The Science of Amino Acid Absorption and Bioavailability
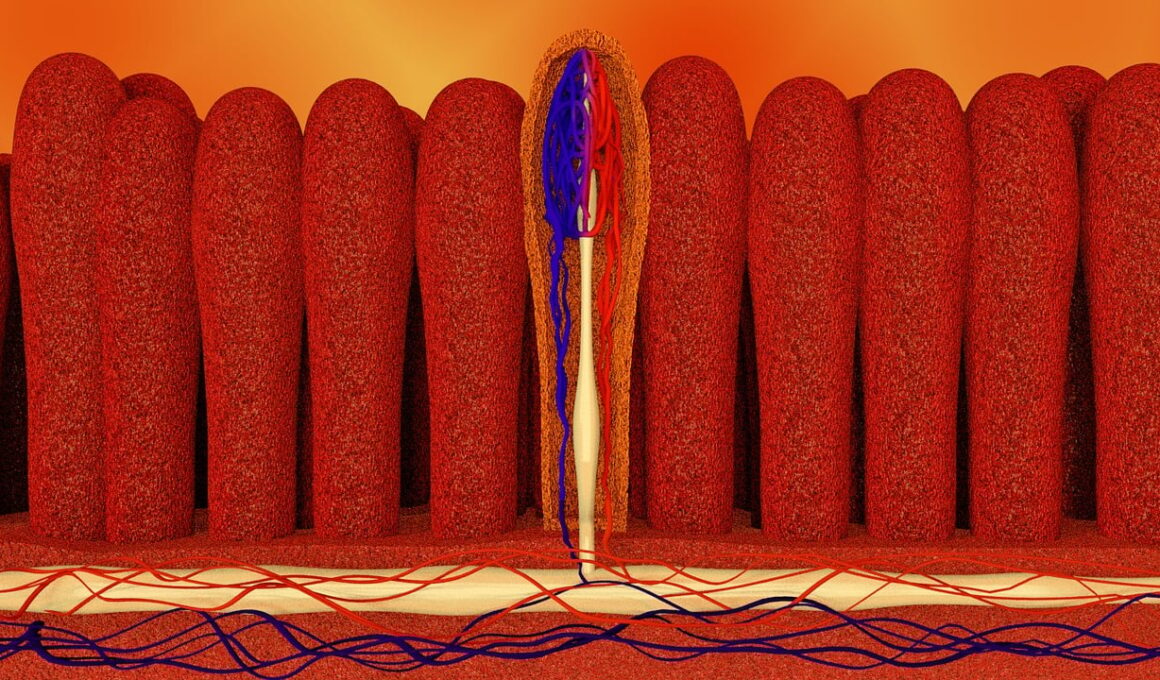
Amino acids play a critical role in various physiological processes, including protein synthesis, hormone production, and tissue repair. Understanding how these essential compounds are absorbed and utilized by the body is fundamental for optimizing nutrition and supplementation. The pathway to amino acid bioavailability begins in the digestive system, where proteins are broken down into their constituent amino acids by enzymes such as pepsin and trypsin. Once freed from their protein matrices, amino acids are absorbed through the intestinal lining into the bloodstream, where they are transported to tissues and organs as needed. Factors such as the form of amino acids, the presence of other nutrients, and the individual’s metabolic state can significantly affect absorption rates. For instance, free-form amino acids are usually absorbed faster than those found in whole protein sources. Additionally, certain amino acids can compete for absorption in the intestine. The significance of optimizing amino acid intake cannot be overstated, particularly for athletes and those engaged in rigorous physical training. Direct supplementation may enhance recovery, strength gains, and overall performance. Educating oneself on amino acid dynamics is vital for health optimization.
The importance of amino acid bioavailability extends beyond mere absorption rates. Various factors influence how effectively these substances can be utilized once in the bloodstream. One crucial consideration is the timing of amino acid intake, particularly around workouts. Consuming amino acids pre- and post-exercise can enhance muscle protein synthesis rates, providing a crucial edge for recovery and performance. Furthermore, different types of amino acids have varying bioavailability levels; branched-chain amino acids (BCAAs), for example, are frequently highlighted for their benefits in muscle recovery and growth. Research indicates BCAAs might be absorbed rapidly, which can stimulate protein synthesis quickly. However, the presence of other dietary components may inhibit or enhance this process. A well-balanced meal containing carbohydrates and fats may facilitate amino acid absorption due to the increased secretion of insulin, subsequently promoting uptake into muscle tissue. Moreover, the source of amino acids, whether from animal or plant-based proteins, holds significance. Animal proteins typically possess higher biological value, leading to more efficient amino acid utilization. Thus, understanding the interaction between amino acids, diet, and exercise is paramount in formulating effective nutritional strategies.
Factors Affecting Absorption of Amino Acids
Several physiological factors also influence amino acid absorption and bioavailability. These include age, gender, and overall health. Younger individuals typically demonstrate higher nutrient absorption efficiencies than older adults due to metabolic differences. Furthermore, hormonal fluctuations throughout life stages can impact amino acid metabolism. For instance, during periods of growth such as adolescence, the body’s demand for amino acids is elevated. This increased demand necessitates a higher intake to support cellular growth and repair. Women might experience differing requirements based on hormonal cycles, particularly concerning muscle-building needs. Individuals managing chronic health conditions may also face challenges related to amino acid absorption due to gut integrity. Malabsorption syndromes could severely limit the efficiency of amino acid uptake, requiring careful dietary management. Additionally, factors such as gut health, characterized by the microbiome’s composition, can significantly influence intestinal absorption. Probiotics and prebiotics have garnered interest for their potential role in promoting optimal digestive function. Understanding these nuances further emphasizes the necessity of personalized nutrition plans, particularly for those engaged in physical activity or those of different age groups wishing to optimize their amino acid intake.
