The Connection Between Gut Health and Immunity
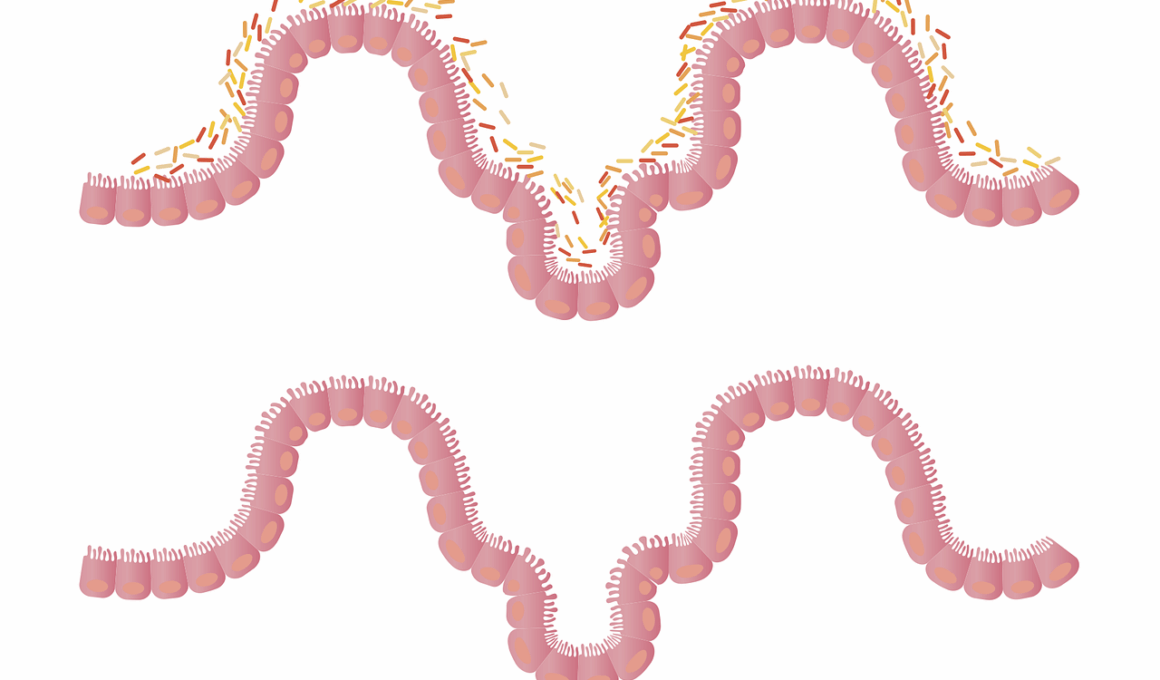
The immune system plays a crucial role in protecting the body from infections, diseases, and other harmful invaders. A significant link exists between gut health and immune function, making it essential to understand how the two systems interact. The gut houses a vast array of microorganisms, known as the gut microbiota, which are vital for proper digestion and overall health. These microorganisms aid in breaking down food, synthesizing nutrients, and supporting the immune system. An imbalance in gut microbiota can result in a weakened immune response, leading to increased susceptibility to infections and diseases. Ensuring a healthy gut environment supports a well-functioning immune system. Factors such as diet, lifestyle, and stress levels can influence gut microbiota composition. A diet rich in fiber, prebiotics, and probiotics can promote the growth of beneficial bacteria essential for immunity. Probiotics, found in fermented foods like yogurt and kefir, can enhance gut health. Equally important is maintaining a balanced diet that includes a variety of nutrients to aid the immune system. Overall, prioritizing gut health can significantly impact one’s overall immune response.
One of the prominent ways gut health influences immunity is through the production of antibodies. Antibodies are proteins that help to neutralize pathogens that threaten the body, and a healthy gut microbiota is instrumental in their production. When gut bacteria metabolize certain nutrients and fibers within food, they produce short-chain fatty acids (SCFAs) that are significant for immune function. SCFAs support the gut lining, preventing pathogens from entering the bloodstream and triggering an immune response. Additionally, they can modulate inflammatory responses and strengthen intestinal barrier function. Moreover, certain gut bacteria can stimulate various immune cells, such as T-cells and B-cells, providing the body with a robust defense against infections. A well-balanced diet featuring fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and fermented foods is crucial for feeding beneficial gut bacteria, promoting their proliferation. Regular physical activity also benefits gut health and immunity, reducing stress and inflammation levels that can harm gut flora. For example, maintaining a healthy weight through exercise can affect gut microbiota positively. Maintaining optimal gut health, supplemented with a comprehensive lifestyle approach, is vital in supporting a resilient immune system.
