The Link Between Food Allergies and Intestinal Inflammation
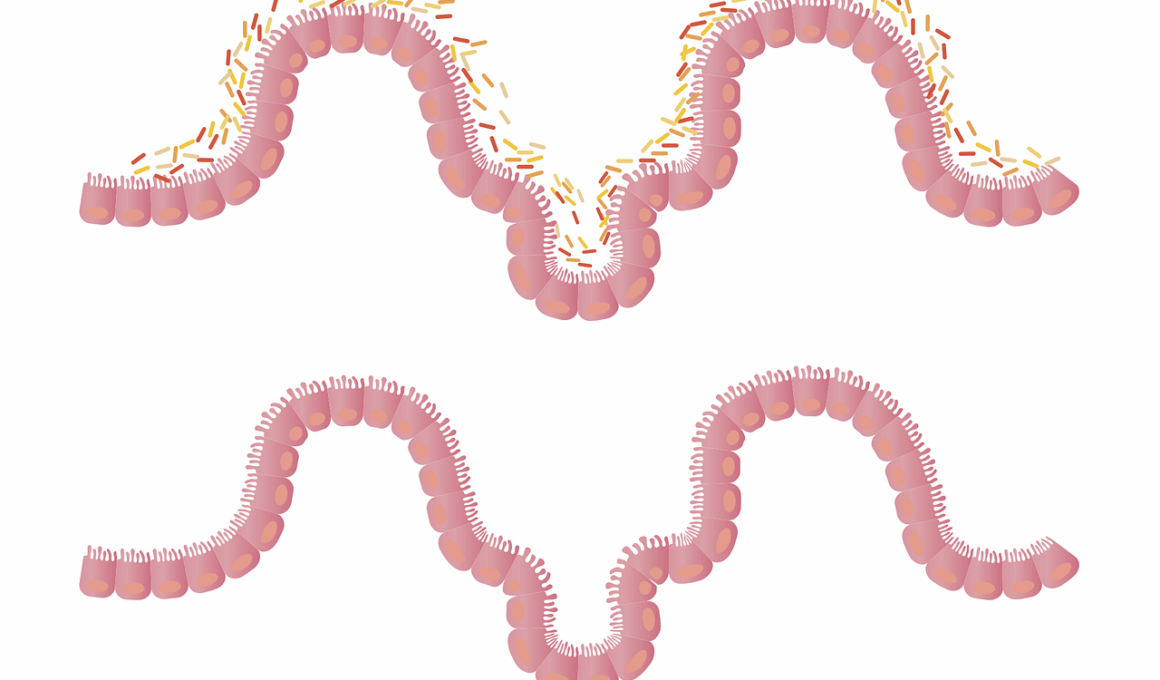
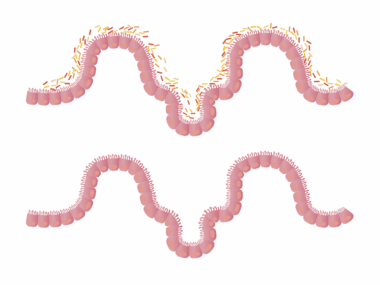
Understanding the correlation between food allergies and intestinal inflammation is essential for improving gut health. Food intolerances or allergies can trigger increased inflammation in the intestines, which may lead to various digestive disorders. For many individuals, this connection is not widely known. The immune system reacts differently when exposed to certain foods, leading to adverse symptoms. This phenomenon connects food allergies directly to inflammatory responses in the gut. Eating allergenic foods can cause discomfort, ranging from bloating to chronic pain. When we consume particular items, the body might mistake them as threats. Consequently, it produces antibodies causing inflammation in the intestines, implying additional stress on digestive organs. Additionally, consistent exposure to allergens can compromise the gut barrier function, creating a cycle of inflammation, digestive symptoms, and even more food intolerance. It’s crucial to identify and avoid specific allergens to manage inflammation effectively. Various diagnostic methods can help identify food allergies and intolerances to provide relief. Ultimately, nutrition plays a vital role in maintaining gut health, highlighting the need for personalized dietary plans. Knowledge about these dietary restrictions is essential to optimize individual health and well-being.
Food allergies often result in significant intestinal responses, albeit unnoticed by many. Chronic inflammation in the gut can be attributed to a range of food items that commonly trigger allergies. This inflammation contributes to various health issues, including conditions such as irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) and inflammatory bowel disease (IBD). In these cases, the immune response can exacerbate gut permeability, leading to further complications. Additionally, managing food allergies and gut health requires understanding which foods are problematic for specific individuals. Keeping a food journal can be invaluable in tracking symptoms and identifying patterns when consuming certain foods. Common allergens linked to inflammation include dairy, gluten, nuts, and shellfish. Identifying these triggers is a crucial step toward preventing inflammation and discomfort. Probiotics may help in reducing inflammation while also providing a form of harmony within the gut. Furthermore, maintaining a varied and balanced diet can contribute to overall gut health. Adequate nutrition is critical when managing allergies or intolerances. Collaborating with a healthcare professional can guide individuals in creating a diet that is both nourishing and avoids potential allergens, minimizing inflammation and improving health outcomes.
Impact of Inflammation on Gut Health
Intestinal inflammation can have profound implications for gut health, impacting digestion and nutrient absorption. When inflammation occurs in the digestive tract, it can disrupt the microbiome balance. A balanced microbiome is necessary for digestion, fermentation, and vitamin production. This imbalance may lead to harmful bacteria overgrowth, which can further exacerbate inflammation. Chronic inflammation can result in symptoms such as diarrhea, constipation, and abdominal pain, which are indicative of a disturbed gut. Moreover, long-term inflammation may lead to damage of the intestinal lining, resulting in a condition known as leaky gut syndrome. This condition allows undigested food particles and toxins to enter the bloodstream, potentially causing systemic inflammation. In time, this can provoke allergic reactions or autoimmune responses. Treating the causes of inflammation, especially through dietary interventions, can minimize these negative outcomes. It may involve identifying and avoiding specific food intolerances, adopting anti-inflammatory foods, and incorporating supplements. Specifically, emphasizing antioxidants from fruits and vegetables can aid in reducing inflammation. Overall, addressing intestinal inflammation is crucial for someone suffering from food allergies to improve their quality of life and training the body to tolerate more foods without reaction.
