Nature Therapy: Using the Outdoors to Heal
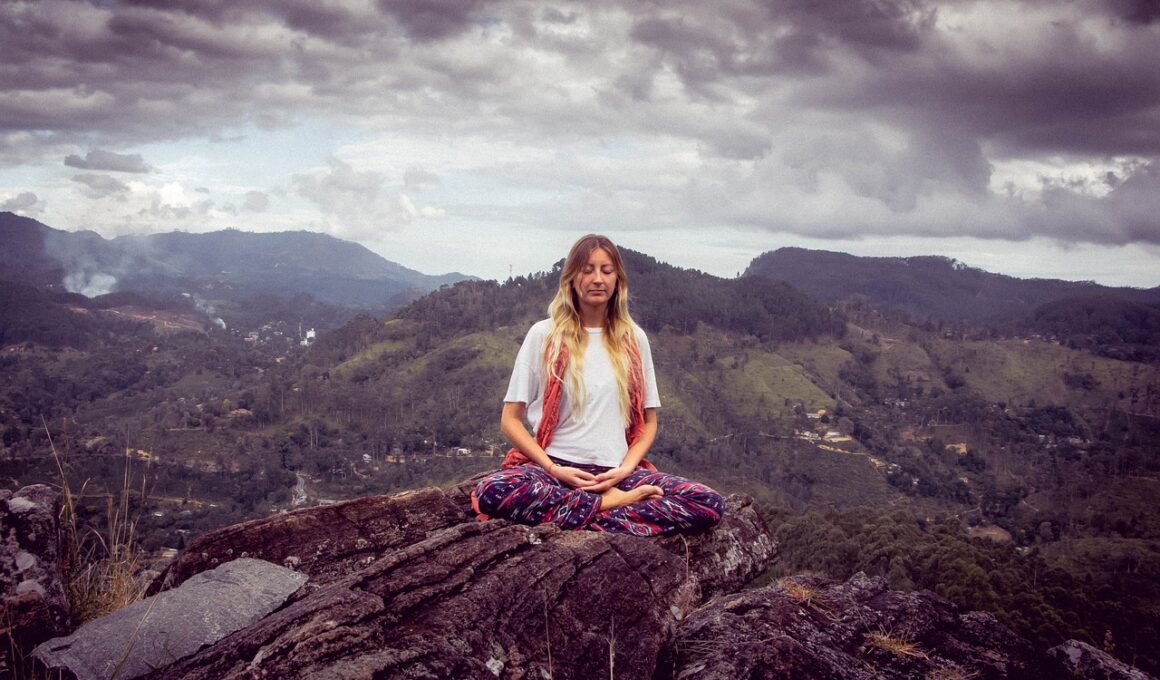
Mental health is an essential aspect of our overall well-being, influencing our emotional and psychological states. Nature therapy, an emerging trend, utilizes the great outdoors to promote mental wellness. Immersing oneself in natural environments can help reduce anxiety, depression, and psychological stress. Studies have shown that just being in nature can lower cortisol levels, the stress hormone, and promote feelings of relaxation and peace. This connection to the external environment is fundamental, providing *holistic* benefits that integrate mind and body. Spending time outdoors fosters mindfulness, encouraging individuals to appreciate the present moment. Activities such as hiking, gardening, or simply walking in the park can greatly impact mental health. Nature therapy also promotes physical activity, leading to overall health improvements. Traditional therapeutic approaches, such as cognitive behavioral therapy, can be complemented through outdoor therapy, creating a healing synergy. Many therapists now incorporate nature therapy into treatment plans, understanding its significance in fostering emotional regulation. Ultimately, nature offers a free and vast resource for healing, invaluable in today’s high-stress, fast-paced society, where mental health issues are prevalent. Connecting with nature helps reconnect individuals to themselves.
The Principles of Nature Therapy
Nature therapy operates on several key principles designed to enhance mental health through biophilia, human beings’ innate affinity for nature. These principles encourage individuals to engage with the outdoors, fostering a purposeful relationship with the environment. One primary tenet is *mindfulness*, wherein participants learn to focus on their surroundings, allowing feelings of stress to dissipate. Through mindful observation, individuals can cultivate a deeper awareness, which can lead to greater emotional resilience. Another principle is *restoration*, as natural settings provide a reprieve from urban chaos. Forests, parks, and gardens create spaces that facilitate relaxation and rejuvenation. *Connection* to nature also plays a vital role, helping people bond with their environment and discover personal significance in these interactions. Therapeutic interventions are designed around pivotal aspects such as engagement and contemplation. Additionally, *social interaction* in nature is crucial, as shared experiences promote a sense of belonging and community. By understanding these core principles, mental health professionals can guide individuals on nature therapy journeys. These elements create environments conducive to personal growth and emotional healing while providing natural strategies for coping with life’s challenges.