The Role of Diet in Gut and Immune Health
Diet plays a significant role in determining gut health, which ultimately impacts immune response. Consuming a variety of foods can lead to a diverse gut microbiome, which is generally associated with better health. A fiber-rich diet can help promote beneficial gut bacteria, fostering a balanced gut environment. Foods like whole grains, fruits, vegetables, and legumes are excellent sources of dietary fiber. Furthermore, incorporating fermented foods such as kimchi, sauerkraut, and miso can deliver beneficial probiotics to the gut. These foods introduce live bacteria that can strengthen and replenish the gut microbiota. On the other hand, a diet high in processed foods, sugars, and unhealthy fats can disrupt gut health, leading to dysbiosis. Dysbiosis refers to an imbalance of gut bacteria, which can weaken immune function and predispose individuals to infections. Staying hydrated is also essential for gut health, as water aids digestion and nutrient absorption. Additionally, certain micronutrients, such as vitamins A, C, D, and E, along with minerals like zinc and selenium, are crucial for maintaining a robust immune system. Balancing these nutrients can further enhance immune function.
Stress is another critical factor that can negatively impact both gut health and immune response. Chronic stress can lead to the disruption of gut microbiota, contributing to increased inflammation and a weakened immune system. Stress hormones, like cortisol, can alter the composition of gut bacteria, diminishing their beneficial effects. Managing stress is therefore vital for maintaining both gut health and effective immune responses. Techniques such as mindfulness, meditation, and adequate sleep can help alleviate stress and support a healthier gut environment. Additionally, staying connected with loved ones and participating in community activities can promote mental well-being, ultimately benefiting gut health. Furthermore, avoiding excessive alcohol consumption and quitting smoking can positively affect gut microbiota. Both alcohol and tobacco can lead to inflammation and disrupt gut barrier integrity, making the body more susceptible to infections. Acknowledging lifestyle factors contributing to stress is essential in creating a well-rounded immune-supporting plan. Overall, understanding and managing stress levels can have a profound impact on gut health and resilience against infections.
Probiotic Supplements for Immunity
Probiotic supplements have gained popularity as a means to enhance gut health and, by extension, immunity. These supplements contain live microorganisms intended to confer health benefits when consumed in adequate amounts. Research shows that certain strains of probiotics can aid in restoring balance to gut microbiota disrupted by factors such as poor diet, stress, and antibiotics. By promoting beneficial bacteria, probiotics can improve gut barrier function, reducing inflammation and potentially lowering the risk of infections. Some studies suggest that specific probiotic strains can enhance the immune response by increasing antibody production. Additionally, they may help regulate immune responses, making them a valuable addition to an immunity-supporting regimen. However, it’s crucial to choose the right probiotic strain that aligns with individual health needs, as not all probiotics provide the same benefits. Consulting healthcare professionals can offer guidance on selecting appropriate supplements. Incorporating probiotics into daily routines alone cannot replace a balanced diet, but they can complement a healthy lifestyle aimed at supporting gut and immune health. For best results, it’s recommended to combine probiotics with other gut-friendly foods for optimal health outcomes.
While probiotics play a vital role in gut health, it is equally important to consider the impact of prebiotics. Prebiotics are naturally occurring fibers and compounds that feed beneficial gut bacteria, fostering their growth and activity. Foods rich in prebiotics include garlic, onions, asparagus, leeks, and bananas. These foods can help maintain a healthy gut microbiome, promoting optimal immune function. By enhancing the presence of beneficial bacteria, prebiotics contribute to producing SCFAs, essential for inflammation regulation and gut barrier maintenance. This symbiotic relationship between prebiotics and probiotics enhances the effectiveness of gut health interventions aimed at bolstering immunity. When consumed together, they can work synergistically to foster a healthy gut environment. Moreover, the ongoing research in this area is shedding light on the potential of prebiotics in enhancing the efficacy of vaccines and reducing the incidence of specific infections. Adopting a diet that combines both prebiotic and probiotic sources greatly contributes to overall health and wellness. Ultimately, considering this dual approach can yield significant benefits for immune response and overall health.
Conclusion
In conclusion, understanding the connection between gut health and immunity is crucial for overall wellness. A healthy gut microbiome serves as a foundation for a strong immune response, highlighting the importance of maintaining gut health through dietary choices, lifestyle practices, and stress management. The right balance of probiotics and prebiotics can truly make a difference in improving gut flora and immune function. By prioritizing whole foods, fermented products, and stress-reducing activities, individuals can support their immune systems more effectively. Additionally, considering supplements like probiotics as needed can be a beneficial strategy for those with imbalances in gut health. Awareness and education surrounding gut health and immunity can empower individuals to make informed choices that positively affect their well-being. As ongoing research continues to explore deeper links between gut and immune health, the importance of these connections becomes increasingly evident. By taking proactive steps in nurturing gut health, we can significantly help our immune systems meet daily challenges, leading to healthier lives overall. Emphasizing the gut’s role in supporting immunity ultimately enhances quality and longevity of life.