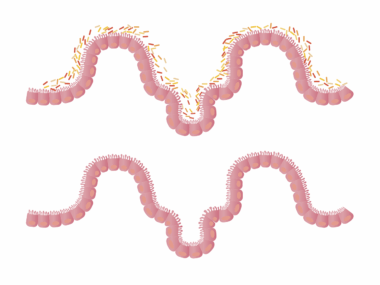
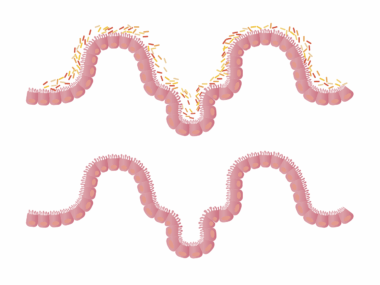
The Relationship Between Eating Patterns and Gut Microbiota
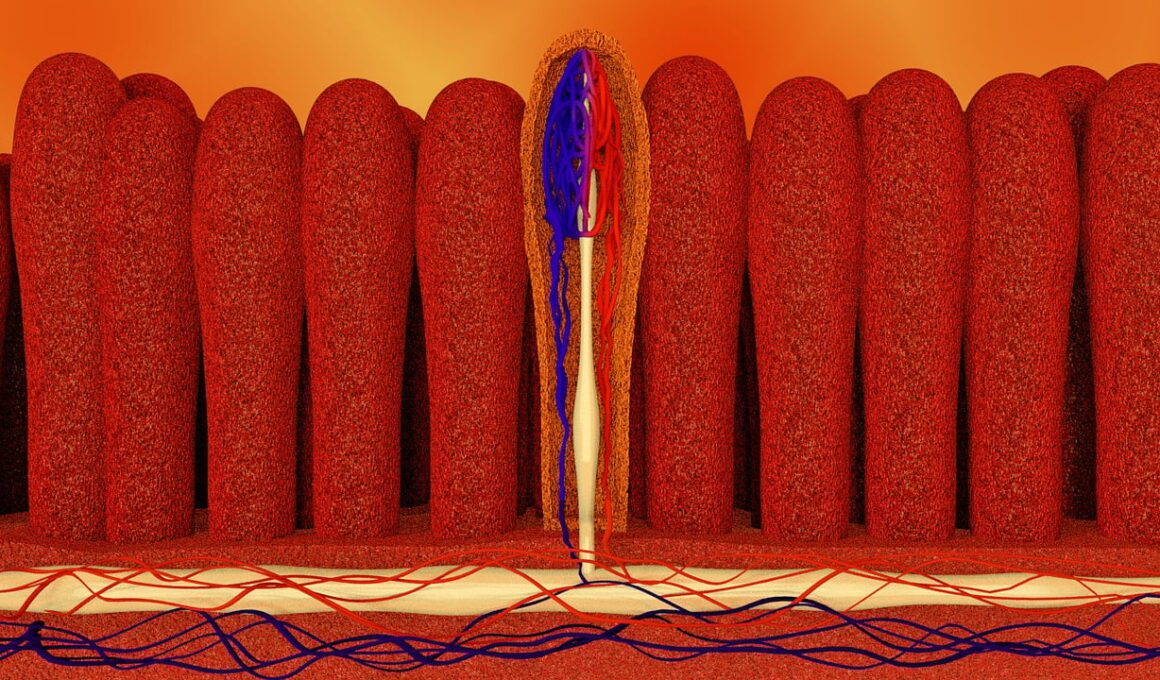
Gut health has become a focal point of interest in wellness and nutrition. Emerging research highlights that gut microbiota—the plethora of microorganisms residing in our intestines—plays a crucial role in various bodily functions, including digestion, immunity, and even mental health. One significant factor influencing gut microbiota composition is meal timing. The foods we consume and the time at which we eat them can profoundly impact the variety and abundance of gut bacteria. Altered eating patterns, such as irregular meal timings or late-night snacking, can disrupt the natural circadian rhythms that govern digestion and metabolism. Understanding this relationship can help in making more informed dietary choices. Proper meal timing, in conjunction with a balanced diet rich in fiber, prebiotics, and probiotics, can support gut health. A diverse microbiota is linked to numerous health benefits, including improved digestion and reduced risk of diseases like obesity and diabetes. Hence, this interplay between eating patterns and gut microbiota merits further exploration, particularly for those seeking to optimize their gut health through dietary strategies.