Participating in nature therapy can take various forms, and understanding these forms can help individuals find the best fit for themselves. Popular methods include eco-therapy, wilderness therapy, and horticultural therapy. Eco-therapy emphasizes the healing power of being outdoors, where people engage in activities designed to promote emotional health while surrounded by beauty. Wilderness therapy focuses on adventurous expeditions in remote locations, combining survival skills with personal development. Here, participants bond with nature in a transformative way. On the other hand, horticultural therapy involves actively engaging with plants and nature through gardening, which has been shown to alleviate symptoms of anxiety and depression. Other forms include guided nature walks that promote mindfulness, outdoor meditation practices, and art therapy in natural settings. Each of these variations fosters connections between participants and their environments, allowing for unique pathways to healing. Guided sessions also often include psychologist support, further strengthening recovery efforts. This diversification in approaches appeals to various preferences and needs, making nature therapy accessible to many people. By exploring these forms, individuals can create personalized treatment plans aligned with their goals for mental health recovery.
The Science Behind Nature Therapy
Scientific research increasingly validates the benefits of nature therapy for mental health improvement. Recent studies extensively document measurable improvements in mood and cognition when individuals spend time outdoors. Neurological responses to nature are also notable; exposure to natural environments activates brain areas associated with relaxation and emotional regulation. Natural stimuli promote serotonin release, a neurotransmitter crucial for mood stabilization. Other research indicates that green spaces contribute significantly to reduced feelings of stress and anxiety. A notable study presented in the *International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health* concluded that spending as little as twenty minutes in nature can lead to substantial mental health benefits. Also highlighted was how natural light exposure positively affects sleep patterns, enhancing overall well-being. Furthermore, the *Japanese practice of Shinrin-yoku*, or “forest bathing,” has gained popularity and scientific backing for promoting mental and emotional wellness. By providing empirical evidence to support nature therapy, researchers continue encouraging mental health practices merging outdoor experiences. This growing body of research empowers mental health practitioners and individuals to embrace nature therapy as a viable method for enhancing emotional well-being.
Incorporating nature therapy into daily routines can significantly alleviate stress and promote positive mental health outcomes. Exploring local parks is an excellent way to start, as these areas are often designed to encourage relaxation and connection. Establishing a walking routine or a regular jog among trees offers opportunities for physical health improvement as well. Furthermore, gardening at home or participating in community gardens lets individuals nurture plants while enjoying the sensory experiences provided by nature. Volunteering for clean-up initiatives can foster a sense of purpose, bringing social connections with like-minded individuals. Engaging with wildlife through birdwatching or participating in guided nature hikes adds enriching layers to nature therapy experiences. For those less mobile, simply sitting in a garden, focusing on the rhythm of nature, can yield calming benefits. Digital detoxification during these times allows individuals to eliminate distractions and fully embrace the healing properties of nature. Overall, integrating nature experiences fosters a lifestyle that prioritizes mental wellness. By creating time for outdoor activities and committing to them, individuals cultivate improved mental health while rediscovering the beauty of life intertwined with nature.
Challenges and Considerations
While nature therapy offers substantial benefits, it also comes with challenges and considerations. Accessibility can be a significant barrier, particularly for individuals living in urban areas with limited green spaces. Additionally, some may face physical limitations that hinder participation in outdoor activities. Unequal exposure to natural environments can lead to disparities in mental health outcomes among different communities. Therefore, innovative solutions, such as local therapy groups or city-based initiatives to convert vacant lots into community gardens, are necessary. Another consideration is weather; adverse conditions can deter individuals from engaging in outdoor activities, thus limiting opportunities for nature therapy. To address this, flexible scheduling for sessions can accommodate various weather conditions. Furthermore, mental health professionals must understand clients’ needs, creating personalized plans that foster confidence and motivation. Lastly, it’s essential to recognize that not every individual will respond positively to nature therapy, signaling the need to integrate it with other therapeutic approaches. Balancing traditional methods with nature therapy allows for comprehensive care, maximizing the chances of healing. Acknowledging these challenges will ultimately strengthen mental health services involving nature, helping to reach more individuals in need of support.
In conclusion, nature therapy represents a promising avenue for enhancing mental health and overall wellness. The benefits associated with spending time outdoors are well-documented, and numerous methods exist to incorporate nature into therapeutic practices. Individuals are encouraged to explore various approaches, fostering a personal relationship with nature that caters to their mental health needs. The principles of mindfulness, restoration, and connection with the environment play a pivotal role in emotional recovery and growth. As scientific evidence continues to support nature therapy, more mental health professionals are likely to integrate it into their practices. This merging of nature and therapy opens doors to innovative approaches, further enhancing mental health care. By addressing challenges and promoting accessibility, society can create environments that encourage nature engagement for all. Whether through solo adventures, group activities, or guided experiences, individuals can find healing in the outdoors. Embracing nature therapy may not only improve personal mental health but also inspire collective well-being. As we reconnect with the environment, we foster a more profound connection with ourselves, paving the way for healthier lives that harmonize mind, body, and nature.