Preventing Cross-Contamination in School Cafeterias: A Guide for Parents and Staff
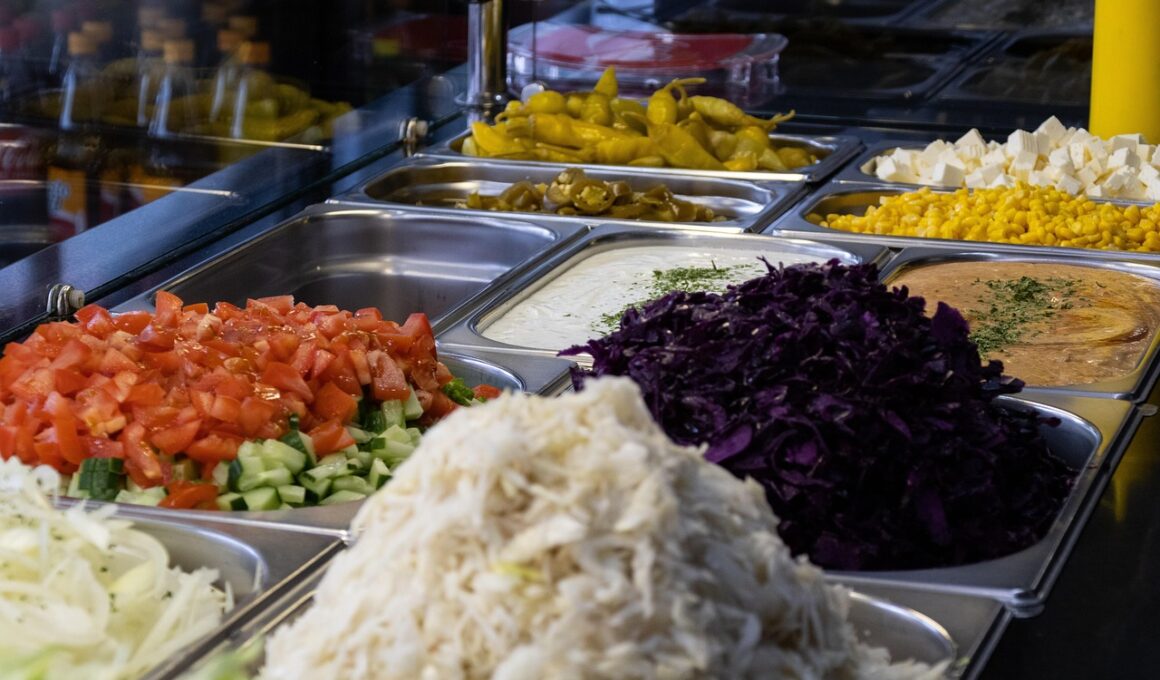
Cross-contamination in school cafeterias presents serious concerns for children with food intolerances and allergies. It occurs when allergens inadvertently mix with safe foods, potentially causing severe reactions. Awareness is crucial to ensure the well-being of every student in the cafeteria. Parents, staff, and children must be educated on monitoring food sources and preparation processes. Schools should implement best practices for food service, including strict protocols for handling allergens. Simple measures such as using separate utensils for allergy-safe meals can drastically reduce risks. It’s essential that all individuals in the cafeteria, including students, collaborate to maintain safety standards. Educating kids about their specific dietary needs will empower them to communicate effectively. Staff should undergo thorough training on cross-contamination risks and safe food practices. All parties must understand the importance of keeping allergenic foods separate from non-allergenic ones. Schools should encourage open communication and foster an environment where children feel comfortable discussing their dietary restrictions with peers and staff. Enhanced collaboration can ensure that all students enjoy safe and nutritious meals, leading to a happier and healthier school environment for everyone.
Implementing a robust cross-contamination prevention policy is vital for school cafeterias. This policy should be accessible and clear to all parents, staff, and students. A well-documented procedure ensures that everyone involved understands their roles and duties. One suggestion is to create visual reminders about allergenic foods and safe practices prominently displayed in food preparation areas. Additionally, ensuring that all kitchen staff is trained regularly can strengthen compliance with safety protocols. Using color-coded cutting boards, utensils, and serving trays for different food groups can help avoid cross-contact. Establishing designated areas for allergen-free meals can also be beneficial. Moreover, conducting periodic reviews of the cafeteria’s practices would help maintain these standards. Continuous improvement is important; feedback from parents and students is invaluable in fine-tuning procedures. Training sessions should incorporate practical demonstrations and discussions about allergy avoidance. Furthermore, parents can take an active role by providing feedback regarding their child’s specific needs and experiences in the cafeteria. Open dialogues between parents, students, and staff pave the way for a safer environment for all students, making the cafeteria a place where every child can thrive without fear of allergenic exposure.
Ongoing Training and Awareness
Ongoing training and awareness programs are fundamental to managing food allergies effectively in school cafeterias. Staff should participate in recurring seminars to keep updated on food safety practices. This education should encompass understanding allergies, recognizing signs of allergic reactions, and familiarizing themselves with safe food handling methods. Utilizing external resources, such as healthcare professionals specializing in allergies, can enhance staff knowledge and skills further. Implementing refresher courses every semester ensures that the knowledge remains current and relevant. In addition, introducing student-led initiatives can promote a culture of awareness among peers. Engaging students in discussions about allergies and intolerances creates empathy and understanding. Activities such as workshops, demonstrations, and informational posters can heighten awareness about safe eating. Schools can encourage student participation by allowing them to share personal experiences regarding food allergies. Furthermore, developing partnerships with local allergy advocacy groups can provide additional resources and support networks for families. These connections help foster a robust community that prioritizes health and safety. Thus, consistent training, combined with community involvement, empowers schools to maintain a safe environment where each child feels included and protected from potential dangers within the school cafeteria.
