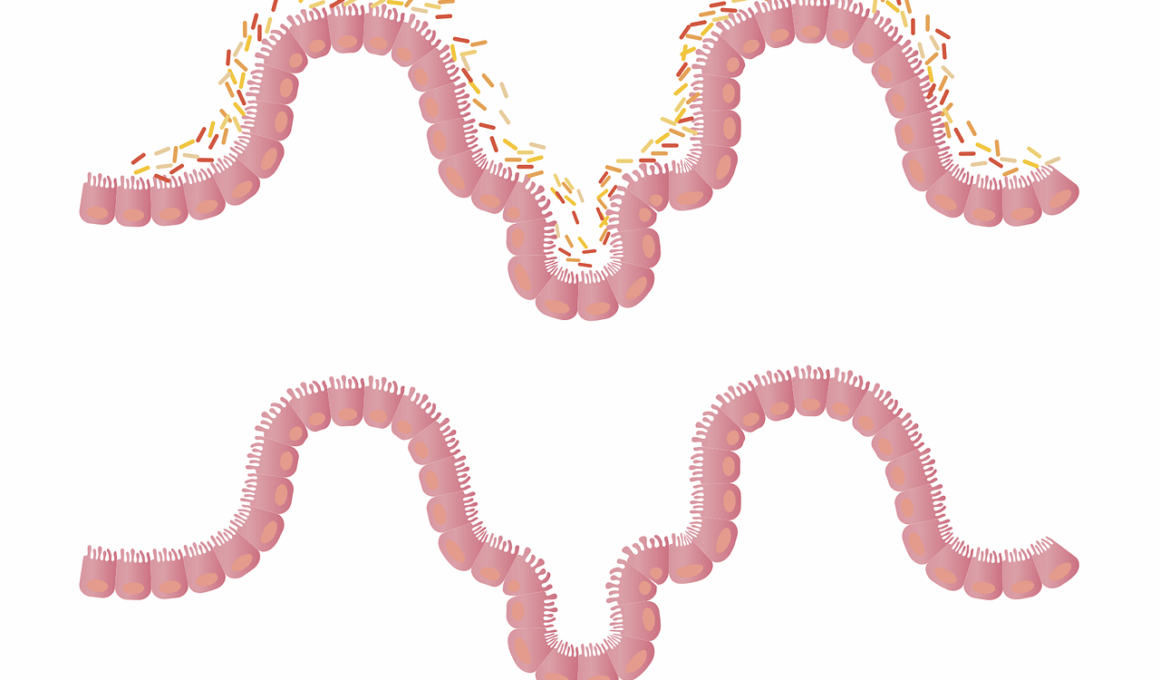
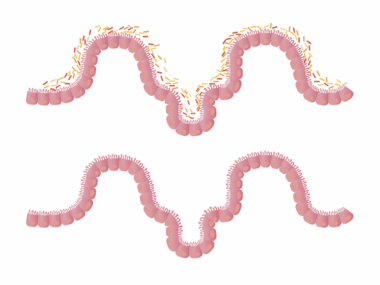
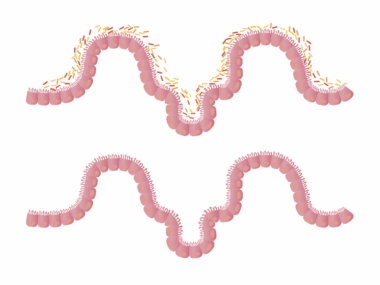
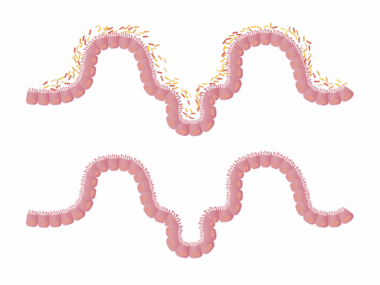
Meal Timing’s Effect on Gut Barrier Integrity
Meal timing has a significant impact on gut microbiome health, influencing gut barrier integrity. When meals are consumed consistently at regular intervals, this schedule helps in creating a rhythm for gut microbiota. Disruption of these eating patterns can lead to dysbiosis, where the balance of beneficial and harmful bacteria is compromised. This imbalance can result in increased intestinal permeability, often referred to as ‘leaky gut syndrome.’ Evidence indicates that irregular meal timings, such as eating late at night or erratic snacking, have harmful effects on gut barrier function. The body’s internal clock, or circadian rhythm, plays a vital role in optimizing digestion and absorption. Furthermore, a well-timed meal can support healthy metabolic processes, reducing inflammation in the gut. This includes a diverse diet rich in fibers, prebiotics, and probiotics, which can further enhance gut health. Understanding meal timing is crucial for individuals focusing on overall wellness. By ensuring consistent eating times, one can potentially reap the benefits of a healthier gut microbiome, preventing many related health issues while promoting better digestive function.
