Brain Health and Protein: An Essential Nutritional Relationship
Understanding the connection between brain health and protein sources is critical for maintaining cognitive function and overall well-being. The brain utilizes various nutrients to produce neurotransmitters that regulate mood, memory, and learning. Consuming adequate protein is fundamental for the synthesis of these crucial neurotransmitters. Foods rich in protein contain amino acids, which serve as its building blocks. As we age, our brain health may decline, making proper nutrition even more essential. Incorporating protein-rich foods can help revitalize cognitive function and promote mental clarity. This article explores the importance of protein sources for brain health, highlighting essential nutrients required for optimal brain performance. Moreover, the relationship between dietary choices and cognitive health is becoming clearer, indicating a strong need to focus on nutrition. In comparison, various brain-boosting foods can enhance cognitive abilities significantly. The right balance of nutrients, particularly proteins, can improve brain function, prevent cognitive decline, and potentially ward off neurodegenerative diseases. By prioritizing protein in your diet, you help ensure not just physical strength but also mental acuity, making this an area worthy of our attention.
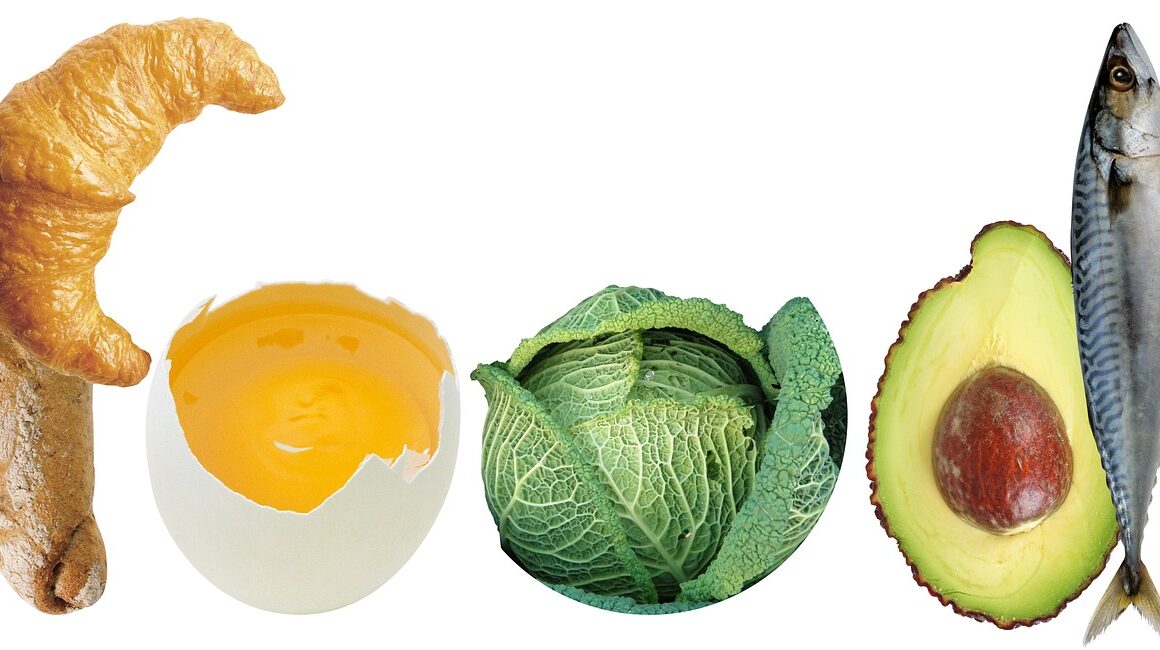
To emphasize this relationship more clearly, particular protein sources stand out for their brain health benefits. For example, fatty fish, which are high in omega-3 fatty acids, provide DHA, essential for neuronal health and the formation of synapses. Additionally, lean meats and eggs deliver high-quality proteins and vital nutrients like B vitamins. Beans and legumes are also excellent food sources that are rich in essential amino acids, antioxidants, and fiber, contributing to overall brain health and stability. A balanced diet that includes various protein sources is crucial for sustained cognitive function. Research suggests a connection between protein intake and cognitive performance, asserting that increased consumption of certain proteins can result in improved memory and learning capacity. Moreover, plant-based protein sources present an important alternative, appealing for vegetarians and vegans alike. Nuts and seeds are fabulous sources of protein as they provide healthy fats, antioxidants, and vitamins which aid in cognitive preservation. Incorporating a variety of these foods into your diet can help maintain your brain’s vitality and efficiency over time, ultimately supporting overall brain well-being.
Specifically, let’s explore the protein superstars that can positively affect brain health. Fish, particularly salmon and sardines, are packed with omega-3 fatty acids, vital for brain cell structure and function. These fats help decrease inflammation and promote healthy blood flow within the brain. Additionally, eggs are excellent for brain health, offering choline, which is crucial for producing acetylcholine, a neurotransmitter responsible for memory and muscle control. Equally important, nuts and seeds, such as walnuts and flaxseeds, deliver protein along with omega-3 fatty acids and antioxidants. They have been linked to improved cognitive function and protection against age-related decline. Incorporating these foods into daily meals can implement more focus and enhance learning abilities. Consuming adequate fiber through whole grains can also serve to stabilize blood sugar levels. This balance is vital because unstable blood glucose levels can impact mood and cognitive function negatively. Therefore, it’s crucial to consider how the proteins consumed affect overall cognitive health in the long term. Emphasizing diverse protein sources will lay a strong foundation for a healthier brain.
