Fermented Foods: A Time-Tested Approach to Wellness and Diet
Fermented foods are an integral part of various culinary traditions around the world. They have been consumed for centuries, providing unique flavors and numerous health benefits. Fermentation is an ancient preservation technique that enhances the nutritional value of food. It employs the activity of microorganisms like bacteria, yeast, and molds, which convert sugars into acids and alcohol. These changes not only preserve the food but also improve digestibility and introduce probiotics. Probiotics are beneficial bacteria that promote gut health and overall wellness. Examples of fermented foods include yogurt, kimchi, sauerkraut, and miso. Each of these foods has distinctive properties and tastes, contributing uniquely to dietary diversity. The practice of fermentation allows for the transformation of simple ingredients into nutritious options, making it an excellent choice for those looking to enhance their meals. Incorporating fermented foods into your diet can lead to improved digestion and enhanced immune function. It is worth exploring various fermented options to appreciate their culinary and health benefits fully. Discover how traditional fermentation methods can positively impact modern diets and contribute to healthier lifestyles.
The Science Behind Fermentation
The process of fermentation involves biological processes that transform raw ingredients into something new and nourishing. Microorganisms, including yeast and bacteria, play a crucial role in this transformation. For example, in the case of yogurt, lactic acid bacteria ferment lactose, the sugar in milk, producing lactic acid that thickens the milk and gives yogurt its distinctive tang. Similarly, in alcoholic beverages, yeast converts sugars into alcohol and carbon dioxide. This dual action not only prevents spoilage but also enhances flavor and nutritional profiles. Fermentation also produces bioactive compounds that possess health-promoting properties. These compounds can help reduce inflammation, lower cholesterol levels, and strengthen the immune system. Different cultures have developed unique methods of fermentation over generations, adapting techniques to local ingredients. The diversity in fermentation practices reflects a rich culinary heritage. Each fermented product carries a unique blend of flavors, showcasing the creativity and resourcefulness of traditional cultures. Understanding the science behind these processes highlights the importance of fermented foods in our diets and their role in promoting health and longevity.
Traditional fermentation methods vary widely across cultures and regions, creating a rich tapestry of flavors and techniques. For instance, in Asia, fermentation commonly yields products such as kimchi and soy sauce, while European traditions include sauerkraut and pickles. These methods often rely on natural fermentation, where microorganisms from the environment initiate the process. In many cultures, communities have passed down recipes, ensuring that techniques remain consistent throughout generations. For instance, making miso involves fermenting soybeans with a specific mold for an extended period, resulting in a nutrient-dense product. The same goes for sourdough bread, where wild yeast naturally present in grains creates a uniquely tangy flavor. Each of these techniques not only preserves food but also adds depth to dishes served at the table. In some cases, foods are fermented in clay pots or wooden barrels, which can impart additional flavors unique to that region. Such methods allow for the preservation of seasonal ingredients, making the best of what is available. Exploring these traditional methods fosters a deeper appreciation for how diverse culinary practices enhance our diets.
Health Benefits of Fermented Foods
Incorporating fermented foods into your daily diet can yield numerous health benefits. These foods are rich in probiotics, which are beneficial bacteria that support optimal gut health. A balanced gut microbiome can improve digestion, enhance nutrient absorption, and even bolster immunity. Research indicates that a diverse gut flora correlates with better overall health and may reduce the risk of various diseases. Furthermore, fermented foods can alleviate digestive issues such as bloating and constipation. They promote the production of digestive enzymes, aiding in the breakdown of food. Additionally, fermented items often contain higher levels of certain vitamins, like B vitamins and vitamin K2, which are vital for overall health. Regularly consuming these foods may aid in mental health management, as emerging studies suggest a link between gut health and mental well-being. Furthermore, many fermented foods are lower in sugar and calories than processed counterparts, making them a healthier choice for those watching their weight. Introducing a diverse range of fermented foods into your diet is a simple yet effective way to enhance your health.