The timing of meals influences the circadian rhythms of gut microbiota, which play a crucial role in various metabolic processes. Recent studies indicate that the gut microbiome may follow a circadian pattern, reflecting the cycles of day and night. Disruption of these biological rhythms by irregular meal timings or late-night eating can lead to detrimental changes in microbial populations. Altered gut microbiota composition is associated with metabolic disorders and inflammation, highlighting the importance of meal timing. A consistent eating schedule helps stabilize gut microbiota and associated metabolic functions, positively influencing health outcomes. People who eat at regular intervals can maintain better gastrointestinal health and overall well-being. Additionally, specific eating regimens, like intermittent fasting or time-restricted feeding, have shown to provide benefits, including weight loss and metabolic regulation. Incorporating these practices could lead to a healthier gut microbiome. Overall, aligning meal patterns with natural circadian rhythms is crucial for enhancing gut health. Future research is needed to provide a clearer understanding of how precise eating times affect gut microbiota and their implications for health.
Understanding how meal timing affects gut health necessitates examining individual variations. Various factors, including genetics, lifestyle, and dietary habits, influence how our microbiota respond to different eating patterns. For instance, a high-fiber diet can enhance gut microbiome diversity, especially when consumed at regular intervals. However, the same diet consumed inconsistently may not provide optimal benefits. Additionally, consuming meals late at night may lead to undesirable shifts in gut flora, potentially resulting in dysbiosis. Such an imbalance can affect metabolic functions and contribute to a range of chronic diseases. Hence, individuals should consider both the quality and timing of their meals to support a healthy microbiome. Studies have shown that eating breakfast can set a positive tone for gut health throughout the day. In contrast, skipping meals or mindlessly snacking can disrupt gut rhythms. Therefore, establishing a consistent meal routine can promote diversity among gut bacteria, supporting metabolic processes essential for good health. The synchronization of meal timings with daily activities is equally important, making it possible to enhance the overall well-being.
The Impact of Late-Night Eating
Late-night eating poses unique challenges for gut health, often leading to negative consequences for the microbiota. Consuming meals close to bedtime can hinder digestion, leading to altered metabolic processes during sleep. This disruption impacts how our body metabolizes nutrients from these meals. As the digestive system is less active at night, late-night snacks can result in inefficient nutrient absorption and increased fat storage. Moreover, research indicates that late-night eating may foster the growth of specific bacterial strains while diminishing beneficial ones, potentially leading to an imbalanced gut microbiome. An unbalanced microbiota can trigger digestive issues, increased inflammation, and even weight gain over time. To mitigate these effects, it is advisable to establish cut-off times for eating, ideally a few hours before bedtime. This practice promotes better digestion and sleep quality, ultimately fostering a healthier gut environment. Mindful eating habits, which promote awareness of meal timing, can enhance gut health strategies. As society becomes increasingly aware of gut health’s significance, paying attention to late-night eating habits is essential for long-term well-being.
