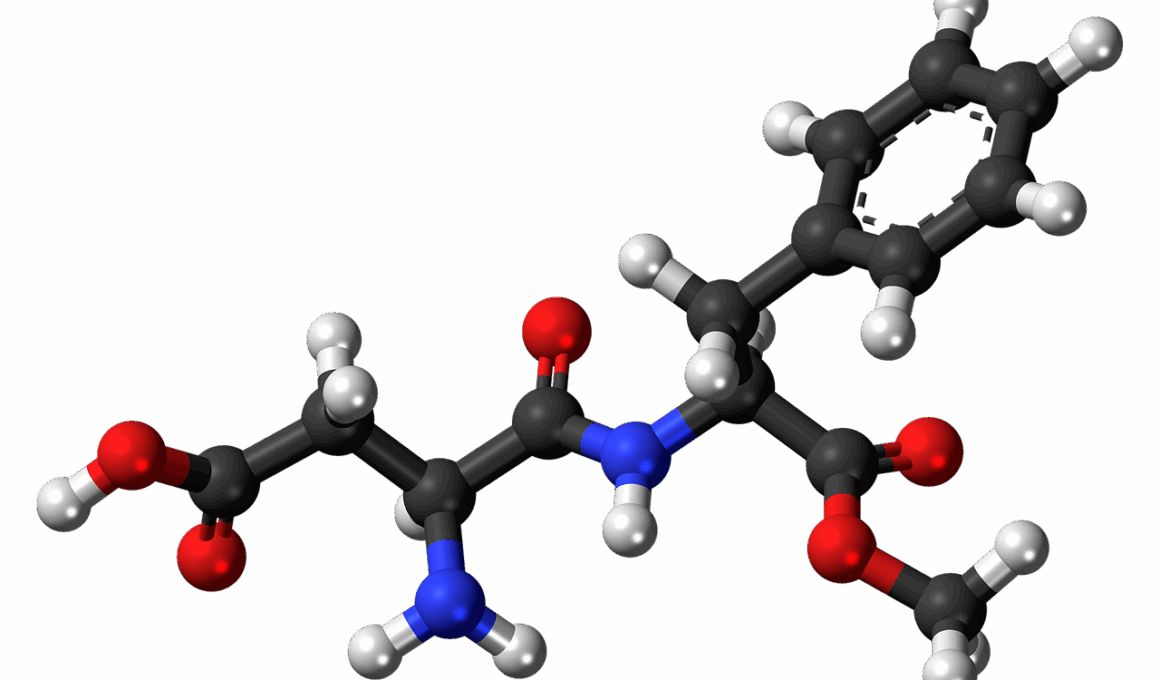
Can Artificial Sweeteners Cause Cancer? Investigating the Evidence
The debate surrounding artificial sweeteners and their safety has long persisted, with various claims suggesting they can pose health risks, including cancer. Among these, the notion that these sugar alternatives are pernicious has gained attention. The most commonly used artificial sweeteners include aspartame, saccharin, and sucralose. Understanding the origins of these myths is essential. Experts have raised alarms about potential consequences linked to cancer risks. However, it’s important to rely on scientific studies to draw logical conclusions. Regulatory authorities like the FDA and WHO have extensively reviewed artificial sweeteners. Their evaluations consistently conclude that these substances are safe for human consumption at recommended levels. Interestingly, the skepticism around these sweeteners often arises from misinformation and an undue focus on anecdotal evidence rather than solid research. Therefore, it’s essential to differentiate between fact and fiction. Advocating for a balanced diet is crucial, focusing on moderation and informed choices. Many people use artificial sweeteners as a means to reduce calories and sugar intake, especially for those managing weight. Ultimately, addressing misconceptions surrounding these products is vital for informed consumer choices.
Scientific Studies on Artificial Sweeteners
Numerous scientific studies have investigated the potential cancer risks associated with artificial sweeteners. One of the earliest major studies came from the National Toxicology Program in 2000, which examined aspartame’s long-term effects. Researchers found no conclusive evidence linking aspartame to cancer. They recommended continuing its use within established consumption limits. Another study published in the Journal of the American Medical Association also concluded that artificial sweeteners are generally safe for consumption. Conversely, some earlier studies raised concerns but were later criticized for methodological flaws. These flawed studies often relied on animal testing that lacked relevance for human consumption. Importantly, the International Agency for Research on Cancer evaluated many of these sweeteners and classified them as safe. Further flagging any alleged cancer risks may stem more from consumer misunderstanding than actual harm. By emphasizing fact-based education surrounding artificial sweeteners, healthier food choices can emerge. Encouraging stringent safety assessments for these products promotes public health awareness. A primary focus should remain on credible research, ensuring consumers make well-informed dietary choices that contribute positively to their overall well-being.
Understanding the specific types of artificial sweeteners can provide clarity. For instance, aspartame, a popular artificial sweetener, consists of phenylalanine, aspartic acid, and methanol. Each of these components occurs naturally in various foods. Conclusively, regulations establish acceptable daily intake levels to ensure safety for individuals consuming these products. The discernible traits of sucralose and saccharin also exhibit similar safety profiles. The consumption of these sweeteners has increased in recent years, especially as health-conscious consumers seek alternatives to sugar. However, this rise has also fueled myths proliferated through misrepresented information. Avoiding over-generalizations is essential for making balanced decisions surrounding sweeteners. Many foods claim to be “sugar-free” yet contain these ingredients. Therefore, consumers should be aware of these products and their effects on their overall diet. Research continually affirms that artificial sweeteners can serve as effective tools for managing weight and controlling diabetes. Additionally, understanding the broader context of these sweeteners within nutrition will be beneficial to consumers grappling with their dietary choices. Heightened awareness and advocacy for informed eating habits should go hand-in-hand with the growing prevalence of artificial sweeteners.