Encouraging parents to communicate their child’s dietary needs effectively is paramount in preventing cross-contamination. Schools should create an open line of communication through newsletters, meetings, or online platforms where parents can express concerns or provide relevant information. Providing a standard form for parents to outline their child’s allergies and intolerances can streamline this process. Additionally, schools can host informational evenings that educate parents about cafeteria procedures and how families can contribute to positive outcomes. Encouraging parents to volunteer in the cafeteria can also help them gain insight into daily operations. This involvement fosters collaboration between parents and staff, promoting a united approach to managing food allergies. Moreover, schools can provide resources for parents to educate their children about dietary restrictions. Children who understand their food needs are more likely to advocate for their safety. They can learn to ask questions about their meals or remind others of their allergies in social situations. Thus, supporting parent engagement encourages proactive communication, which can significantly enhance safety measures within the school. When parents, staff, and students work collectively, everyone benefits from a more comprehensive understanding of allergy management and cross-contamination prevention strategies in cafeterias.
Safe Food Preparation Guidelines
Adhering to safe food preparation guidelines is essential in preventing cross-contamination in school cafeterias. Cafeteria staff must follow established protocols for preparing food, particularly when dealing with allergens. This includes thoroughly washing hands and equipment between handling different food items. Additional practices include storing allergenic ingredients separately from safer options to prevent cross-contact. Implementing a rotation system for food items ensures older ingredients are used first, minimizing the chance of spoilage or unsafe consumption. Each batch of food should be prepared with careful attention to avoid the introduction of allergens inadvertently. Serving tools must also be exclusive to specific food types, ensuring that allergens do not transfer when serving meals. Labels indicating allergen presence should be clearly displayed on food items for transparency. Staff should regularly sanitize surfaces to eliminate residue, which could lead to cross-contamination. Additionally, an allergen-free zone within the kitchen area can further safeguard against exposure. Regular audits of the food preparation process can identify areas of improvement. By maintaining high standards in food handling, schools contribute significantly to the health and safety of their students while ensuring that all meals are both nutritious and safe for consumption.
Engaging students in the cross-contamination prevention efforts cultivates a sense of responsibility around food safety. Initiatives that involve students can be extremely effective in teaching them about allergies and how to maintain safe eating habits. Schools can introduce programs where students learn about the importance of strict hygiene practices. Initiating student-led campaigns focusing on safe eating can help raise awareness among peers. Activities such as creating informative brochures or hosting school assemblies can enhance understanding of dietary restrictions and cross-contamination. Encouraging kids to participate in discussions about their needs fosters an inclusive environment. Establishing a “Buddy System” where students with allergies are paired with peers can provide additional support in cafeteria settings. By fostering friendships and understanding, students learn empathy while ensuring their friends’ safety during meals. Furthermore, inviting guest speakers, such as nutritionists or allergy specialists, to speak can add depth to the learning experience. An informed student body contributes to a culture of safety within the cafeteria. Thus, strategies that engage students directly can create lasting impacts on their attitudes toward food safety. When empowered, students become advocates for themselves and others, reinforcing the importance of cross-contamination prevention throughout their school.
Monitoring and Feedback Mechanisms
Implementing monitoring and feedback mechanisms is key to enhancing the effectiveness of cross-contamination prevention strategies in school cafeterias. Regularly assessing the implemented practices ensures the school environment is safe for all students. Schools can initiate surveys or suggestion boxes for students and parents to provide feedback on their dining experiences, particularly regarding food allergies. This feedback helps identify potential gaps and areas for improvement within the food service operations. Periodic audits can be conducted in collaboration with local health departments to evaluate compliance with safety standards. Establishing clear metrics to track incidents can be equally beneficial. Schools must maintain records of any reported allergic reactions or near-misses to understand how to tailor their safety procedures better. Analyzing these incidents allows for prompt adjustments that can prevent further occurrences. Hosting regular review meetings involving cafeteria staff, parents, and students can facilitate open discussions about food safety practices and experiences. This collective approach to monitoring fosters a culture of accountability where continuous improvement is prioritized. Collaboration in feedback creates a proactive atmosphere in the cafeteria, ensuring every student feels secure and valued while enjoying their meals, free from the fear of cross-contamination and allergic reactions.
Ultimately, preventing cross-contamination in school cafeterias requires a comprehensive strategy involving parents, staff, and students. The collaboration enhances awareness and reinforces the importance of food safety best practices. Schools must commit to ongoing education, ensuring that everyone understands the necessary precautions for preventing cross-contact with allergens. Establishing procedures for safe food preparation, training staff regularly, and creating open dialogue with parents creates a robust framework for managing food intolerances and allergies. When all parties work together, they foster an inclusive and safe school environment. Children will feel more assured that their dietary needs are respected and integrated into the cafeteria experience. Additionally, continuous improvement must remain a priority, identifying new challenges and responding effectively to maintain safety. Efforts should involve attracting partnerships with local organizations specializing in food allergies to share resources and insights. Schools can also leverage technology to keep parents informed and involved in their children’s dietary experiences. With a united front, the school community can ensure that every meal served meets safety standards while allowing every student to thrive. In conclusion, a proactive approach toward cross-contamination prevention can truly make a difference in the lives of children navigating food allergies and intolerances in the school cafeteria.