Can an Anti-inflammatory Diet Reduce the Risk of Chronic Diseases?
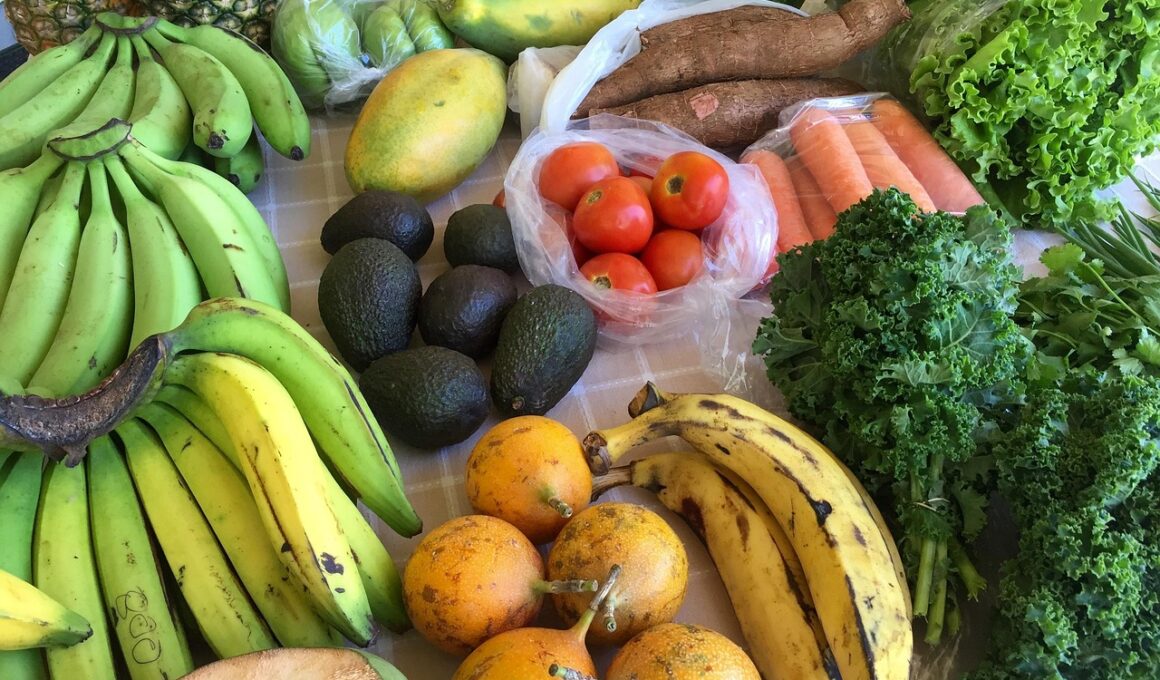
An anti-inflammatory diet focuses on foods that help reduce inflammation in the body, which can be a contributing factor in various chronic diseases such as heart disease, diabetes, and arthritis. Chronic inflammation is linked to oxidative stress and can trigger severe health issues. Incorporating specific foods into your diet can enhance your overall health. Focusing on fruits, vegetables, nuts, seeds, whole grains, and healthy fats can promote a more balanced body. Omega-3 fatty acids found in fish and flaxseeds are particularly renowned for their anti-inflammatory properties. Moreover, spices like turmeric and ginger can enhance the effectiveness of this diet. Limiting processed foods, sugars, and trans fats is also crucial. These foods may provoke inflammation and contribute to various health issues. Whether it’s heart disease or autoimmune diseases, an anti-inflammatory diet may play a pivotal role in reducing health risks. Additionally, maintaining a healthy weight greatly aids the anti-inflammatory effects of the diet. Regular physical activity, alongside dietary changes, can significantly impact inflammation levels.
The question arises: how can an anti-inflammatory diet directly reduce the risk of chronic diseases? It is essential to understand the underlying mechanisms at play. Chronic diseases often result from long-term inflammation, which can cause damage to tissues and organs. By adopting an anti-inflammatory diet, individuals can actively combat inflammation and protect their health. Research indicates that foods rich in antioxidants and polyphenols can combat oxidative stress. Antioxidants help neutralize free radicals, reducing the likelihood of chronic disease development. Some prominent antioxidant-rich fruits include blueberries, strawberries, and avocados. Vegetables like kale, broccoli, and spinach also provide significant anti-inflammatory benefits. Furthermore, whole grains like quinoa and brown rice contribute to health and inflammation reduction. Lifestyle factors like lack of exercise and poor sleep amplify inflammation. Therefore, a well-rounded approach, incorporating both diet and lifestyle changes, is vital. By focusing on nutritious food choices, individuals can potentially manage their weight and stave off chronic diseases. Staying informed and adjusting dietary habits ensures better health outcomes and enhances quality of life.
