Incorporating Whole Grains for a Stronger Gut Microbiome
The gut microbiome plays a crucial role in our overall health, influencing digestion, immunity, and even mood. One of the most effective ways to support this complex ecosystem is through diet, particularly by integrating whole grains into our meals. Whole grains are rich in dietary fiber, which serves as food for beneficial gut bacteria. Foods like brown rice, quinoa, barley, and oats are excellent sources. These grains help promote the growth of healthy microbes, which contribute to a balanced gut environment. When the gut microbiome is thriving, it can help reduce inflammation and improve gut health. According to research, consuming a diet rich in whole grains has been linked to a lower risk of various diseases. While refined grains lack essential nutrients and fiber, whole grains maintain their natural nutritional profile, making them a superior choice. To reap the most benefits for your gut, aim to choose whole grains over processed options. Additionally, introducing a variety of grains can help diversify the microbiome further enhancing its resilience and function. Therefore, consider adding more whole grains to your diet today!
Whole grains can be easily incorporated into everyday meals, making them a practical choice. Start by swapping white pasta and bread for whole grain versions, such as whole wheat pasta or sprouted bread. These simple changes can significantly boost your fiber intake. Another delicious way to include whole grains is to enjoy a warm bowl of oatmeal topped with fruits and nuts for breakfast. Quinoa can be used as a base for salads, providing a nutritious foundation. When preparing soups and stews, consider using barley for added texture and nutrition. Not only do whole grains enhance the flavor of meals, but they also provide essential vitamins and minerals. They are an excellent source of B vitamins, iron, magnesium, and antioxidants, all of which contribute to better health. Moreover, whole grains can aid in weight management, as their fiber content helps keep you feeling full longer. Ultimately, by making these straightforward adjustments, you can significantly impact your gut health. Remember, the key to a healthy gut microbiome is not just the quantity but the variety of whole grains consumed throughout the week.
The Benefits of Whole Grains
Incorporating whole grains like oats, brown rice, and whole wheat into your diet can yield numerous benefits for colon health. Firstly, these grains are rich in fiber, which is essential for healthy digestion and regular bowel movements. Improved digestion helps prevent constipation, hemorrhoids, and even some colorectal diseases. Due to the high fiber content, whole grains also promote satiety, which can assist with weight management. The gradual release of energy from whole grains can help maintain energy levels throughout the day. Moreover, fiber works in the gut to balance microorganisms, promoting the growth of beneficial bacteria while inhibiting harmful ones. Research has shown that whole grains are associated with a lower risk of diseases like type 2 diabetes and cardiovascular health issues. This suggests that consuming these foods can enhance overall physiological health beyond just digestion. In addition to their numerous health benefits, whole grains can be delicious. Experimentation in the kitchen with different types of grains can lead to exciting and healthy culinary creations.
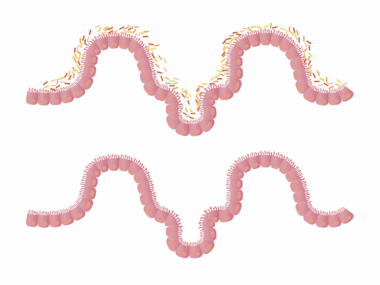
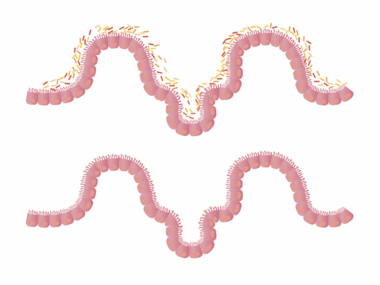
Understanding the role of fiber in gut health is crucial when discussing whole grains. Fiber can be classified into two categories: soluble and insoluble. Soluble fiber dissolves in water and forms a gel-like substance in the gut, helping regulate blood sugar levels and cholesterol. Foods rich in soluble fiber include oats, barley, and legumes. On the other hand, insoluble fiber adds bulk to the stool and aids in movement through the digestive tract, preventing constipation. Whole grains provide both types of fiber, making them highly beneficial for gut health. A study published in the journal ‘Gut’ emphasized the importance of fiber-rich diets, connecting them to improved gut microbiome diversity. A diverse gut microbiome is essential, as it supports numerous bodily functions, from digestion to immune response. Therefore, including a variety of whole grains in your diet not only ensures an ample supply of fiber but also promotes a healthy, dynamic microbiome. With many innovative ways to incorporate these grains into daily meals, it’s easier than ever to boost fiber intake and improve gut health.