Studies suggest that the timing of food intake directly correlates with gut microbiome composition. Observations reveal that more stable meal timings lead to enhanced diversity within gut microbiota. Diverse microbiota are crucial because they help maintain gut health and protect against various diseases. For instance, high-fiber diets coupled with regular meal patterns foster beneficial bacteria growth. This improvement in microbial balance contributes positively to gut barrier integrity. Certain ultra-processed foods, when consumed at irregular times, can disrupt this balance, worsening conditions in the gut. Therefore, creating a consistent eating schedule is pivotal. It is essential to limit eating episodes to specific times during the day. This method reduces stress on the digestive system. Emerging research shows that both meal frequency and duration also influence gut health. Eating larger meals less frequently can yield different outcomes than frequent smaller meals. Thus, strategic meal timing could become a key aspect of nutritional guidance. Further research in this area underscores the potential of timing in nutritional strategies aiming at improving gut health and overall well-being.
The Role of Circadian Rhythms
Circadian rhythms significantly influence metabolism and gut microbiome activity. They dictate when various bodily functions such as digestion and absorption occur, aligning these processes with environmental cues like light and darkness. Irregular meal timings can disrupt these rhythms, leading to misalignment and subsequent gut health issues. Gut bacteria thrive on predictability; hence, feeding them at similar intervals daily encourages a stable environment for growth and functioning. As our bodies operate on a hormonal and metabolic cycle, adhering to a schedule that resonates with these natural cycles optimizes nutrient absorption and gut function. Disruptions in these rhythms can, therefore, lead to conditions like obesity, diabetes, and gastrointestinal disorders. Research indicates that consuming food in accordance with these natural cycles positively affects not just gut health but also general metabolic outcomes. Consequently, maintaining a regular meal schedule coinciding with daily and seasonal rhythms is vital for optimal gut barrier integrity. Lifestyle modifications concerning eating patterns are recommended for those aiming to improve overall digestive health and reinforce the gut’s protective mechanisms.
Acknowledging the influence of meal timing on gut microbiota advocates for deliberate approaches to eating. For instance, skimming through multiple studies highlights how a time-restricted eating pattern can enhance the microbiome composition favorably. Time-restricted eating involves consuming all meals within a specific window each day, typically around 8 to 10 hours. This method not only respects the body’s natural rhythms but also reinforces the gut’s resting period, allowing it to recuperate and regenerate. Furthermore, aligning meal timing with individual biological clocks has become a significant discussion point. Early eating, especially breakfast, has shown favorable outcomes on gut health compared to skipping breakfast or eating late. In contrast, late-night eating tends to spur metabolic disturbances and gut health deterioration. Hence, prioritizing earlier eating schedules can promote optimal gut barrier integrity while enhancing cognitive function and energy levels throughout the day. Much focus needs to be placed on this aspect, as it can influence societal shifts towards healthier eating habits more broadly.