Another vital component of an anti-inflammatory diet involves proper hydration. Water is essential for cellular functions and can assist in flushing out toxins that trigger inflammation. Additionally, staying hydrated helps in maintaining optimal body function. Herbal teas like green tea offer added benefits due to their high antioxidant content. They can support the body in combating inflammation as well. Furthermore, regular meals with nutrient-dense foods can help maintain consistent energy levels while protecting the body. Frequent small meals can also prevent consistent blood sugar spikes, which may exacerbate inflammation. Combining physical activity with the right nutrition can be incredibly effective. Low-impact exercises like yoga and walking can lower inflammation levels while promoting mental clarity. Along with the connection between diet and inflammation, it’s crucial to note the correlation between stress and inflammation. Chronic stress can elevate inflammation levels by altering hormone levels in the body. Incorporating mindfulness techniques like meditation, coupled with a healthy diet, provides a holistic approach to health. These integrated practices can significantly improve life quality and may greatly reduce disease risk.
Common Misconceptions
Many individuals have misconceptions about what constitutes an anti-inflammatory diet. A common belief is that it requires strict rules on food consumption. However, this approach emphasizes balance rather than restriction. It’s about making better food choices rather than avoiding everything that is deemed unhealthy. Gradually replacing inflammatory foods with more nutritious options can help ease the transition into this lifestyle. For instance, swapping out red meat for fish can be beneficial due to omega-3 fatty acids that counter inflammation. Additionally, some people think that an anti-inflammatory diet is expensive. In reality, many anti-inflammatory foods like beans, lentils, and seasonal vegetables are budget-friendly. Meals can be both nutritious and economical when planned effectively. Furthermore, focusing on plant-based options does not imply abandoning all animal products completely. Incorporating them in moderation can also yield health benefits. Another misconception involves the effectiveness of supplements. While some may think that taking antioxidant supplements is a quick fix, research indicates whole foods offer superior benefits. The synergy of nutrients found in whole foods is vital in fighting inflammation, making them far more effective than isolated supplements.
Consultations with healthcare professionals can also guide individuals seeking to transition to an anti-inflammatory diet. Dietitians and nutritionists can tailor plans to meet specific needs, making the journey to health easier. Listening to one’s body is key to understanding how different foods affect individual health. Keeping a food diary may help pinpoint reactive foods, making it easier to optimize dietary choices. As awareness about inflammation and its consequences continues to grow, many are reconsidering their dietary habits. Embracing an anti-inflammatory lifestyle can be an empowering journey toward overall wellness. Grocery shopping should also be part of this educational process. Reading food labels and understanding ingredients may help individuals identify inflammatory products. Additionally, connecting with communities and groups focused on health can provide support and motivation. They often share tips, recipes, and experiences that can encourage healthier eating habits. Moreover, managing expectations is crucial. Significant changes may not happen overnight. It may take time to see improvements in overall health. Patience, combined with persistence, often leads to the best long-term results.
Practical Tips for Implementation
Incorporating an anti-inflammatory diet into daily life may appear daunting, but numerous practical tips can facilitate the transition. Begin by gradually introducing one or two anti-inflammatory meals per week. Simple recipes can be easily prepared and modified based on preferences. For instance, a salmon and vegetable stir-fry offers healthy fats and nutrients that combat inflammation. Additionally, meal prepping can save time and reduce the worry about last-minute unhealthy food choices. Preparing meals in advance can help ensure that an anti-inflammatory diet becomes a regular habit. Including variety is crucial to preventing monotony. Exploring different cuisines can introduce new flavors and recipes. Furthermore, spices can enhance both taste and health benefits. Common spices such as turmeric, garlic, and cinnamon boast anti-inflammatory properties. They can be incorporated into various dishes to enhance both flavor and nutritional value. Engaging the whole family in meal planning makes the process enjoyable. Teaching children about wholesome foods from an early age promotes healthy habits. Overall, adopting an anti-inflammatory diet should be seen as a lifestyle change rather than a temporary fix. Consistency is vital for achieving long-term benefits.
In conclusion, understanding the connection between diet and chronic diseases is essential, especially regarding their prevention. An anti-inflammatory diet may indeed play a crucial role in reducing the risk of various health concerns. Focusing on incorporating more fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and healthy fats lays a solid foundation for improved health. Furthermore, doing so can prevent chronic diseases from developing and can also assist in managing existing health conditions more effectively. The journey towards better health is multi-faceted; it involves meal choices, hydration, exercise, and stress management. Awareness and education about food choices can empower individuals to make healthier decisions. Overall, embracing an anti-inflammatory diet is not simply about food but creating a holistic approach to overall well-being. Making small, sustainable changes can lead to significant health improvements over time. Therefore, getting started today can drastically change one’s health trajectory. Exploring, discovering, and committing to a better dietary path may redefine health and how individuals age. Ultimately, knowledge and personal experiences will shape each person’s unique relationship with food.