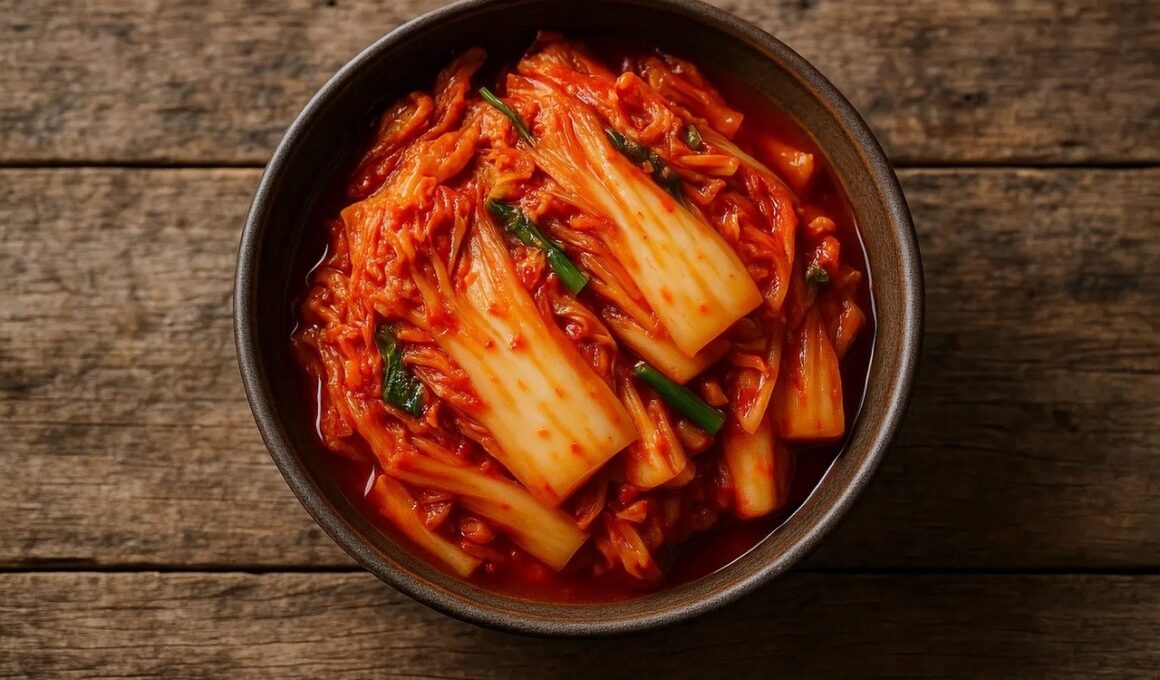
When integrating fermented foods into your diet, it’s essential to explore the various types available. Each offers unique health benefits and flavors. Common options include yogurt, known for its creamy texture, and vegan alternatives like coconut yogurt, which is lactose-free. Both provide an excellent source of probiotics. Sauerkraut, made from fermented cabbage, is rich in vitamins C and K and can enhance flavor in dishes. Similarly, kimchi, a spicy Korean dish, is packed with nutrients and offers a bold kick to meals. Miso is another versatile option, elevating soups and dressings while providing essential amino acids. Kombucha, a fermented beverage made from tea, offers a refreshing alternative and can serve as a naturally fizzy drink. These options can be easily found in grocery stores or prepared at home, providing flexibility in dietary choices. Exploring local markets may also reveal unique, region-specific fermented foods that enrich the culinary experience. As you integrate these flavors, experiment with pairing them in meals, enhancing both taste and health benefits seamlessly. There is a world of flavors and nourishment waiting to be discovered.
Preservation and Sustainability Through Fermentation
Fermentation is an incredibly effective method for food preservation. Historically, it allowed communities to store seasonal produce for use throughout the year. This way of preserving food not only minimized waste but also ensured that people had access to nutritious options during periods of scarcity. In today’s context, it’s a sustainable practice that aligns with the growing need to reduce food waste in our modern food systems. When fruits or vegetables begin to age, fermenting them can turn them into flavorful products like pickles or chutneys instead of throwing them away. These fermented items often last much longer than their fresh counterparts. For instance, sauerkraut can last several months if stored properly, making it a practical choice. Additionally, engaging in home fermentation can be an educational activity, encouraging individuals to become more connected to their food sources and the importance of reducing waste. This engaged mindset supports the broader goal of sustainability while also enhancing personal health. The benefits of fermentation extend well beyond flavor; they also touch upon environmental impact, encouraging conscious choices in our food consumption.
In recent years, the popularity of fermented foods has surged, with many chefs and home cooks embracing these practices. This revival emphasizes the appreciation of traditional food methods and the benefits they bring. Fermentation classes and workshops have emerged, allowing individuals to learn how to create their own delicious fermented staples at home. This trend signifies a shift toward valuing artisanal food preparation and reconnecting with culinary roots. As more people seek out homemade and probiotic-rich foods, restaurants and food brands have begun to incorporate fermentation into their menus and products. The rise of kombucha taprooms or dedicated kimchi manufacturers showcases the demand for quality ingredients and diverse offerings. Consumers are increasingly looking for foods that not only satisfy their taste buds but also contribute to their overall well-being. Additionally, food labels now often highlight probiotic contents, appealing to the health-conscious buyer. This renewed interest in fermentation invites everyone to appreciate the artistry of food preservation, driving individuals to embrace these timeless techniques as part of a balanced and healthy lifestyle.
Conclusion: Embracing Fermented Foods
As awareness of the health benefits of fermented foods continues to grow, integrating them into our diets offers an effective means of improving overall well-being. These foods not only enrich our diets but also provide us with valuable probiotics, essential for maintaining a healthy gut. The flavors they introduce make meals exciting and new, enhancing our culinary journey. Embracing traditional fermentation methods can deepen our understanding of food ecology while promoting sustainable practices. Whether you enjoy yogurt, sauerkraut, or kombucha, each fermented food has a unique character that adds depth to our meals. Recognizing the critical role fermentation plays in food preservation and preparation encourages us to appreciate the artistry involved in these processes. Exploring and learning about the craft of fermentation allows us to connect with cultural traditions around the world. In a society increasingly focused on dietary health, incorporating fermented foods represents a delicious and practical way to nourish and sustain ourselves purposefully. So dive into the world of fermentation, experiment with different ingredients, and enjoy the myriad benefits and flavors that await you.