The Link Between Gut Health and Immune System Strength
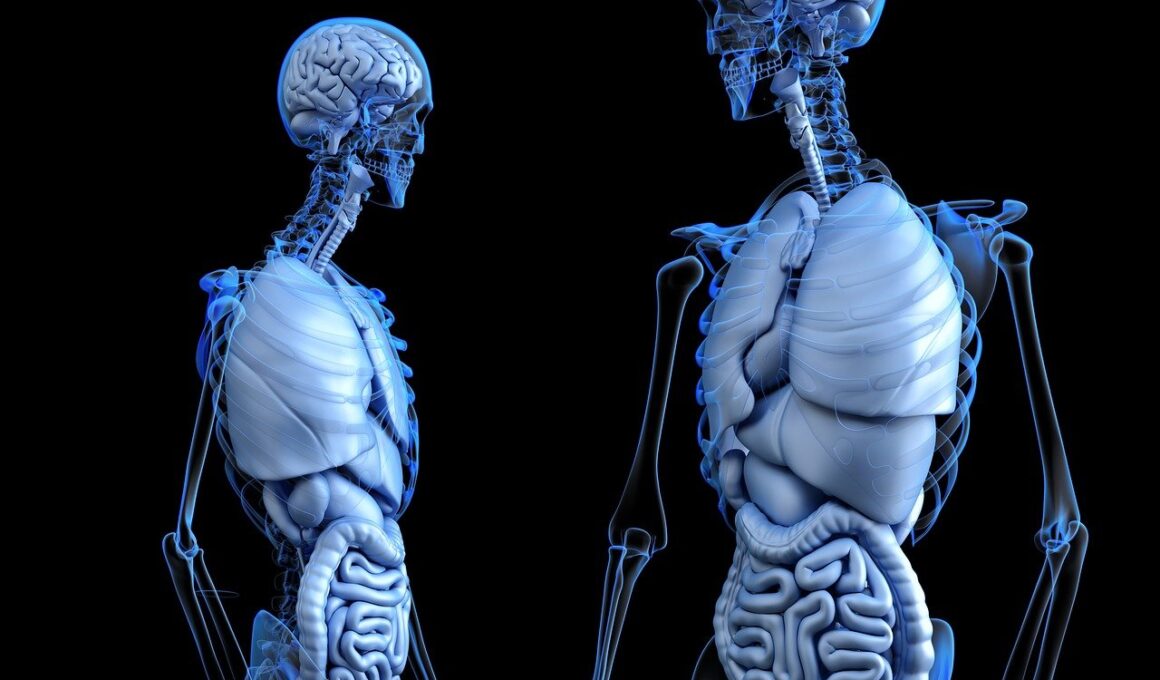
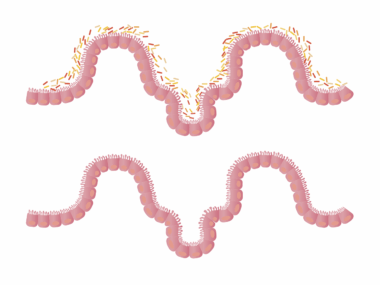
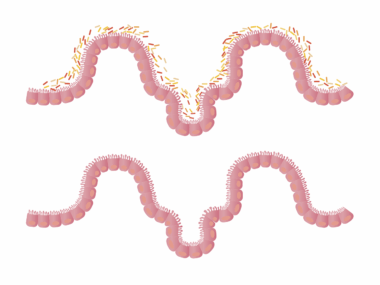
The gut is often referred to as the “second brain” and plays a crucial role in overall health. Its significant impact on the immune system is increasingly gaining recognition in the health community. When the gut flora is balanced with beneficial bacteria, it enhances immune function, supporting the body’s defense against infections. The gut-associated lymphoid tissue (GALT) is a critical component in this process, acting as a frontline defense. A diverse range of gut bacteria can help modulate immune responses, ensuring that inflammation is managed effectively. Factors such as a poor diet, stress, and lack of exercise can disrupt this delicate balance, leading to vulnerabilities in the immune system. By maintaining a healthy gut, we can promote our immunity holistically. Incorporating prebiotics and probiotics into our diets can help fortify gut health, thereby supporting immunological resilience. Furthermore, understanding the connection between our gut microbiome and general health outcomes can empower individuals to make better dietary choices, contributing positively to their immune capabilities. A comprehensive approach to gut health is essential for fostering a robust immune system.
Numerous studies have highlighted the profound impact of gut microbiota composition on immune function. The gut is home to trillions of bacteria, which play a pivotal role in shaping the immune system. Disruptions in this community, known as dysbiosis, can lead to an overactive immune response. This can manifest as autoimmune diseases, where the body’s immune system mistakenly attacks healthy cells. Conversely, a healthy gut microbiome fosters immune tolerance, ensuring a balanced and effective immune response. Immunity is significantly influenced by dietary patterns; foods rich in fiber, polyphenols, and omega-3 fatty acids can bolster beneficial bacteria. Fermented foods like yogurt, kefir, and sauerkraut can also populate the gut with valuable probiotics. These dietary components enhance the body’s defenses while reducing inflammation and modulating immune reactions. A diet that promotes gut health is not just about adding specific foods but also eliminating pro-inflammatory agents like sugar and processed fats. Educating oneself about these factors can pave the way to improved health outcomes and better immunity. Focusing on gut health is an investment in long-term well-being, reducing healthcare costs associated with immune-related diseases.
