Using an Elimination Diet to Identify Food Allergies vs Intolerances
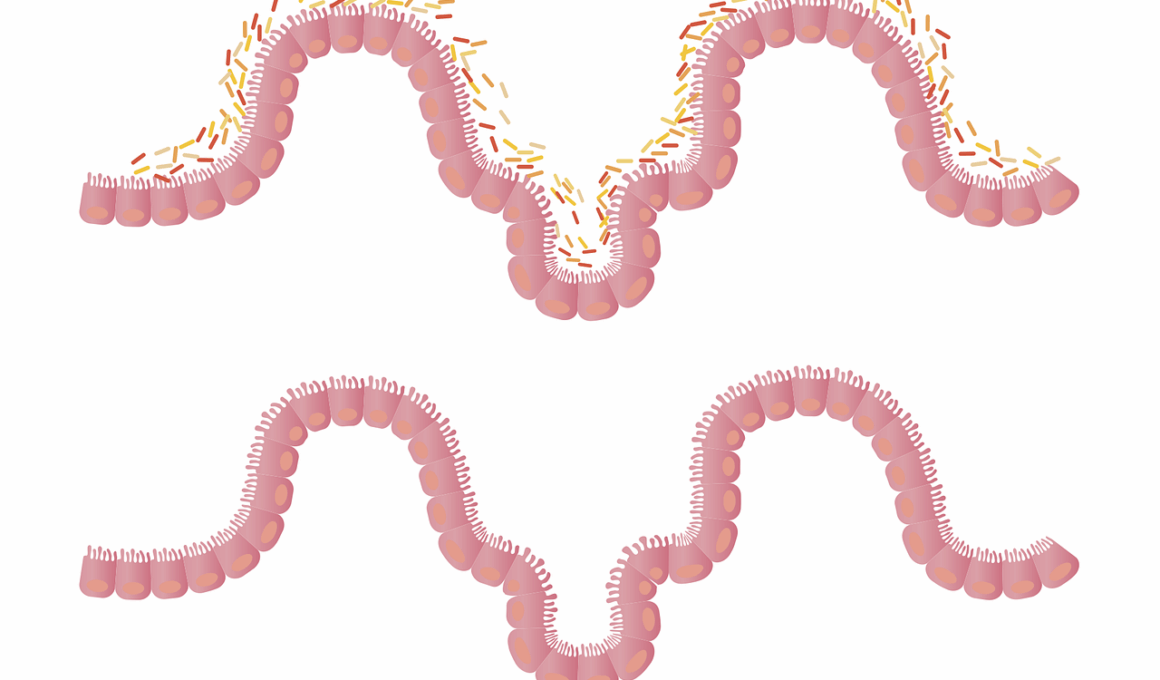
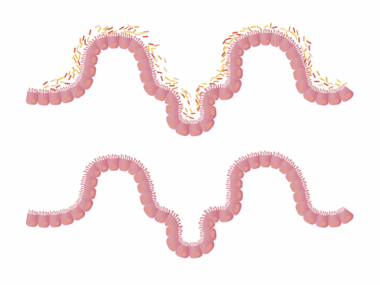
Understanding the difference between food allergies and intolerances is crucial for effective gut health management. An elimination diet can be an invaluable tool in this process. This diet involves removing certain foods from your daily intake temporarily, followed by a gradual reintroduction of those foods. By carefully monitoring your body’s reactions, one can identify specific foods that trigger allergy-like symptoms. Food allergies, typically immune system responses, can cause severe symptoms, including anaphylaxis. Conversely, food intolerances usually result in digestive issues, such as bloating and gas, often due to enzyme deficiencies. Adopting an elimination diet may help uncover underlying issues without the need for invasive tests. This systematic approach allows individuals to pinpoint problem foods, fostering better dietary choices and enhancing overall wellness. Consulting a healthcare professional is advisable to ensure that the diet is balanced and safe. Keeping a detailed food diary can also help in tracking meals, symptoms, and feelings. This method not only informs dietary adjustments but also promotes a thoughtful approach to food consumption.
How the Elimination Diet Works
The elimination diet consists of two main phases: elimination and reintroduction. During the elimination phase, participants remove identified potential trigger foods from their diets. Common offenders include dairy, gluten, nuts, and eggs. This phase generally lasts between two to six weeks, allowing the body ample time to detoxify. The goal is to observe any significant changes in health or symptoms, such as improved digestion and reduced inflammation. After the elimination period, foods are gradually reintroduced one at a time, ideally spaced several days apart. This careful reintroduction helps discern the effects of each food on the body. If symptoms reappear, one can identify that food as a trigger. It’s essential to remain observant and record any changes meticulously. This aspect of the elimination diet has significant implications for understanding personal tolerances. Individuals may find that they can tolerate small amounts of certain foods, allowing for more flexibility in their diets. In contrast, others might discover they need complete avoidance of specific items to maintain optimal gut health. Throughout this process, self-advocacy and education are paramount.