Nutrition’s Influence on Gut Health
Nutrition plays a pivotal role in shaping gut microbiome health and integrity. Certain dietary patterns influence how well the gut barrier functions and reacts to external pressures. Diets rich in fiber, fruits, and vegetables support beneficial bacteria that create short-chain fatty acids. These acids play crucial roles in maintaining gut barrier integrity and lowering inflammation. Not only do these nutrients serve to nourish the body, but they also foster a balanced gut environment. However, highly processed foods consumed at irregular timings can promote detrimental bacteria growth, affecting overall gut function negatively. Consequently, the relationship between nutrition, meal timing, and gut microbiome emphasizes the importance of making healthy dietary choices. Moreover, drinking plenty of water throughout the day aids digestion and further supports gut health. It becomes evident that foregoing unhealthy habits, such as late-night snacking, could yield significant benefits. Aligning nutrient-rich meals with consistent timings fosters a strong and resilient gut barrier. Therefore, the commitment to nutritious eating habits can transform one’s gut health and overall wellness in potent ways.
In conclusion, meal timing is a formidable yet often underestimated factor impacting gut barrier integrity. The interplay between the timing of food intake, circadian rhythms, and nutrition shapes the gut microbiome landscape. As mentioned throughout the discussion, adherence to consistent meal times lends itself to improved microbiome diversity, leading to better gut health. The awareness of gut health benefits stemming from regular meal patterns fuels the motivation for lifestyle changes. By embracing time-restricted eating patterns, individuals can potentially enhance gut barrier function and overall wellness significantly. The suggestion is clear: prioritize consistency and precision in meal timings for optimal health outcomes. Future studies are ongoing to explore these connections unaddressed, intending to refine recommendations concerning meal timings. In light of growing health concerns tied to gut issues, a keen understanding of meal timing emerges as essential knowledge for individuals seeking better quality of life. To achieve a well-functioning gut microbiome is to embrace routine, and the timing of meals should not be taken lightly. This knowledge empowers individuals as they embark on their journey towards improved health.
Encouraging optimal gut health means seamlessly integrating knowledge about meal timing into everyday practices. By doing so, individuals initiate dynamic changes in their gut microbiome composition. As new research emerges in this promising area, the potential for meal timing to provide compelling health benefits becomes increasingly undeniable. Advocating healthy meal timing along with nutritional quality leads to a holistic approach whereby individuals can achieve excellent health outcomes. The synergy between consistent meal patterns and nutritious choices forms an integral part of fostering gut integrity. Through these viable adaptations, individuals strengthen their gut barrier while promoting overall mental and physical well-being. Educating communities about the systemic benefits of aligning meal timing with natural rhythms will also play a foundational role in enhancing public health perspectives. Awareness and practice of beneficial meal timing will be crucial in tackling growing health issues. Eliminating fast-food habits, for example, can have immediate positive effects on gut health when timed consistently. Ultimately, reevaluating meal timings while embracing nutritional wisdom can pave the way for significant wellness transformations. Therefore, integrating these principles is essential for every individual aiming for optimal health.
The connections drawn between meal timing and gut microbiome health underscore the importance of ongoing research in this field. As scientific insights continue to unfold, the broader implications for dietetics and public health will become clearer. Emphasis on meal timing represents a new frontier in understanding the complex relationship between diet and health. This evolving narrative encourages dietitians and health professionals to incorporate temporal aspects into their dietary guidelines. The future beckons for a more personalized approach to nutrition that considers individual metabolic rhythms and preferences while underscoring the significance of gut health. A gradual shift towards integrating these principles within clinical practices is on the horizon to enhance patient outcomes significantly. Additionally, stakeholders in the food industry must also consider how meal timing can be incorporated into product offerings. The merging of innovation and education in this way will foster healthier consumer habits and choices. Overall, commitment to a better understanding of meal timing will likely continue driving the evolution of nutritional science, vital for addressing health concerns at population levels.