The Science Behind Digestive Enzymes and Gut Flora
Understanding digestive enzymes is crucial to appreciating their impact on gut flora. Digestive enzymes are biological molecules that facilitate the breakdown of food substances in our digestive system. They play pivotal roles in the digestion process, helping to convert food into energy and nutrients. Enzymes like protease, lipase, and amylase help in digesting proteins, fats, and carbohydrates, respectively. These enzymes are secreted by various organs, including the pancreas and stomach. A healthy gut relies on the proper functioning of these enzymes to maintain a balanced microbiome. When the activity of these enzymes is impaired, digestive issues may arise, leading to discomfort and an imbalance in gut flora. Effective digestion ensures that our bodies can absorb essential nutrients and eliminate toxins. This delicate balance is crucial for overall health. Thus, integrating digestive enzyme-rich foods can support gut health. Fermented foods such as kimchi, yogurt, sauerkraut, and kefir enhance the production of these enzymes and nurture beneficial bacteria. Incorporating these into your diet can foster a thriving gut ecosystem that enhances digestion naturally.
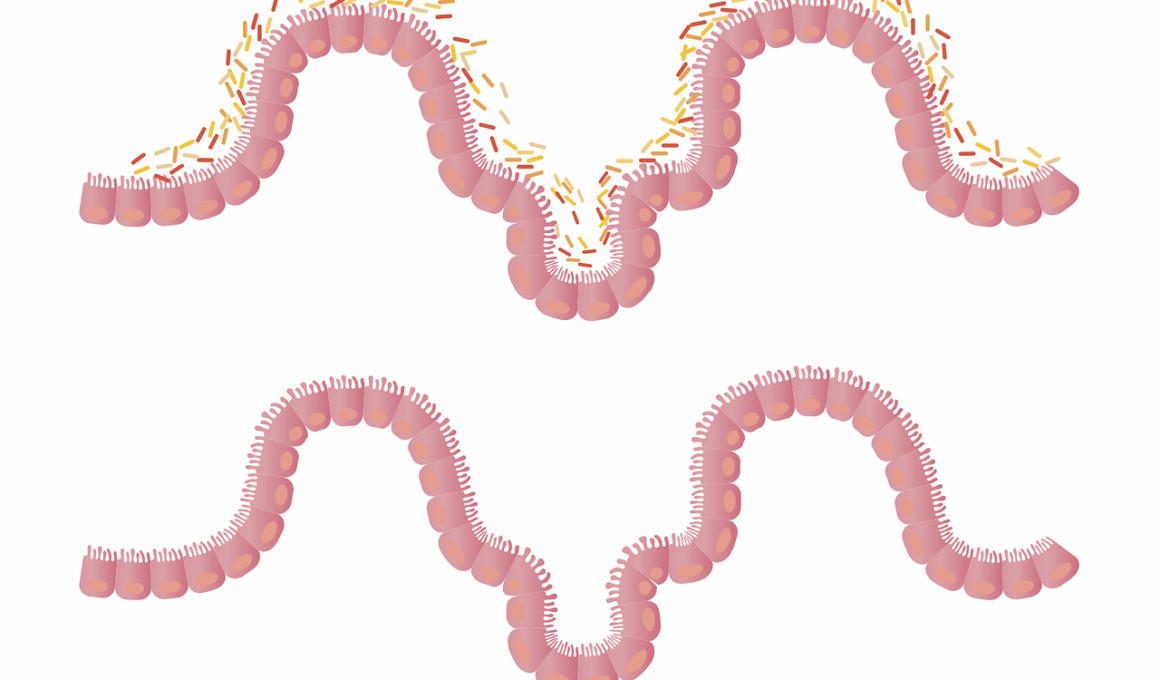
In addition to supporting digestive function, digestive enzymes also interact closely with the gut microbiome. The gut microbiome consists of trillions of microorganisms, including bacteria, fungi, and viruses, residing in our intestines. This diverse community plays an essential role in human health, influencing metabolism, immunity, and overall wellness. The balance of gut flora is critical, as beneficial bacteria outnumber harmful pathogens to maintain gut harmony. Digestive enzymes optimize the environment for healthy gut bacteria, helping them thrive. Without adequate enzymes, beneficial bacteria may struggle to proliferate, leading to dysbiosis. Dysbiosis can manifest as symptoms like bloating, gas, or food intolerances. Moreover, certain foods, such as whole grains and fruits, can promote the growth of these microorganisms while providing essential nutrients and fiber. Probiotics, found in fermented foods, complement the function of digestive enzymes by enhancing the stability of the microbiome. However, enzyme insufficiency can be linked to various health issues, highlighting the importance of these molecules. Ensuring proper enzyme function through a balanced diet and supplementation can lead to improved gut health and flora balance.
Types of Digestive Enzymes and Their Functions
Digestive enzymes are categorized primarily into three types: proteases, lipases, and amylases. Each type plays a unique role in breaking down specific macronutrients. Proteases break down proteins into amino acids, allowing for better absorption and utilization by the body. They are vital for muscle repair and immune function. Lipases, on the other hand, specialize in digesting fats, converting them into fatty acids and glycerol. These components are essential for cellular structure and energy production. Lastly, amylases are responsible for breaking down carbohydrates, such as starches into simpler sugars. This process supports energy needs and maintains stable blood sugar levels. Our bodies naturally produce these enzymes, but several factors can influence their effectiveness, including age, diet, and gastrointestinal health. For instance, individuals with gastrointestinal disorders may have a reduced enzyme secretion level. Supplementing with additional enzymes might help alleviate symptoms associated with digestive insufficiency. It’s also beneficial to consume enzyme-rich foods and maintain a nutritious diet to support natural production. Knowledge of the types of enzymes can empower individuals to make informed decisions that improve digestion.
