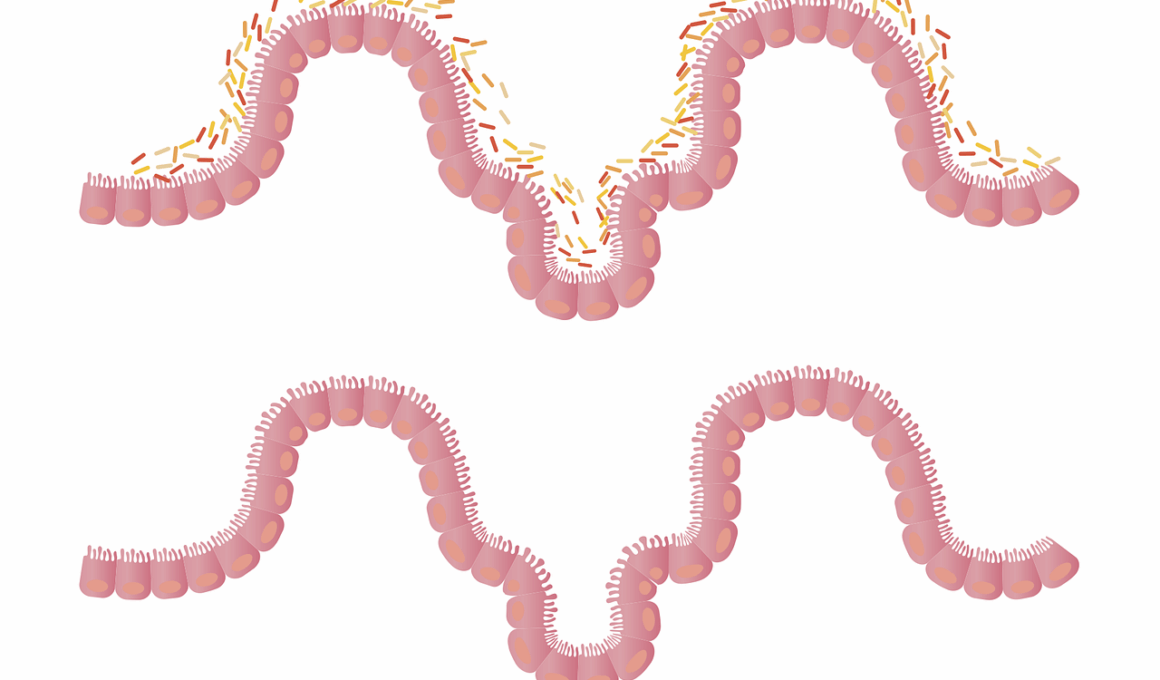
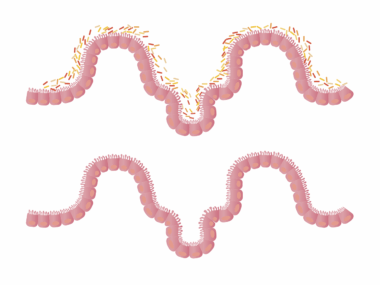
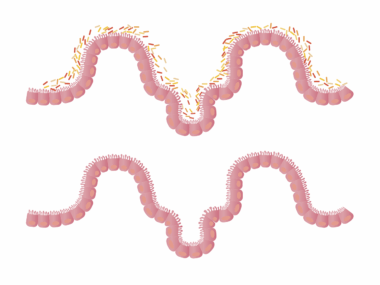
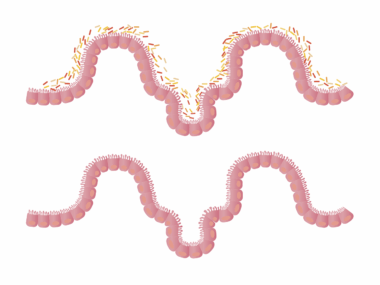
Sugar and Gut Health: A Guide for Athletes and Active Adults
Understanding the impact of sugar on gut health is crucial for athletes and active individuals. The intestines contain a vast microbiome, populated by good and bad bacteria. Excess sugar intake can lead to an imbalance, resulting in adverse health effects. Increased sugar consumption promotes the growth of harmful bacteria and yeast, which can harm digestion. Opting for natural sources of sugars, such as fruits, enhances nutritional value and supports gut flora. Moreover, refined sugars often lead to chronic inflammation, impairing athletic performance. For a well-rounded diet, it’s advisable to monitor one’s intake of added sugars. Aim for a balanced diet that includes fiber-rich foods, which act as prebiotics. Regular meals rich in whole ingredients nourish the gut biota effectively. Athletes should consider the timing of sugar intake; excessive levels during training can detract from energy levels and recovery. Ultimately, staying informed about the quality and quantity of sugars consumed can lead to optimized health and performance. Education on gut health is vital for maintaining optimal functions, particularly in active communities striving for excellence.
The Role of Sugar in Athletic Performance
When we discuss sugar in terms of athletic performance, it’s vital to differentiate between refined sugars and natural sugars. Refined sugars are often found in processed foods and can cause spikes in energy followed by crashes, which are detrimental. As athletes, learning to choose the right type of sugars can help maintain energy levels. Natural sugars, sourced from fruits, provide a more steady release of energy and are often paired with beneficial nutrients and fibers. This steady release supports longer training sessions and enhanced recovery. Moreover, consuming too much sugar can lead to digestive difficulties, impacting performance metrics. It’s crucial to plan out meals and energy sources to avoid excessive refined sugar consumption before physical activities. Notably, maintaining hydration is equally essential during sugar consumption, as sugars need adequate fluid for processing. Using low-sugar snacks—such as nut butter paired with apples—can offer energy without overwhelming the gut. Athletes should monitor their body’s response to sugar to find the optimal balance that enhances performance and gut health. Awareness and strategic choices in sugar consumption can lead to improved training outcomes for dedicated athletes.