Optimizing amino acid absorption can involve strategic dietary choices and supplement modifications. When planning meals, consider combining protein and carbohydrates to enhance insulin response for improved amino acid uptake. High-quality sources of protein such as lean meats, fish, dairy, legumes, and whole grains can provide a range of amino acids necessary for overall health. For athletes or individuals with increased protein needs, amino acid supplementation can bolster dietary intake. High-quality amino acid supplements are designed to address absorption issues, delivering precisely formulated ratios of essential and non-essential amino acids to the body. For example, whey protein is absorbed rapidly and thus favored after workouts for quick recovery. In contrast, casein protein digests more slowly, making it more suitable for nighttime recovery. Moreover, certain formulations may include digestive aids, such as enzymes, to further enhance absorption rates. Maintaining hydration also plays a vital role in nutrient absorption; water facilitates the transport of amino acids and other nutrients throughout the body. Therefore, individuals aiming for maximum amino acid bioavailability should consider the quality of both their dietary choices and their hydration status.
Amino Acid Sources and Their Significance
Amino acids can be derived from a variety of food sources, each imparting unique benefits and absorption rates. Animal sources, known for their complete profile of essential amino acids, may lead to greater biological value and enhanced muscle protein synthesis compared to many plant sources. Meats, fish, eggs, and dairy products are excellent options for obtaining high-quality protein. Conversely, while plant proteins often present incomplete amino acid profiles, a well-planned vegetarian or vegan diet can combine different foods to achieve a complete amino acid profile. For instance, combining legumes with grains can help provide all essential amino acids. Additionally, supplementation can bridge gaps when dietary intake falls short, especially for individuals with specific fitness goals or dietary restrictions. It’s also important to note the processing of foods; how food is prepared and cooked can affect amino acid bioavailability. Overcooking can lead to the loss of vital nutrients, including amino acids. Therefore, understanding various protein sources and their impacts on amino acid absorption allows for more informed dietary choices that align with individual health needs.
When considering supplements, the choice of product can significantly affect results. Various formulations of amino acid supplements are available, each serving distinct purposes. These include BCAAs, glutamine, and essential amino acids, all targeting different aspects of muscle health and recovery. BCAAs, consisting of leucine, isoleucine, and valine, have garnered attention for their role in reducing muscle soreness and stimulating protein synthesis. Studies have repeatedly shown that adequate BCAA intake during and post-exercise can enhance workout performance and recovery times. Glutamine, another conditionally essential amino acid, is crucial during times of physical stress such as intense exercise. It helps to support immune function and intestinal health, ensuring optimal recovery. Essential amino acid supplements provide all nine essential components needed for protein synthesis, especially useful for individuals with restricted protein intake. When selecting amino acid supplements, ensure that you are opting for high-quality brands with transparent ingredient lists. Beware of products containing excessive fillers or unknown substances that could compromise efficacy. Proper timing and dosing of these supplements can further optimize results, ensuring that your body has what it needs when it matters most.
Conclusion
In conclusion, understanding amino acid absorption and bioavailability is essential for maximizing health and performance. The journey of amino acids from dietary sources to tissues emphasizes the complexity of nutrient metabolism. With multiple factors influencing absorption, such as age, health status, and dietary composition, personalized approaches are crucial. Athletes, in particular, stand to benefit from a well-structured plan that incorporates strategic timing of amino acid intake and may include utilizing high-quality supplements when necessary. Furthermore, considering the quality of amino acid sources, whether from animal or plant origins, can make a significant difference in overall intake and effectiveness. Educating oneself about amino acid dynamics empowers individuals to make informed dietary choices tailored to their specific health goals. As we continue uncovering the science behind amino acids, it becomes increasingly clear that these compounds are not merely building blocks; they are fundamental components supporting overall health. By optimizing their intake in conjunction with a balanced diet and hydration, you can lay the groundwork for improved well-being and athletic performance.
Moreover, as the research evolves, more advanced supplementation methods are likely to emerge, potentially enhancing amino acid bioavailability even further. Innovations in technology may lead to developments in formulations that maximize nutrient absorption and improve overall health outcomes. Future studies could explore various combinations of amino acids and other nutrients, examining their synergistic effects on both performance and recovery. Keeping pace with these advancements will enable individuals to adapt their nutritional strategies according to evidence-based findings. Engaging with professionals such as dietitians and nutritionists can also enhance understanding and implementation of optimal amino acid strategies in daily life. As you navigate your journey into the world of amino acids, remember to remain curious and informed. Embrace the benefits that come from knowledgeable choices about dietary intake and supplementation. With awareness of how amino acids function and their importance to our health, you are better positioned to achieve your wellness goals. Ultimately, prioritizing quality sources of amino acids and understanding absorption factors will lead to substantial improvements in energy levels, recovery, and performance. Empower yourself with knowledge and make every amino acid count in your diet!