports digestion. Maintaining regular meal timing enhances the gut-brain axis and promotes feelings of well-being. By incorporating these strategies into daily routines, individuals can positively influence their gut function and overall health.
The relationship between meal timing and gut function extends to the importance of nighttime eating habits. Consuming large meals late in the evening can disrupt sleep patterns and negatively affect gut health. Research indicates that eating close to bedtime can increase the likelihood of experiencing heartburn, acid reflux, or indigestion during sleep. Moreover, late-night eating can influence the balance of hormones related to appetite and digestion. It is advised to finish eating at least two to three hours before bedtime. This practice not only improves sleep quality but also allows better recovery of the gut overnight. The stomach requires time to process food, and a healthier pattern of meal timing can facilitate optimal digestion during the day and rest periods for gut recovery overnight. Furthermore, focusing on lighter meals in the evening can help maintain a healthy digestive process. Ultimately, observing meal timing and portion control contributes to a better gut-brain connection and emotional wellbeing. By adopting these practices, individuals can achieve better digestive health and improved lifestyle habits for optimal daily functioning.
The Role of Gut Microbiota
Gut microbiota plays a key role in digestion and influences a wide range of physiological processes. The composition of gut microbiota can shift based on meal timing, impacting how well the gut functions. Eating consistently at the same times can support a more harmonious environment for these microorganisms. Gut microbiota thrives on diverse and balanced diets, especially when meals are spaced appropriately throughout the day. For instance, studies have highlighted the impact of a high-fiber breakfast in enhancing gut microflora diversity. In contrast, skipping meals or delaying eating can lead to decreased microbial diversity. Such changes can trigger digestive issues and affect overall health, as diverse microbiota contributes to better nutrient absorption. Personalized meal timing could greatly influence these factors, making it an essential area of interest for nutritional and medical research. Additionally, lighter, plant-based meals are increasingly encouraged to maintain gut health effectively. Supporting gut microbiota through proper meal timing enhances digestion and offers mental health benefits. Overall, fostering a conducive environment for the gut microbiome through mindful meal timing leads to lasting health advantages.
The gut-brain connection highlights the critical role that gut health plays in overall mental and physical well-being. Understanding the timing of meals can provide a pathway to better emotional health and cognitive function. For example, irregular eating patterns have been associated with higher stress levels and mood swings. Consistent meal schedules can lessen anxiety and promote a sense of stability. Furthermore, incorporating mindfulness during meals fosters greater awareness of food choices and their effects on the body. This can lead to healthier cravings and improved decision-making related to food. Deepening the connection between nutrition and mental wellness, recent studies highlight that the composition of gut microbiota impacts neurotransmitter production. Neurotransmitters like serotonin, which are crucial for mood regulation, have been shown to correlate with gut health. Thus, prioritizing meal timing and composition directly influences our mental landscape. Engaging in practices that enhance gut health through proper timing and nutrient intake can pave the way for improved emotional resilience. Taking steps to promote intentional eating nurtures not just the gut but supports overall mental clarity and emotional balance, key factors in holistic health.
Conclusion: Meal Timing and Its Impact
In conclusion, meal timing is undeniably linked to gut health and consequently affects the gut-brain axis. By understanding how when we eat impacts gut function, individuals can adopt better eating habits that promote digestive health and emotional well-being. Regular meal patterns bolster digestive efficiency and ensure balanced gut microbiota. Furthermore, this relationship underscores the importance of daily routines in achieving optimal health outcomes. Practical meal timing approaches such as time-restricted eating and maintaining consistent meal schedules can foster a healthier gut environment. Emphasizing lighter meals in the evening and achieving a balanced diet rich in fiber will further support gut function. Therefore, being mindful of when and what we eat significantly impacts our gut health, paving the way for improved emotional and mental clarity. These strategies can empower individuals to take charge of their health through informed dietary choices. As research continues to evolve, we can expect a deeper understanding of the intricate connections between gut health and various bodily functions. Implementing these meal timing strategies may lead to enhanced well-being and digestive comfort for many.
In summary, embracing the role of meal timing in gut health is essential for achieving overall well-being. Our daily routines play a significant role in digestive processes and emotional stability. Adopting a consistent eating schedule along with nourishing meals can create a positive feedback loop of health throughout the body. Being aware of how timing influences digestive activity can lead to more informed choices. As we recognize the gut-brain axis’s significance, it becomes clear that understanding meal timing provides us with tools for enhancing health. For those interested in optimizing their gut function, experimenting with different meal schedules can yield beneficial results. The journey towards better gut health can begin with mindful choices regarding when to eat. Continued research will provide deeper insights into these connections, paving the way for personalized dietary choices that align with individual needs. Furthermore, by incorporating an understanding of meal timing, we can promote healthier gut microbiota and support mental well-being. Thus, taking control of meal timing is not just a dietary choice; it’s a holistic approach to nurturing the body and mind in unity.