Incorporating a balanced approach towards sugar can enhance gut health, particularly in active adults. Dietary changes should be gradual to allow the gut microbiota to adjust accordingly. Foods rich in probiotics, like yogurt or fermented options, complement a lower sugar intake. Probiotics help restore healthy bacteria, counteracting the effects of excessive sugar. Additionally, prebiotic foods—such as garlic and onions—can support the health of existing beneficial bacteria. Athletes should incorporate these foods regularly for improved digestive health. Meal planning can further ensure a diverse intake of nutrients essential for optimal performance. This planning should emphasize whole foods, minimizing processed items. Focusing on hydration will also prove crucial; water supports digestion and nutrient absorption. Moreover, fiber-rich foods assist in regulating sugar levels and promoting regular bowel movements. Understanding sugar’s short and long-term effects enables athletes to make informed dietary decisions. Also, experimentation with dietary choices may be necessary to find the best approach for individual needs. Ultimately, a holistic view on nutrition revolving around reduced sugar can promote sustainable health and energetic well-being.
Tips for Reducing Sugar Intake
Reducing sugar should be a gradual process, particularly for individuals accustomed to high amounts. Start by identifying hidden sugars in various products; these can be found in sauces, cereals, and beverages. Reading labels carefully helps discern the sugar content and make informed choices. Switch to alternate sweeteners that provide less impact on blood sugar levels, such as stevia or monk fruit. Incorporate whole foods into meals that naturally have lower sugar content. Implement a meal prep strategy that helps avoid impulsive decisions regarding snacks. Focus on foods with a high satiety level such as proteins and healthy fats to curb sugar cravings. Hydrating adequately can also reduce the temptation for sugary snacks. Keep healthy snacks on hand, like nuts or fruit, to support energy without unwanted sugar. Creating an environment that encourages lower sugar choices is beneficial. Educate family and peers about the importance of reducing sugar, creating a supportive atmosphere. The journey towards reduced sugar intake may have challenges, but the efforts will eventually lead to significant health benefits, fostering enhanced performance for athletes.
The gut-brain connection is a fascinating aspect of gut health that can significantly influence an athlete’s performance. Scientific research highlights how the state of gut health can affect mood and cognition. A well-balanced microbiome often leads to improved mental clarity and focus, enhancing performance in sports. High sugar intake has been linked to negative emotional states and fatigue, which can impede an athlete’s drive. Striving for a nutrient-dense diet helps support both physiological and psychological health. Incorporate omega-3 fatty acids found in fish and flaxseeds, which have profound anti-inflammatory properties beneficial for the gut and overall wellness. Consider also including adaptogenic herbs like ashwagandha or rhodiola, which can reduce stress levels and support mental resilience. Positive mental health influences motivation and training outcomes, showing that nutrient quality matters just as much as quantity. Understanding the gut-brain axis and optimizing gut health can lead to improved emotional states. Additionally, regular practice of mindfulness techniques can complement dietary efforts, enhancing overall performance. Consistently nurturing the gut will contribute to enabling athletes to perform at their best by improving both mental and physical health.
Conclusion: Building a Sustainable Healthy Lifestyle
The path towards better gut health involves a long-term commitment to dietary and lifestyle changes for athletes and active adults alike. Prioritizing natural foods over processed versions creates a solid foundation for well-being. Start by gradually reducing sugar, focusing on balance and moderation over complete elimination. Incorporating regular physical activity, paired with a healthy diet, enhances gut health significantly. Wellness routines should also include stress management, hydration, and adequate rest, all critical for recovery and overall performance. Track progress and make adjustments as needed; the journey can be personal and may require experimentation to find what works optimally. Engage with nutritionists or dietary specialists to gain insights tailored to specific needs. Explore resources and literature on nutrition to stay informed. Additionally, building a supportive community by sharing knowledge and experiences plays a significant role in fostering motivation. Sustaining a background of low sugar alongside whole food consumption can improve not only athletic performance but also overall lifestyle quality. Ultimately, understanding how sugar impacts gut health enables athletes to strive for excellence while embracing a holistic approach to their health and wellness.
Committing to a lower sugar lifestyle can pave the way for enhanced gut health for athletes and active individuals. It’s important to remember that every small change contributes to significant outcomes. Developing healthy habits takes time and requires consistency, making it crucial to stay motivated. Use online tools or apps to track food intake and identify patterns related to sugar consumption. Often, just becoming aware of daily intake can prompt meaningful changes. Social support networks can provide accountability, encouraging consistent efforts. Exercise should also align with nutrition; pairing them creates a synergistic relationship that maximizes health benefits. Through practice and commitment, the goal of achieving optimal gut health can be accomplished. Consider also consulting with a trained professional to tailor approaches specifically to individual needs. The path may include challenges, yet it also leads to rewarding experiences. Long-term benefits encompass overall health improvements, greater athletic performance, and increased energy levels. Continuing education about sugar reduction and gut health becomes essential. Finally, celebrate each achievement, no matter how small, as they all contribute positively towards achieving a healthier, fulfilled life.