Role of Stress on Gut-Immune Connection
Stress is a significant factor that can adversely affect gut health, thereby compromising immune function. When under stress, the body releases cortisol, which can lead to changes in gut permeability. This increased permeability allows toxins and undigested food particles to enter the bloodstream, triggering inflammatory responses. Chronic stress can lead to conditions such as irritable bowel syndrome (IBS), which negatively impacts gut flora balance. Furthermore, emotional health is closely tied to the gut via the gut-brain axis, a complex communication network. Ensuring effective stress management techniques can aid in maintaining gut health, including practices such as yoga, meditation, or simple deep-breathing exercises. Lifestyle changes aimed at reducing stress can cultivate a healthier gut environment, promoting beneficial microbial activity. Regular physical activity and sleep hygiene are also critical components in managing stress and support gut health. Moreover, providing the body with adequate rest can significantly improve its ability to regulate the immune system. Thus, addressing mental health can empower an individual to mitigate stressors, leading to enhanced gut integrity and, consequently, superior immune resilience.
Besides stress, other lifestyle choices, such as inadequate sleep, can adversely influence gut health and immune response. Sleep deprivation has been shown to lead to increased inflammation and altered microbiome diversity. Quality sleep enables the body to undergo essential processes, such as healing and repair. The ideal sleep duration for adults is typically between seven to nine hours. Lack of sleep not only weakens immune response but can also unleash an overactive immune system, leading to chronic inflammation. To sustain gut and immune health, it is crucial to prioritize sleep hygiene by creating a conducive sleep environment. This involves limiting screen time before bed, maintaining a consistent sleep schedule, and establishing calming pre-sleep routines. Additionally, nutritional choices also play a role; avoiding heavy meals close to bedtime can improve sleep quality. Ultimately, investing in proper sleep habits contributes to overall health, including optimizing digestive and immune functions. Continuous learning about the interconnection between sleep, gut health, and immunity can promote healthier lifestyle decisions. Improving sleep quality is one key strategy in developing a resilient immune system through robust gut health maintenance.
Importance of a Balanced Diet
The significance of a balanced diet can’t be overstated when it comes to gut health and immune support. Consuming a variety of colorful fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and healthy fats is crucial for ensuring adequate nutrient intake. These foods provide essential vitamins and minerals that bolster the immune system, such as vitamin C, D, and zinc. Antioxidants found in fruits and vegetables help combat oxidative stress which is detrimental to both gut and immune health. Moreover, a diet rich in fiber promotes the growth of beneficial bacteria in the gut, directly impacting immune function. As a general rule, try to include diverse food groups to enrich the microbiome. Foods like legumes, nuts, seeds, and seafood have unique compounds that actively work to enhance gut flora diversity. Incorporating fermented foods also plays a significant role in introducing probiotics into the digestive system. The combination of prebiotics and probiotics can create a synergistic effect that fosters a more resilient immune system. Making dietary adjustments to ensure a balanced nutrient intake can control inflammation and improve overall health status.
Hydration is often overlooked in discussions about gut health and immunity but plays a vital role. Sufficient water intake supports digestion, nutrient transport, and the elimination of waste materials from the body. Dehydration can severely affect the mucosal lining of the intestines and impair the gut’s ability to function optimally. Staying hydrated ensures the proper flow of digestive juices and provides a medium for essential metabolic processes. Moreover, water is a key factor in the production of mucus, which serves as a protective barrier in the gut lining. A well-hydrated body is better equipped to fend off infections and inflammation. In addition to plain water, hydration can be supported by consuming herbal teas, fruits, and vegetables with high water content. As part of an overall wellness strategy, prioritizing hydration can significantly enhance gut health, directly impacting immune performance. Research supports the correlation between hydration, gut health, and a more effective immune response. Therefore, integrating hydration awareness into daily routines can yield substantial health benefits while promoting efficacy in the human immune system.
Conclusion: Holistic Approach to Gut and Immune Health
In summary, a holistic approach to gut health effuses numerous benefits, significantly impacting immune strength. Understanding the interplay between diet, stress, sleep, hydration, and gut bacteria can lead to better health outcomes. Implementing small lifestyle changes can compound over time, contributing to overall well-being. Engaging in mindful eating, staying hydrated, and addressing mental well-being can enhance gut microbiota diversity, thus promoting effective immune responses. Regular health check-ups and listening to the body’s signals can help individuals identify potential issues early on. Besides, sharing knowledge about gut health within communities fosters a more health-conscious society. Each of these aspects serves as an integral component toward achieving an optimized immune system. Furthermore, individualized dietary and lifestyle adjustments can yield unique benefits according to personal health profiles and needs. One must remember that a robust immune system begins in the gut; nurturing it through a variety of thoughtful practices can drive profound health improvements. In conclusion, respecting the connection between gut health and immune function is essential for leading a healthier, more vibrant life overall.
To continue learning about gut health and its importance, consult reliable health resources or speak to a healthcare provider for personalized advice. Empowering oneself with knowledge can lead to informed decisions that positively affect overall wellness. The journey toward better gut and immune health may involve experimentation with different foods and lifestyles, but the rewards are well worth the effort. Achieving a healthy gut is an ongoing process, underscoring the need for continuous education and lifestyle reflection. Participating in communities that focus on holistic health can provide valuable support and guidance for maintaining gut health. This creates a culture of awareness around the health benefits of focusing on the gut-immune connection. Additionally, engaging with research articles and scientific studies can help deepen your understanding of this vital relationship. Therefore, commit to a lifelong learning approach when it comes to your health, particularly the intricate links between gut health and immunity. Following the steps outlined above, individuals can work towards a significant enhancement in their health and longevity.