Creative Ways to Include Whole Grains
Including whole grains in your diet doesn’t have to be monotonous; there are plenty of ingenious and tasty options. For breakfast, try overnight oats prepared with Greek yogurt, chia seeds, and fresh fruits. This not only packs a fiber punch but offers a mix of protein and nutrients as well. For lunch, consider a quinoa salad loaded with mixed vegetables and protein like grilled chicken or chickpeas. Introduce barley in soups to enhance texture and nutrition. For snacks, popcorn made from whole grains serves as a light, crunchy treat, while whole grain wraps filled with lean proteins and vegetables can provide a fulfilling meal. Experimenting with healthy grain-based alternatives, such as rice paper rolls using brown rice or whole grain tortillas for wraps, can also diversify your diet. Additionally, you can prepare whole grain rice pudding for a delightful dessert. Whole grains can enhance meals’ taste and nutritional value while ensuring you enjoy every bite. These innovative ideas will support your gut health and make your eating experience more satisfying!
Some health guidelines recommend that at least half your grain intake comes from whole grains. This can be achieved by gradually incorporating more whole grain options into your diet and can significantly impact gut health. When transitioning to whole grains, start slowly, introducing one new grain at a time. This will allow your digestive system to adjust to the increased fiber intake. Drink plenty of water as you increase fiber—this helps mitigate any minor digestive discomfort that may arise. It’s critical to be mindful of portion sizes as well. Whole grains are nutrient-dense, and while they offer various health benefits, moderation is key to overall dietary balance. Additionally, consult with a healthcare professional for personalized dietary advice, especially if you have preexisting digestive issues or conditions. Making dietary changes is often like a puzzle; the right pieces need to fit together for the best results. Remember, the goal is to create a healthy, varied, and enjoyable meal plan that nourishes the body and enhances gut health over time.
Monitoring Your Progress
Tracking your dietary habits can be beneficial in understanding the impact whole grains have on your gut microbiome. Journaling meals can help identify what works best for your body and which grains you enjoy the most. Over time, noting improvements in digestion, energy levels, and overall feelings of well-being can illustrate the positive effects of a whole-grain-rich diet. Some people may feel changes quickly, while for others, it can take longer to experience the benefits. It is crucial to remain patient and consistent with your dietary choices, as shifts in your gut microbiome can take weeks or even months. Regular check-ins with healthcare providers can provide additional insights and refinement of dietary choices. In addition, consider periodically diversifying the types of whole grains consumed. This can help maintain a balanced microbiome and keep meals exciting and enjoyable. Taking the time to evaluate how different grains influence your body can empower you to make informed choices regarding your health. Remember, the journey to better gut health is personal and varies among individuals!
In summary, integrating whole grains into your daily diet is a positively impactful way to support gut health. Not only do these grains provide essential nutrients and fiber, but they also encourage the growth of beneficial gut bacteria. This leads to improved digestion, reduced inflammation, and a lower risk of chronic diseases. The versatility of whole grains allows for creative cooking and experimentation, making meal preparation enjoyable. Whether it’s a satisfying bowl of oatmeal, a wholesome quinoa salad, or hearty barley soup, each dish can contribute to a healthier gut. Remember, gradual changes make for the best results; hence slowly incorporating different types of whole grains into your meal plan is advisable. By focusing on this aspect of your diet, you foster a thriving gut microbiome. As more research highlights the connection between diet and gut health, the benefits of including whole grains in your meals become increasingly clear. So, take the leap and enrich your meals with whole grains—your gut will thank you for it!