Gut Health and Immunity: Myths and Facts
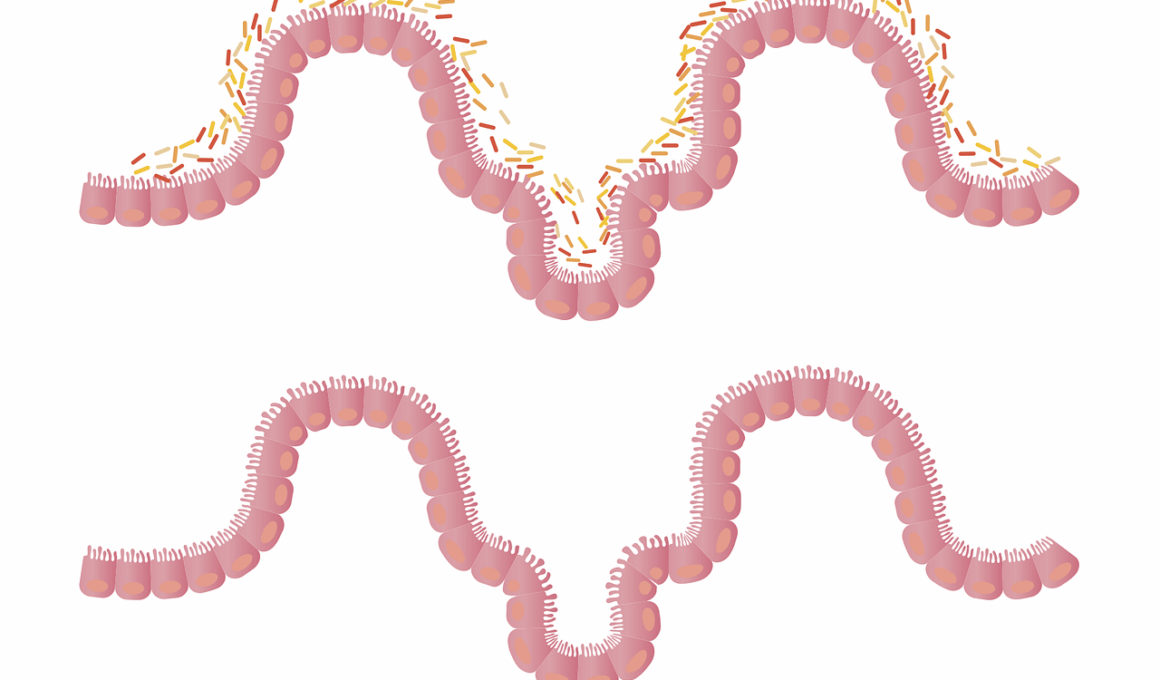
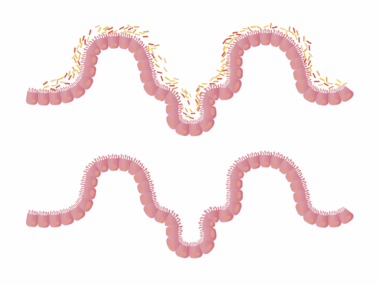
Understanding the relationship between gut health and immunity is crucial for overall wellness. The gut houses trillions of microorganisms, including bacteria, viruses, and fungi, known collectively as the microbiome. This complex ecosystem facilitates digestion, provides essential nutrients, and plays a pivotal role in influencing immune responses. Recent studies have indicated that a balanced microbiome can enhance the body’s ability to fend off infections and may even reduce the risk of autoimmune diseases. Conversely, an imbalanced gut can lead to inflammation and a weakened immune system. Thus, nurturing gut health through a well-balanced diet, rich in fiber and probiotics, is essential for maintaining an optimal immune response. Foods like yogurt, sauerkraut, and fiber-rich fruits and vegetables can promote the growth of beneficial bacteria. It is also important to consider hydration, sleep, and stress management as additional factors that significantly impact gut health. In the subsequent sections, we will explore some common misconceptions about gut health and immunity, providing scientific insights and practical tips to optimize your gut and immune systems.
Myth #1: Probiotics Solve All Gut Problems
A pervasive myth surrounding gut health is that probiotics can instantly resolve any digestive issue or immune deficiency. While probiotics are beneficial, their efficacy greatly depends on the specific strains used, the individual’s health status, and the balance of microorganisms present in the gut. Not all probiotics are the same; some are tailored for specific conditions, like diarrhea or irritable bowel syndrome, while others aim to support general gut flora. Moreover, the effects of probiotics can take time to manifest, and one should not rely solely on them without lifestyle and dietary adjustments. In fact, a diet high in processed foods and sugars can inhibit probiotic effectiveness. To reap the benefits of probiotics, it’s essential to consume a diverse range of foods that support gut health, such as prebiotics. These are dietary fibers that feed beneficial bacteria. Incorporating garlic, onions, and bananas into your meals can foster a thriving gut microbiome, alongside any probiotic supplementation. Ensure to consult a healthcare provider prior to commencing any new supplements.