Personal Experience and Popular Myths
Anecdotal reports often fuel the myths surrounding artificial sweeteners. Many people have expressed concerns regarding potential side effects after consuming these products. It’s crucial to scrutinize these personal experiences critically. While individual reactions can vary, scientifically validated reports generally do not support the idea that artificial sweeteners cause cancer. Common myths have emerged, suggesting that consuming sweeteners leads to increased cravings for sugar; however, studies show mixed outcomes regarding their effects on appetite. Consumer reports sometimes erroneously link weight gain or health complications to these sweeteners. Reports are often misconstrued or based on limited data sets that don’t truly reflect overall trends. However, a major health organization’s stance remains that consuming these sweeteners in moderation offers benefits over sucrose. Awareness of how sweeteners influence behavior and energy levels can guide consumers in making healthier decisions. Staying informed about emerging research can empower individuals to navigate potential misconceptions calmly. Lastly, using artificial sweeteners as part of a balanced approach to nutrition is essential. Reliable sources of information can foster greater understanding and ultimately dispel damaging myths surrounding their safety.
Artificial sweeteners’ role extends beyond simply being sugar substitutes. These compounds can aid in reducing total caloric intake, which has significant implications for managing obesity rates. As dietary patterns shift toward healthier lifestyles, sweeteners provide accessible avenues for consumers. Studies categorize artificial sweeteners under high-intensity sweeteners, which are far sweeter than regular sugar, making them appealing for people watching their sugar consumption. Substituting sweeteners may help individuals maintain energy levels without falling prey to blood sugar spikes. Comprehensive evaluations by health professionals have led to increased acceptance of these substitutes in mainstream dietary practices. Such acceptance emphasizes moderation to achieve optimal benefits while minimizing risks. Consequently, it is pertinent for consumers to balance their needs and preferences while ensuring informed consumption. Public health education should aim to dispel myths surrounding sweeteners, focusing on facts derived from research and evidence. By doing so, stakeholders can positively influence consumer perceptions. Meanwhile, reaching out to registered dietitians for personal advice can enhance knowledge and understanding of nutritional choices. Overall, adopting realistic approaches toward artificial sweeteners will ultimately lead to informed lifestyles and healthier, more sustainable nutrition habits.
Final Thoughts: Debunking the Myths
In conclusion, addressing the myths about artificial sweeteners requires solid evidence and societal awareness. The ongoing dialogue surrounding their safety illustrates the importance of skepticism but also highlights the need for evidence-based discussions. Consumers need to look critically at claims made, especially those rooted in anecdotal accounts without scientific backing. Regulatory bodies like the FDA have established safety protocols, continually reviewing sweeteners to ensure they meet safety standards. Combined with ongoing research, consumers can feel more secure about the compilation of studies showing that daily consumption within established limits does not increase cancer risks. Familiarizing oneself with credible dietary recommendations can significantly mitigate fears stemming from negativity associated with these sweeteners. Enhanced education initiatives can play a crucial role in fortifying public health. As more people become aware of their safety, using sweeteners responsibly will help maintain healthy dietary choices. Ultimately, society should emphasize the ability to have informed discussions surrounding nutrition without perpetuating unfounded myths. Creating awareness about research will strengthen public trust regarding these substitutes. Adopting strategies for debunking misinformation surrounding artificial sweeteners fosters a healthier, informed society overall.
Moreover, considering an individual’s dietary preferences enriches the understanding of artificial sweeteners. Individuals should assess how these alternatives fit into their unique nutritional needs and health goals. Engaging with registered dietitians can offer personalized insights while ensuring individuals make informed decisions regarding various sweeteners. Furthermore, consumer experiences can meld with scientific findings, leading to thorough discussions about these products’ implementation within diets. Creatively incorporating low-calorie options leads to comprehensive dietary management strategies while simultaneously addressing health concerns. Significantly, compiling resources that outline both benefits and potential drawbacks can provide consumers with clear frameworks for their choices. Key populations, such as those with diabetes, can find that artificial sweeteners assist in managing their sugar levels effectively. Education and dialogue will only amplify as nutrition science progresses and adapts to consumer needs. Ultimately, individuals should prioritize personal preferences blended with scientific evidence. The closure towards familiarizing oneself with credible resources fosters understanding and helps dispel fear rooted in misunderstanding. Embracing a mindset of curiosity opens the door to leveraging artificial sweeteners for healthier living and vitalizes ongoing exploration within nutrition itself.
As research continues to evolve, it’s vital for both consumers and health professionals to stay informed about artificial sweeteners and their potential health implications. New studies emerge regularly, drawing fresh conclusions based on ever-evolving science. This reality implies that society must remain engaged with credible nutritional guidelines and public health recommendations. The challenge lies in recognizing and filtering out sensational headlines often driving fears about food products. Simultaneously, embracing scientific literacy will empower consumers with tools needed to differentiate between fact and fallacy. It is essential for advertisers and manufacturers to ensure transparency regarding the ingredients in their products. Building trust through clear communication can ultimately lead to greater acceptance of these sweeteners. Furthermore, communal dialogue about nutrition trends can pave the way for more knowledgeable consumption patterns. Recognizing the need for ongoing collaboration among stakeholders, consumers, and the scientific community will enhance public awareness. Engaging with research-based approaches may effectively reduce doubts about artificial sweeteners, allowing space for honest reflections on health. By concentrating on evidence, individuals can maintain balanced lifestyles and healthy food choices, aiming towards wellness and decreased health-related anxieties.