In addition to recognizing specific food allergies, understanding the role of diet in managing gut health is paramount. Certain anti-inflammatory diets can be beneficial in soothing the gut and alleviating symptoms tied to food intolerances. Such diets generally prioritize whole foods, healthy fats, and fiber while minimizing processed foods that can contribute to inflammation. The Mediterranean diet is an excellent model, emphasizing fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and healthy fats like olive oil. Incorporating sources of omega-3 fatty acids, such as fish, can also play a role in reducing intestinal inflammation. Spices like turmeric and ginger have anti-inflammatory properties that can further support gut health. Moreover, staying hydrated can help maintain optimal digestive function. Eliminating foods that provoke allergenic responses is critical in alleviating inflammation and promoting better digestion. While focusing on dietary changes, it’s equally important to monitor other lifestyle factors that can influence gut health. Stress management, regular physical activity, and adequate sleep are all integral components. Completing a holistic approach, these factors together lay the foundation for positive gastrointestinal health outcomes, providing individuals with greater dietary freedom and improved overall well-being.
Probiotics and Gut Health
The incorporation of probiotics into one’s diet can significantly influence gut health, especially for those with food intolerances. Probiotics are beneficial bacteria that help restore and maintain microbial balance and integrity in the intestines. This restoration can aid in reducing intestinal inflammation and managing symptoms associated with food allergies. Fermented foods, such as yogurt, kefir, sauerkraut, and kimchi, are excellent natural sources of probiotics. Including these foods in the diet encourages a friendly gut environment, thereby curbing symptoms tied to inflammation and food intolerances. Additionally, probiotic supplements can be beneficial for individuals who may not have adequate access to these foods. The benefits of probiotics extend beyond gut health; they also contribute to overall immune function. For individuals suffering from food allergies, strengthening the immune system can prove critical in reducing reactions. However, it is essential to select the right strains of probiotics that target specific digestive issues. Professional guidance can help tailor probiotic use efficiently. Establishing a routine involving probiotics, in conjunction with dietary adjustments, can further assist in reducing the burden of food allergies and inflammation.
Future research on the interplay between food intolerances, inflammation, and gut health remains crucial for understanding these relationships. Developing targeted nutritional therapies may yield innovative ways to manage food allergies effectively by reducing intestinal inflammation. Ongoing studies highlight how different diets can influence the microbiome composition and subsequently gut health. Collaborative efforts between nutritionists and immunologists may yield beneficial guidelines for individuals struggling with allergies and gastrointestinal concerns. Furthermore, there is a pressing need to explore individualized approaches rather than generalized ones for dietary interventions. Personalized nutrition could revolutionize how we understand food intolerances, leading to tailored strategies that consider unique responses among different people. Similarly, there are possibilities of utilizing genetic information to identify intolerance risks and inflammation patterns strategically. These insights could enhance prevention efforts and create targeted screening processes. As awareness grows about the relationships involved, better diagnostic tools will emerge, promoting proactive measures for individuals navigating food allergies. Optimizing gut health through these innovative approaches may redefine the future of nutritional therapy for many individuals dealing with allergies and gastrointestinal issues. Ultimately, continual progress promises improved quality of life.
Conclusion
In summary, the connection between food allergies and intestinal inflammation is complex but important for gut health. Recognizing and addressing the causes of inflammation through dietary modifications can yield significant improvements. Engaging in a proactive, individualized approach to managing food intolerances is necessary, taking into account symptom patterns and reactions. Research underscores the importance of holistic dietary practices that support gut health while reducing inflammation. Collaborating with healthcare professionals can offer invaluable insight into nutritional plans aimed at minimizing allergic responses. Furthermore, incorporating probiotics, anti-inflammatory foods, and nutrient-dense diets plays a crucial role in maintaining balance within the microbiome. Individuals living with food intolerances must empower themselves with knowledge about their condition and actively participate in improving their gut health. Ultimately, understanding the links between food allergies and intestinal inflammation can pave the way toward healthier lifestyles. As ongoing research sheds light on these connections, individuals will develop tailored strategies to manage their conditions effectively. In embracing these approaches, we can foster better health outcomes and improve overall quality of life in those affected by food allergies.
To enhance understanding of food allergies and their impact on gut health, public awareness campaigns are essential. The more individuals know about their health, the better equipped they are to navigate dietary choices. Sharing personal stories and insights can also encourage discussions and create supportive communities. Online platforms, workshops, and health seminars provide valuable avenues for disseminating information on food intolerances. Increasing visibility for those with food allergies can help shift perceptions and encourage empathetic responses within wider society. Moreover, schools and workplaces should prioritize education on food allergies to create safe environments. Promoting inclusive policies can substantiate preventive measures that recognize the importance of dietary restrictions. This includes ensuring that all meals served consider potential allergens. As communities work toward better understanding food intolerances, there is an opportunity to challenge stereotypes. Creating spaces that foster understanding can strongly enhance well-being and acceptance. Ultimately, a collective effort can bolster supportive networks for those living with food allergies, helping them feel empowered and less isolated in their experiences. By emphasizing education, we uplift the discourse surrounding food allergies and promote a culture of compassion and advocacy.