Myth #2: All Gut Bacteria Are Bad
A common misunderstanding is that all bacteria in the gut are harmful, leading to an exaggerated fear of microorganisms. In reality, the majority of gut bacteria are beneficial and play a crucial role in digestion, metabolism, and immune function. Beneficial bacteria help to break down dietary fibers, produce essential vitamins, and prevent harmful pathogens from settling in the gut. This healthy balance fosters a resilient immune response, allowing the body to defend against infections. Disruptions in this microbiome can lead to conditions such as dysbiosis, which can result from poor diet, antibiotics, or stress. Maintaining a diverse diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and fermented foods promotes the growth of beneficial bacteria. It is particularly important to avoid excessive antibiotics, which can wipe out both harmful and helpful bacteria indiscriminately. Instead of demonizing all bacteria, understanding that a balanced microbial population is essential for gut health and a robust immune system is key. Embracing a lifestyle that encourages good bacteria is essential for long-term health and vitality.
The Role of Diet in Gut Health
Diet significantly impacts gut health and, consequently, your immune system’s effectiveness. A well-rounded diet that includes various food groups provides the necessary nutrients and fibers to nourish beneficial gut bacteria. Foods high in fiber, such as whole grains, nuts, seeds, and legumes, help maintain a healthy gut microbiome. Fermented foods like kimchi, yogurt, and kefir introduce live beneficial bacteria that can enhance gut diversity. Additionally, antioxidants found in fruits and vegetables help reduce inflammation in the gut. Reducing the intake of processed sugars and artificial additives is equally important. These can negatively affect gut flora and lead to imbalances. Furthermore, consuming adequate hydration supports gut motility and function, while moderate caffeine intake can be beneficial for gut health. To optimize gut health, incorporating various colors of fruits and vegetables can also be advantageous; colorful produce often contains different phytonutrients that can support gut health. Adopting mindful eating habits, such as taking time to chew food thoroughly, can improve digestion. Making informed dietary choices will promote a balanced microbiome, enhancing both gut and immune health.
Myth #3: Gut Health is Irrelevant to Overall Health
Another misconception is that gut health doesn’t influence overall health, particularly the immune system. Research has shown a strong interconnectedness between the gut and other body systems, including the brain and immune system. The gut produces various signaling molecules that can directly affect immune responses. For example, gut bacteria can influence the production of antibodies and cytokines, which are crucial for regulating immune reactions. Moreover, the gut lining acts as a barrier to pathogens; thus, any compromise in gut health can lead to increased susceptibility to infections and illnesses. Chronic gut issues, such as inflammation or leaky gut syndrome, can allow toxins and pathogens to enter the bloodstream, sparking systemic inflammation. This connection extends beyond mere digestion; a healthy gut also contributes to mental well-being through the gut-brain axis. Therefore, maintaining gut health through diet, regular exercise, and stress management is essential for overall health. Prioritizing foods that support both gut health and immune function can yield significant benefits for general well-being, showing that every system in the body is interwoven.
Practical Tips for Enhancing Gut Health
To foster a healthy gut and support immunity, consider implementing several practical tips into your daily routine. First, focus on a balanced diet rich in a variety of foods that promote microbial diversity. Incorporate plenty of fruits and vegetables, whole grains, and lean protein sources to ensure a range of nutrients. Emphasize the inclusion of probiotics and prebiotics, as these work synergistically to support healthy gut bacteria. Next, limit processed and sugary foods, which can disrupt the gut microbiome. Regular physical activity is equally beneficial; exercise can enhance gut motility and promote bacterial diversity. Aim for at least 30 minutes of moderate physical activity most days. Additionally, manage stress through mindfulness practices such as yoga or meditation, which can positively impact gut health. Always ensure you drink plenty of water to stay hydrated, as this plays a vital role in digestion. Lastly, prioritize quality sleep; insufficient sleep can contribute to dysbiosis and immune system dysfunction. By adopting these strategies, you can cultivate a healthier gut, inevitably boosting your immune function and promoting overall well-being.
Conclusion: Nurturing Gut Health
Nurturing gut health is a cornerstone in promoting a strong immune system and overall well-being. Understanding the myths associated with gut health can empower individuals to make informed choices for better health. By acknowledging the importance of beneficial bacteria and their roles in our body, we can appreciate the necessity of a balanced diet and lifestyle. Focus on incorporating whole, natural foods, and stay hydrated to support the microbiome. Avoid misconceptions that can lead to fear or unhealthy practices regarding gut health. The knowledge that gut health is intricately linked with immunity encourages a proactive approach toward wellness. Additionally, developing a comprehensive understanding fosters an awareness of how lifestyle choices, such as diet, exercise, and stress management, impact gut health. Overall, a harmonious gut leads to a healthier body and mind, promoting resilience against diseases. As you embark on your journey to better gut health, remember that small, consistent changes can lead to significant long-term benefits. Embrace the potential of the gut-immune connection to achieve optimal health and wellness in your life.