Incorporating digestive enzymes into your diet can be achieved through various food sources and supplements. Certain foods are naturally high in digestive enzymes, notably pineapples and papayas, which contain bromelain and papain, respectively. These fruits can aid digestion when consumed fresh and raw. Other foods, such as kiwis, fermented vegetables, and yogurt, can provide additional digestive support. When incorporating enzyme-rich foods, it’s critical to balance them with a variety of nutrients. For example, maintain adequate hydration to help enzymes function optimally. Nutritional supplements containing digestive enzymes are available for those unable to meet their needs through diet alone. However, choosing high-quality supplements is essential to ensure the right dosage and formulation. Consulting with a healthcare professional about supplementation may also be beneficial. Ultimately, the goal is to create a diverse diet that nurtures the gut microbiome. Awareness of food choices and their effects on digestion will lead to improved gut health. A balanced intake of enzymes and their cofactors ensures the body operates at its best.
The Role of Gut Flora in Digestive Health
Gut flora, or the gut microbiome, plays an intricate role in the overall health of the digestive system. A diverse microbiome supports various bodily functions, including digestion, nutrient absorption, and immune response. Maintaining a robust gut microbiome can help ward off infections and inflammation. The composition of gut flora can be influenced by diet, lifestyle, and environment. A fiber-rich diet, probiotics, and prebiotics can encourage the growth of beneficial bacteria while suppressing harmful species. This balance is essential for maintaining digestive health, overall well-being, and emotional health due to the gut-brain connection. Prolonged disruptions in gut flora may lead to gastrointestinal diseases such as irritable bowel syndrome and inflammatory bowel disease. This association highlights the importance of gut health as foundational to overall wellness. To improve gut flora, incorporating foods high in fiber, omega-3 fatty acids, and antioxidants is essential. Natural sources include nuts, seeds, legumes, and oily fish, which collectively promote a balanced microflora. Understanding the complex interplay between digestive enzymes and gut flora empowers individuals to make healthier lifestyle choices.
Probiotics also play a vital role in supporting the function of digestive enzymes and maintaining gut flora. Probiotics are live microorganisms beneficial for gut health and are available in foods like yogurt, kefir, and fermented vegetables. They can help improve the gut’s environmental conditions for enzymes to work effectively. When adequately nourished, probiotics can enhance the activity of digestive enzymes, which can improve nutrient absorption and digestion efficiency. This synergistic relationship demonstrates how important gut health is for overall health. Additionally, some studies suggest probiotics can help alleviate symptoms of digestive disorders and contribute to a healthier gut microbiome. It is essential, however, to select specific strains with proven benefits for efficient digestion. Diversity within the probiotic strains used can also lead to multiple health benefits, as different strains target various gut issues. To maximize intake, combining high-probiotic foods with enzyme-rich foods is advisable. This combination is not only delicious but also a proactive approach to achieving and maintaining robust digestive health and improved gut flora balance. Lifestyle modifications, including diet adjustments and stress management, further enhance gut health outcomes.
Conclusion: Maintaining Digestive Health
In conclusion, understanding the science behind digestive enzymes and gut flora is foundational for maintaining digestive health. A healthy digestive system relies heavily on the proper function of digestive enzymes, which break down food into essential nutrients. By fostering a balanced gut microbiome through diet, individuals can significantly improve their overall health. Including enzyme-rich foods, probiotics, and prebiotics in daily meals creates the perfect ecosystem for digestive enzymes and gut flora. Monitoring the composition of gut flora through regular assessments and consultation with a healthcare professional can lead to tailored dietary recommendations and interventions. It’s crucial to recognize that each person’s digestive system is unique; therefore, personalized approaches yield the best outcomes. Simple alterations in dietary habits can make significant improvements in digestive health. The interplay between enzymes, gut flora, and overall health is complex yet manageable. Taking proactive steps fosters a healthier digestive system, empowering individuals to lead fulfilling and vibrant lives.
Investing in one’s gut health ultimately pays off, as it influences energy levels, mood, and even mental clarity. By becoming aware of how to support digestive enzymes and gut flora, individuals can embark on a journey toward a healthier lifestyle. Practicing mindfulness concerning food choices is vital for nurturing beneficial gut bacteria and ensuring the efficiency of enzymes. Include a variety of foods in your diet, emphasizing whole, unprocessed options for optimal gut function. Daily habits, such as regular exercise, quality sleep, and stress management, also influence gut health positively. All these components work in synergy to support overall well-being, emphasizing the importance of a holistic approach. Encourage discussions with dietitians or nutritionists who can provide personalized advice and recommendations to enhance gut health. A commitment to maintaining digestive health is ultimately a commitment to overall well-being. As research continues to evolve in gut health, so does our understanding of its intricacies. Let this knowledge and awareness empower individuals to prioritize their digestive health for a better quality of life.