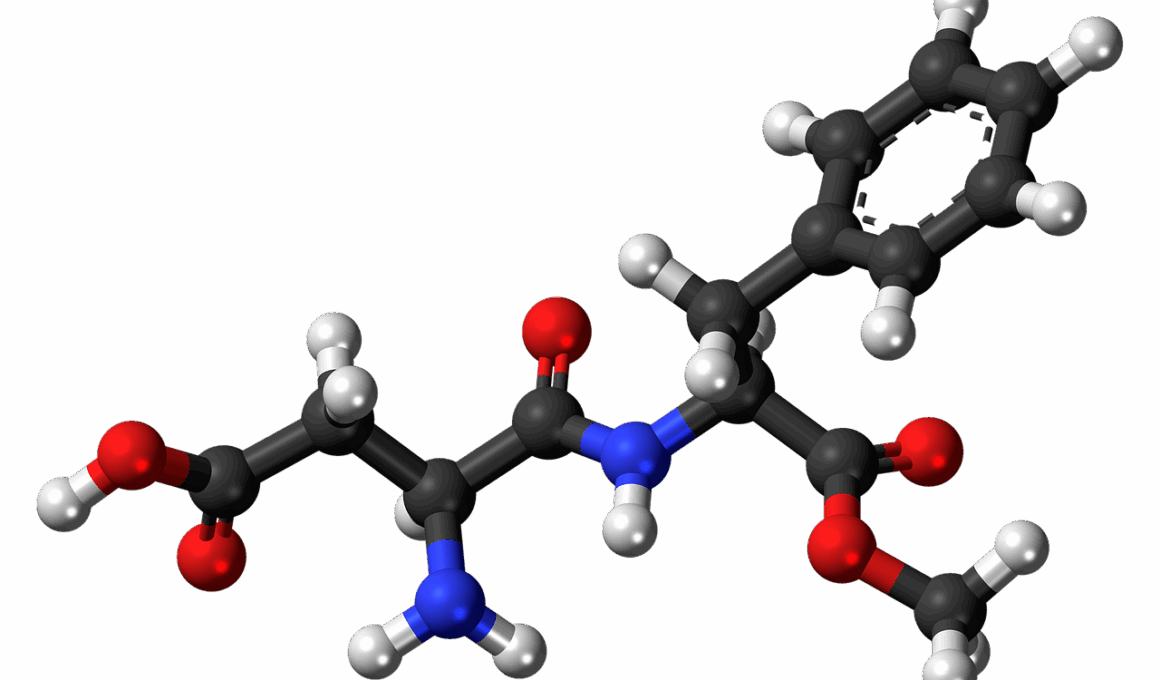
What Are Artificial Sweeteners Made Of? Understanding Their Composition
Artificial sweeteners are synthetically produced substances designed to mimic the sweetness of sugar while containing fewer calories. Commonly found in diet products, these sweeteners are often used as sugar substitutes. The most prevalent artificial sweeteners include aspartame, saccharin, sucralose, and acesulfame potassium. Each of these replacements contains specific chemical structures that contribute to their sweetening properties. Aspartame, for instance, is composed of aspartic acid and phenylalanine, while sucralose is derived from sugar itself through a chlorination process. Saccharin, one of the oldest artificial sweeteners, is manufactured from coal tar. Acesulfame potassium, also known as acesulfame K, is frequently combined with other sweeteners to enhance sweetness. Despite concerns surrounding these sweeteners, extensive research has generally deemed them safe when consumed in moderation. However, individuals with phenylketonuria (PKU), a rare genetic disorder, should avoid aspartame due to its phenylalanine content. Consulting with healthcare professionals can help navigate the nuances of sweetener choices for health-conscious individuals. Overall, understanding the composition of artificial sweeteners aids in making informed dietary decisions while debunking prevalent myths surrounding their safety.
Understanding the safety of artificial sweeteners is paramount for informed choices regarding dietary options. Critics of artificial sweeteners warn of possible health risks, including cancer and metabolic disorders. The fear surrounding these substances often stems from misconceptions and poorly designed research studies. Regulatory agencies like the FDA and the European Food Safety Authority (EFSA) have conducted rigorous evaluations, deeming many artificial sweeteners safe for consumption. For instance, the acceptable daily intake (ADI) for aspartame is set at 50 mg per kilogram of body weight. Numerous clinical studies support that typical intake levels remain well within these limits. Individuals often misconceive the sweetening power of these compounds, allowing for lower quantities in food formulations. Essentially, a small amount can provide an equivalent sweetness to many teaspoons of sugar. As a result, such products address specific dietary needs. It remains crucial to distinguish between whole, natural foods and processed foods that contain artificial sweeteners. Engaging with reliable sources and scientific literature enhances the understanding of these compounds, allowing for balanced discussions regarding their use. Alongside practical advice, developing a healthy mindset surrounding dietary practices can lead to improved well-being.
Artificial sweeteners provide unique benefits, like weight management and blood sugar control, which can be advantageous for certain populations. Diabetics, for example, often benefit from the low glycemic index of these sweeteners, allowing for better blood sugar regulation. The reduction of calorie intake without compromising sweetness can assist in effective weight management and can foster healthier eating habits. Additionally, manufacturers are continually developing innovative sweetening alternatives. The emergence of sugar alcohols, such as xylitol and erythritol, represents a growing trend in the industry. These compounds, derived from plants, provide a balance between sweetness and digestive tolerance. However, excessive consumption can lead to gastrointestinal discomfort, necessitating mindful intake. Consumers frequently express confusion regarding labels, as products may contain combinations of sugar and artificial sweeteners, creating ambiguity. Understanding product labels helps individuals navigate the options available in stores effectively. By evaluating ingredient lists, consumers can make informed decisions and cultivate healthier habits. Striving for clarity in dietary choices ultimately empowers individuals to optimize their nutrition while enjoying the products they love. Overall, competent decision-making in sweetener choices optimizes health outcomes for diverse dietary needs.