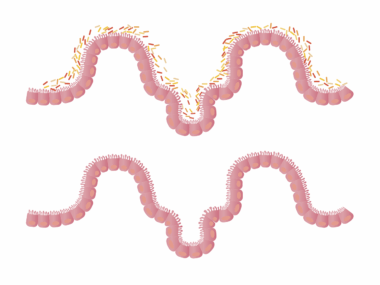
Meal timing is also crucial in maintaining the integrity of the gut barrier, which protects the body from harmful substances. Studies have suggested that misalignment between meal timing and circadian biology can weaken this gut barrier, increasing permeability and allowing toxins to enter the bloodstream. This condition, often referred to as ‘leaky gut,’ can lead to systemic inflammation and various health issues, including autoimmune disorders. Hence, adhering to regular meal schedules aligns with the body’s natural biology and could fortify gut barrier function. Additionally, including foods rich in antioxidants and anti-inflammatory compounds can support gut health. Regularly consuming meals at appropriate times promotes a stable environment for beneficial bacteria to thrive. Moreover, diversity in diet is just as important as meal timing for optimal gut health. Foods such as fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and fermented products can enhance microbial diversity and improve gut function. Therefore, recognizing the interplay between meal timing, food quality, and gut barrier integrity will be vital for anyone striving to enhance their digestive health. Fostering a mindful approach to eating can significantly benefit gut function and overall wellness.
In addition to the timing and content of meals, the rhythm of eating may affect how gut microbiota adapt to changing environments. Research suggests that synchronization of eating habits with activity levels can maximize gut health benefits. For example, aligning meals with wake times can support the proliferation of beneficial bacteria while minimizing the growth of pathogenic bacteria. This synchronization improves digestion and enhances nutrient metabolism, which can optimize energy levels throughout the day. A well-structured eating schedule can prevent fluctuations in insulin levels and support metabolic homeostasis. As such, individuals may experience fewer cravings and mood swings associated with irregular eating patterns. Furthermore, implementing strategies like meal planning and prepping can assist in maintaining consistent meal timings. These approaches can alleviate the stress of making unhealthy food choices on-the-go and enhance adherence to a balanced diet. When individuals prioritize their meal timing alongside nutrient-dense food choices, they facilitate a flourishing gut microbiome. Ultimately, maintaining stable metabolic functions is integral for overall health, underscoring the critical nature of meal timing in relation to gut microbiota.
Practical Tips for Optimal Meal Timing
To promote gut health through meal timing, consider implementing practical tips that can seamlessly integrate into your lifestyle. First, establish regular meal times that align with your daily routine. Aim for consistent breakfast, lunch, and dinner times, allowing your body to thrive on a predictable schedule. Avoid skipping meals and at least try to have your last meal a few hours before bedtime. Choosing balanced meals with whole foods, including proteins, healthy fats, and fiber will also support gut health. Additionally, consider practicing intermittent fasting or time-restricted eating, which has shown potential benefits in promoting gut microbiota diversity. Being mindful of portion sizes and the nutritional content of meals can prevent overeating and contribute to a stable gut environment. Moreover, keeping a food diary may help highlight patterns in your eating behaviors that need adjustment. Don’t forget the influence of hydration; drinking enough water throughout the day stays crucial to digestive processes. By incorporating these practical strategies, individuals can synergistically enhance their gut health by recognizing the significance of meal timing and its implications for microbiota balance.
Finally, ongoing research continues to unveil the complex relationship between meal timing and gut microbiota. Findings suggest that further exploration into personalized nutrition may better inform individuals on how to optimize their gut health based on unique characteristics and lifestyles. The concept of chrono-nutrition—how food timing affects health—is gaining traction, emphasizing the need for individualized dietary recommendations for gut optimization. Upcoming studies could explore how meal timing interacts with factors like exercise, stress, and sleep to produce an aggregated impact on gut health. Additionally, researchers aim to establish clear guidelines offering practical strategies for individuals looking to enhance their gut microbiota through meal timing. As understanding deepens, professionals in nutrition and healthcare may offer more tailored advice to meet health needs. Furthermore, educating the public about the importance of meal timing could foster awareness about gut health’s critical role in overall wellness. As trends toward healthier lifestyles continue to flourish, integrating meal timing principles can empower individuals to take charge of their gut health, paving the way for a more informed approach to nutrition and wellness in everyday life.