How Food Sensitivities Trigger Gut Inflammation
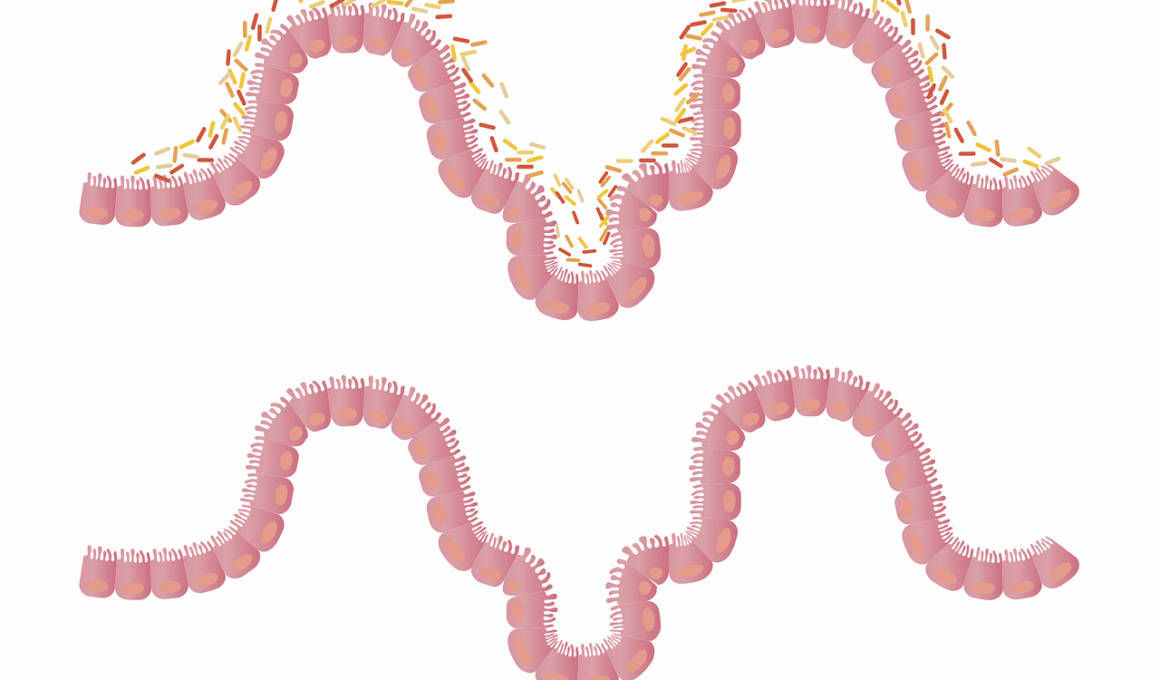
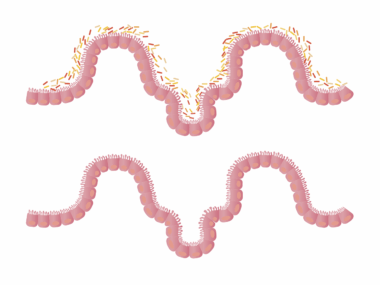
Food intolerances are increasingly recognized as contributors to gut inflammation. These sensitivities lead to adverse reactions within the digestive system, often resulting in discomfort and various symptoms. Common food intolerances, such as lactose or gluten intolerance, can cause significant disruptions in gut flora. When the body struggles to process certain substances, it ignites an inflammatory response. This response occurs when the immune system improperly identifies harmless food components as threats, prompting inflammation in the gut lining. Such reactions can lead to chronic gut issues, including Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS) or leaky gut syndrome. Symptoms can range from bloating and gas to more severe digestive disturbances. To understand these processes, it is important to recognize the role of different foods in triggering sensitivities. Some individuals might not show immediate inflammation; however, consistent exposure can lead to cumulative detrimental effects on gut health. Diet modifications often serve as a primary solution for managing these intolerances, allowing diverse food options that maintain gut balance. Many find relief through food journals, tracking their intake, and understanding which foods worsen or alleviate their conditions. Consulting healthcare professionals is recommended for personalized dietary advice.
Identifying specific food triggers is essential for managing gut inflammation. Various factors influence an individual’s reaction to specific foods, including genetic predisposition, gut microbiome composition, and overall health status. For instance, individuals with a family history of food allergies or intolerances should be particularly vigilant. Certain foods, such as dairy or wheat, are common instigators of sensitivities. When consumed, these foods can lead to an immune response characterized by inflammation and discomfort. An elimination diet can be an effective method to pinpoint problematic foods, allowing individuals to gradually reintroduce them while monitoring for symptoms. Furthermore, supporting gut health through a diverse and nutrient-rich diet can aid in recovery from inflammation. Including fiber-rich foods, probiotics, and fermented options can help restore balance in gut flora. The goal of identifying food sensitivities lies not just in avoidance but also in establishing a healthy relationship with food. Educating oneself about ingredients and being mindful of eating habits contributes to long-term gut health. Community support or online groups for individuals with food sensitivities can also provide emotional comfort and practical advice during the journey.