The Science Behind Artificial Sweeteners
The scientific aspects of artificial sweeteners warrant exploration to dispel ongoing myths and fears. Research regarding their metabolic effects reveals that they do not significantly contribute to caloric intake. In fact, many studies indicate that these sweeteners might aid in weight loss when incorporated into reduced-calorie diets. Additionally, significant investigations have demonstrated that artificial sweeteners do not possess a direct causative link to metabolic disorders or cancer. For example, the American Cancer Society maintains that current evidence does not substantiate claims positing a relationship between sweeteners and increased cancer risk. The human body’s digestive processes differ between natural and artificial compounds, allowing for the distinct metabolization of sweeteners. Furthermore, ongoing scientific inquiries continue to emerge to provide updated insights on their impact on health. Investigations examining the gut microbiome, insulin sensitivity, and appetite modulation reveal complex interactions deserving of further study. A nuanced understanding of the science behind these sweetening agents helps individuals approach dietary choices with a clearer perspective, alleviating concerns surrounding their safety and offering an informed pathway towards healthier living.
Public perceptions of artificial sweeteners often hinge on prevalent myths and media narratives. Advertisements frequently tout sugar substitutes as healthier options, leading to skepticism among consumers. Common myths, such as artificial sweeteners causing weight gain or harmful health effects, have been perpetuated through misinformation. Debunking these myths is essential for promoting a balanced understanding of these compounds. Studies conducted on various populations demonstrate that moderate use of artificial sweeteners does not correlate with adverse health outcomes. An emphasis on researching peer-reviewed literature aids in distinguishing credible evidence from sensational claims. As individuals strive for health-conscious choices, they should weigh the advantages of sweeteners against potential drawbacks. Additionally, discussions surrounding individual preferences in taste and diet can influence choices surrounding sweeteners. Intuitive eater principles encourage the focus on hunger cues and satiety rather than labeling foods as “good” or “bad.” Consequently, understanding how artificial sweeteners fit into personal nutritional goals allows for individualized dietary decisions. As misconceptions persist, conversations about nutrition should evoke curiosity and critical thinking while fostering a culture of informed eating.
Conclusion on Artificial Sweeteners
In conclusion, artificial sweeteners serve as versatile components of modern nutrition. They provide a practical solution for reducing overall sugar intake while maintaining sweetness. Their chemical composition varies, leading to different applications and effects in the diet. Understanding these substances promotes informed consumption and allows individuals to tailor their sweetener choices according to personal health goals. The ongoing debate surrounding their safety beckons the importance of evidence-based discussions to decipher misconceptions. Regulatory bodies consistently reaffirm the safety of artificial sweeteners when consumed within established daily limits. By navigating through scientific findings, consumers can engage in thoughtful dialogue about their dietary ideology. As more people adopt healthier lifestyles, the role of artificial sweeteners will undoubtedly evolve. The creation of innovative products caters to evolving consumer preferences, which include both natural and man-made sweeteners. Ultimately, it is crucial to remain mindful of overall dietary patterns and preferences, making the most suitable choices for individual lifestyles. By integrating diverse sources of information, individuals can efficiently manage their nutrition and health, enabling positive outcomes while enjoying their favorite flavors.
As society progresses, discussions surrounding artificial sweeteners will continuously evolve. Future research endeavors will likely shed light on long-term health effects and elucidate the nuances of individual responses to these sweeteners. By fostering a culture of informed eating habits, consumers empower themselves to make choices best aligning with their health objectives. The cuisine industry will evolve as consumer preferences shift, emphasizing transparency in ingredient sourcing and manufacturing processes. Ultimately, a focus on whole, nutrient-dense foods remains paramount in nutritional discussions. Artificial sweeteners, when used judiciously, can complement varied diets while enabling indulgence in sweet flavors without overconsumption of calories. Encouraging dialogue surrounding sweetening agents fosters empowered decision-making and promotes critical thinking in current nutrition trends. As information proliferates through various channels, embracing a proactive approach to dietary choices remains vital. Understanding the science behind artificial sweeteners encourages balanced choices without undue fear. Navigating the complexities of nutrition allows individuals to thrive in a world abundant in food options. Ultimately, reflective and conscious eating practices can enhance overall health, paving the way for future explorations in nutritional science and diet.
Summary of Key Points
This summary revisits essential aspects of artificial sweeteners, enhancing understanding and reinforcing their role in nutrition. These sweeteners, formulated to replicate sweetness, present unique benefits for individuals managing their weight and dietary choices. The safety concerns surrounding these compounds have largely been addressed by scientific inquiry and regulatory approval. Practical applications in food and beverage products provide enjoyable experiences while maintaining manageable caloric intake. Additionally, consumers should remain aware of claims surrounding sweeteners to ensure that beliefs align with scientific evidence. The clear distinctions between natural and artificial sweeteners help consumers navigate their preferences with confidence. Embracing a balanced approach toward sugar alternatives can foster positive habits for various dietary lifestyles. Finally, ongoing research and dialogue support a growing understanding of artificial sweeteners through a modern lens of nutrition. By engaging critically with available information, individuals can optimize their health journeys while integrating sweet flavors into their lives without compromising their overall well-being. This balanced exploration of artificial sweeteners encourages a re-evaluation of assumptions and bites into the juicy world of sweetening alternatives.