Maintaining a balanced and nutritious diet during the elimination phase is vital. Several foods remain accessible while avoiding common allergens and intolerances. These may include a wide variety of fruits, vegetables, lean meats, and gluten-free grains. Substituting staple ingredients with alternatives allows for continued culinary enjoyment while adhering to diet restrictions. For instance, almond milk can replace dairy milk, and quinoa or rice can substitute for wheat products. This flexibility can help mitigate feelings of deprivation, promoting better adherence to the diet over the weeks. Additionally, educating oneself on food labels and ingredient lists is part of the process. This awareness helps identify hidden allergens in processed foods, improving overall diet quality. It’s also beneficial to experiment with new recipes that utilize safe ingredients, fostering creativity in the kitchen. Online resources and cookbooks focusing on elimination diets can enhance this aspect, making it easier and more enjoyable. Moreover, connecting with support groups or forums can provide encouragement and share personal experiences with others on similar journeys. This shared knowledge enhances the learning experience and can make the transition smoother in developing healthier eating habits.
Identifying Symptoms and Triggers
Identifying specific symptoms and food triggers can be quite intricate. While food allergies often provoke immediate reactions, food intolerances may lead to a delayed response, appearing hours or even days after consumption. Common allergy symptoms can range from hives, swelling, or difficulty breathing to more severe reactions. In contrast, intolerances tend to manifest with digestive issues, including cramping, diarrhea, or nausea, complicating the differentiation between the two. This variability necessitates a careful documentation approach during the elimination diet process. Keeping a comprehensive journal of daily food intake and corresponding symptoms enables clearer insights into possible triggers. This detailed mapping can help establish connections that may otherwise remain unnoticed. The elimination diet empowers participants to reclaim control over their health, ultimately leading to informed dietary choices. Discussing observations with a healthcare professional may also provide additional clarity and direction for the next steps. This collaborative approach ensures accountability throughout the process, fostering a supportive environment conducive to making effective changes. Building an understanding of one’s body response to different foods empowers individuals to make proactive decisions to maintain gut health.
Reassessing dietary habits post-elimination diet is essential for long-term gut health. Once identified food allergens or intolerances are recognized, adopting a proactive approach to meal planning becomes critical. This includes avoiding problematic foods while incorporating a wide array of nutrients for balance. Exploring alternative cuisines or focus on whole, minimally processed foods can enhance dietary enjoyment without sacrificing health. Learning to read food labels attentively becomes second nature, enabling informed decisions when grocery shopping. Furthermore, gradual experimentation with reintroducing previously removed items can be beneficial. This experimentation allows for flexibility in one’s diet when the understanding of tolerances is firmly established. It’s noteworthy that some individuals may revisit certain foods with care after a period of avoidance, discovering they can now manage small portions. This newfound awareness empowers individuals to navigate social settings and avoid food challenges effectively. Additionally, focusing on gut-supportive practices, such as probiotics and a fiber-rich diet, enhances overall digestive health. These elements work synergistically with the elimination diet’s insights. Maintaining a proactive mindset contributes to sustained health benefits, reinforcing the importance of individualized dietary strategies for optimal gut wellness.
Consulting Professionals for Guidance
While an elimination diet can be highly effective, it’s important to seek professional guidance throughout the process. Registered dietitians or nutritionists can provide valuable insight into balanced meal planning, ensuring nutritional adequacy during restrictions. These experts can tailor recommendations that align with personal preferences, dietary restrictions, and health goals. They can also help interpret symptoms accurately, differentiating between allergies and intolerances. Understanding the science behind food reactions allows clients to approach their health holistically. Involving healthcare professionals ensures safety, especially for individuals with severe allergies. This collaborative approach helps individuals feel supported and informed during challenging changes. Moreover, health professionals can assist if significant issues arise, potentially requiring further medical evaluation or allergy testing. This step is crucial for those experiencing unusually severe symptoms. Having a supportive team encourages accountability and motivates adherence to the elimination diet. Furthermore, they may recommend additional strategies to support digestion, such as digestive enzymes or gut-friendly supplements. The knowledge and personalized support from a healthcare professional immensely contribute to the effectiveness of the elimination diet, enhancing its overall impact on gut health and wellbeing.
Finally, recognizing the importance of mental health throughout the elimination diet journey can greatly aid success. Altering eating habits can provoke anxiety and emotional distress, especially during social outings. Having a solid support network is critical. Engaging with family and friends about dietary needs may foster understanding and create a more accommodating environment. Additionally, mindfulness practices can be useful for managing stress when navigating food-related situations. Practicing mindfulness encourages a more reflective approach to food enjoyment while remaining conscious of individual health goals. Additionally, exploring reputable online forums or communities can offer encouragement as shared experiences elevate motivation. Individuals should remember that personal health journeys may vary significantly, and patience is key. The elimination diet requires time and is an ongoing process of discovery. Celebrating small victories along the way can boost morale and inspire commitment. Armed with newfound knowledge about food sensitivities, individuals can enjoy their diets while minimizing negative impacts on gut health. Ultimately, the elimination diet presents an opportunity for personal empowerment, leading to improved digestion, enhanced energy, and greater overall wellness.