How Food Sensitivities Affect Immunity
The gut is often referred to as the body’s second brain and plays a crucial role in immune function. A healthy gut supports the immune system, while food intolerances can disrupt this balance. When the gut becomes inflamed due to sensitivity reactions, it may hinder the body’s ability to fend off pathogens effectively. The inflammation can lead to an increased permeability of the gut lining, commonly known as leaky gut. This condition allows toxins and undigested food particles to enter the bloodstream, leading to systemic inflammation and further immunological challenges. Consequently, individuals may become more susceptible to infections and diseases. Inflammatory responses triggered by food intolerances often deplete the body’s nutrients, necessary for maintaining robust immune health. Therefore, individuals should prioritize gut health through appropriate dietary choices, including antioxidants and anti-inflammatory foods. Healing the gut and restoring its integrity can significantly enhance overall immune function. Moreover, regular check-ups with healthcare professionals can monitor gut health, ensuring that any tolerance issues are addressed promptly, before they escalate to more serious health complications.
Holistic approaches may offer additional benefits for managing food sensitivities and gut health. Mindfulness practices such as yoga and meditation have shown promise in reducing stress, which is known to exacerbate gut issues. Stress can alter intestinal permeability and gut motility, leading to increased inflammation. Incorporating relaxation techniques can aid in regulating the digestive process and promoting gut health. Additionally, lifestyle choices, such as regular physical activity, can enhance gut motility and overall well-being. Engaging in moderate exercise has been linked to a healthier gut microbiome, thus supporting better digestion. Exploring alternative therapies, including acupuncture and herbal remedies, can also provide complementary support for those with food sensitivities. Consulting with a licensed practitioner can help individuals determine the most suitable modes of treatment for their specific circumstances. Fostering a supportive environment through educational workshops will encourage those affected to actively manage their conditions. By blending traditional dietary adjustments with holistic strategies, individuals can significantly enhance their overall quality of life, promoting an optimal relationship between food and gut health.
Seeking Professional Guidance
For those struggling with food intolerances and gut inflammation, seeking professional advice is vital. Registered dietitians or nutritionists can provide tailored interventions based on individual dietary and health needs. These professionals often employ diagnostic testing to evaluate allergies or intolerances effectively. Personalized meal planning is essential, enabling individuals to identify diverse foods that not only minimize symptoms but also promote gut healing. Beyond dietary modifications, potential supplement therapies can play a role in fortifying gut health. Probiotics and digestive enzymes are commonly recommended to aid in reducing symptoms and enhancing nutrient absorption. Regular follow-ups allow healthcare professionals to monitor individual progress and make necessary adjustments as conditions evolve. Furthermore, professional support encourages accountability, making it easier for individuals to adhere to dietary modifications and lifestyle changes. Emphasizing the importance of nutritious food choices reinforces the connection between diet and gut health. Community resources, including support groups and workshops, are invaluable for sharing experiences, obtaining information, and fostering a sense of understanding among peers facing similar challenges.
Maintaining a food diary can prove invaluable for individuals managing food intolerances. Recording daily food intake, symptom occurrences, and overall feelings can establish a clear pattern between foods consumed and reactions experienced. This practice allows for personalized insights into specific sensitivities, aiding in better decision-making regarding dietary choices. By reflecting on this information, individuals can make informed adjustments to their diets. Additionally, organizations and mobile apps dedicated to tracking food symptoms can provide supportive tools for those with intolerances. Over time, monitoring gastrointestinal symptoms can lead to enhanced awareness of gut health. Furthermore, sharing this data with healthcare providers equips professionals with critical insights, supporting tailored recommendations. The act of journaling not only tracks food sensitivities but also contributes to emotional well-being, as individuals validate their experiences. By understanding that they are not alone, individuals can identify empowerment in managing their health. As knowledge about food intolerances continues to grow, remaining observant and adaptable proves essential for achieving long-term gut health improvement.
Conclusion
Food sensitivities undeniably play a significant role in gut health, and inflammation stemming from these intolerances can lead to wider health implications. The exploration of individual reactions to food can enhance understanding and encourage proactive management. Through the identification of triggers, conscious dietary modifications, and professional support, individuals can navigate their sensitivities effectively. Emphasizing the unique relationship between diet and the gut may unlock solutions for those grappling with chronic inflammation and digestive disturbances. Integrating holistic approaches and lifestyle changes fosters opportunity for healing, making it crucial to focus on comprehensive care. Those with food intolerances must cultivate a supportive network, be it through community groups or health professionals. With consistent nurturing of gut health and increased awareness about food sensitivities, it is possible to foster an empowered lifestyle. Education remains a critical component, underscoring the importance of ongoing learning about food impacts on digestion. By prioritizing gut health, individuals can achieve a more balanced, fulfilling relationship with food, which ultimately promotes well-being.
Nutrition provides the foundation for achieving optimal gut health, and understanding food sensitivities is pivotal in creating well-being. Continuous research into the links between diet and inflammation is essential for advancing knowledge and treatment options. Addressing food intolerances appropriately allows for the reduction of inflammation, improving overall quality of life. Individuals often find success through customizable dietary protocols, reflecting their unique preferences and tolerances while promoting gut healing. Future advancements in nutritional science may lead to innovative strategies, refining the management of gut inflammation related to food sensitivities. By merging personal insights with professional guidance and emerging research, individuals can embark on a journey of healing, resilience, and sustained gut health.