Role of Amino Acids in Brain Function
Amino acids obtained from protein consumption play a pivotal role in brain function and health. They serve numerous functions, including creating neurotransmitters, which are critical for communication between neurons. The right amino acids ensure that neurotransmitter levels remain balanced, which influences our emotions, memory retention, and decision-making processes. Tryptophan, for instance, is an amino acid needed to produce serotonin, a neurotransmitter that helps regulate mood and sleep. Conversely, tyrosine, another crucial amino acid, is a precursor to dopamine, which influences focus and motivation. Thus, having a balanced protein intake is essential, as it lays the groundwork for neurotransmitter synthesis. Low amino acid intake can lead to deficiencies, which may manifest in cognitive issues such as poor concentration, mood swings, and memory challenges. Incorporating a variety of proteins into your meals supports amino acid diversity, ensuring that all brain functions operate efficiently. Foods like lean meats, fish, tofu, and legumes can cater to different dietary needs while providing ample amino acids. This diversity is invaluable for optimizing brain health and maintaining cognitive resilience as we age.
Additionally, the quality of protein consumed can significantly influence mental health and cognitive function. High-quality proteins contain all essential amino acids necessary for neurotransmitter production, while lower-quality sources may lack several of these key components. Animal proteins, such as those found in meat, dairy, and eggs, generally provide all essential amino acids in sufficient amounts. On the other hand, plant proteins often require combining different sources to ensure a complete amino acid profile. For example, pairing beans with rice can create a well-rounded protein source. Understanding these differences is crucial for anyone aiming to maintain healthy brain function through diet. Furthermore, specific lifestyle choices and overall dietary patterns affect brain health significantly. Consuming a diet rich in varied nutrient-dense foods that contains healthy fats, antioxidants, and fibers can help augment the positive effects of proteins on cognitive aspects. Hence, it’s not only about including proteins but also ensuring a well-balanced diet supports comprehensive brain health. Ultimately, accomplishing optimal cognitive function rests on a well-rounded and intentional approach to nutrition.
Nutrition Strategies for Enhancing Brain Health
Implementing practical nutrition strategies is essential to enhance brain health effectively. To begin, consider prioritizing whole foods over processed foods that often contain unhealthy additives. Whole foods provide a greater range of nutrients necessary for optimal brain performance. Next, emphasize a varied diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and healthy fats, complemented by quality protein sources. This diversity ensures that all essential vitamins and minerals are available to support cognitive functions. Additionally, consuming adequate hydration is forgotten but essential for maintaining concentration and cognitive performance since proper brain function relies significantly on hydration levels. Moreover, tailored meal planning can foster better choices, helping create a balance of proteins throughout the day. Snacking on brain-boosting foods, such as almonds, yogurt, or dark chocolate, can offer quick energy and nutrients that benefit cognitive health. Furthermore, regular consumption of complex carbohydrates assures sustained energy levels crucial for effective brain functioning. Overall, by combining all these elements, you can create a nutrition strategy that boosts brain health significantly while supporting overall physical health.
Lastly, it’s vital to consider lifestyle factors along with nutrition. Regular physical activity is an incredible complement to nutritional strategies, positively affecting brain health by improving circulation and increasing the growth of new brain cells. Exercise encourages the release of growth factors in the brain, promoting brain plasticity and resilience. Furthermore, adequate sleep is important for cognitive preservation by allowing the brain to recover and consolidate memories effectively. Combining these lifestyle habits with whole, protein-rich foods can create a powerful force against cognitive decline. Practicing mindfulness and stress management through techniques like meditation and yoga can also enhance brain function, reinforcing the positive impacts of healthy eating patterns. Hence, developing a holistic approach to health—encompassing nutrition, exercise, sleep, and mental well-being—is most effective in maximizing brain health. As research in this field grows, understanding how multifaceted our nutritional and lifestyle choices are to cognitive function becomes ever more essential. Ultimately, making informed choices today lays the foundation for a sharper, more resilient brain in the future.
In conclusion, the relationship between brain health and protein sources cannot be understated. Adequate protein intake supports crucial neurotransmitter functions, which safeguard cognitive health. Therefore, including a variety of protein-rich foods in your diet is essential for maintaining mental acuity, particularly as we age. Foods like fish, eggs, nuts, seeds, legumes, and lean meats should form the foundation of your dietary framework. These proteins are not only serving as foundational building blocks for neurotransmitters but also provide essential nutrients like omega-3 fatty acids and B vitamins that significantly enhance brain function. Understanding the importance of amino acid balance is equally vital to ensuring that all brain functions operate optimally. By recognizing the prominence of brain-boosting foods within our dietary patterns, we can make informed choices to preserve cognitive function for years to come. Furthermore, adopting nutrition strategies that emphasize whole foods and balanced meals leads to improved health across the board. Hence, prioritizing protein intake, combined with complementary lifestyle choices, will nurture brain health. Taking these steps today helps build resilience against cognitive decline in the future, making a sustained commitment to these principles vital.