How Exercise Enhances Gut Microbiome Diversity and Function
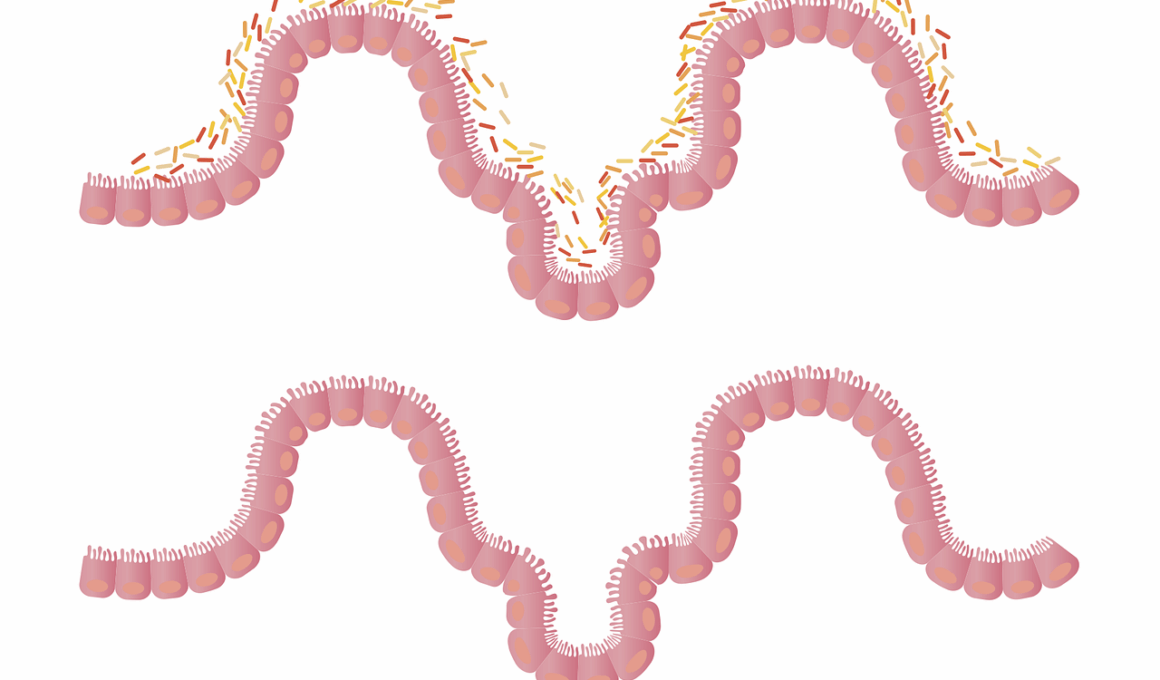
The gut microbiome plays a crucial role in our overall health, influencing everything from digestion to immune function. Emerging research shows that exercise can significantly enhance gut microbiome diversity and function, which is essential for optimal health. A diverse microbiome consists of various beneficial bacteria that help in maintaining metabolic homeostasis. These bacteria help break down food, synthesize vitamins, and protect against harmful pathogens, making gut health paramount. Regular physical activity not only stimulates gut motility but also promotes alterations in the gut environment. Active individuals generally have higher concentrations of short-chain fatty acids (SCFAs), which are produced by fiber fermentation. SCFAs have anti-inflammatory properties that positively impact gut health. Moreover, exercise contributes to a more robust immune response, thereby creating a conducive environment for the growth of beneficial bacteria. The enhanced gut lining helps in nutrient absorption, ultimately leading to better overall health outcomes. By increasing microbial diversity, exercise acts as both a preventive and therapeutic measure against various diseases, highlighting its importance in maintaining a healthy gut microbiome. Establishing a link between physical activity and gut health opens new avenues for improving wellness through lifestyle choices.
The importance of a healthy gut microbiome extends beyond digestion. It influences mental health, metabolism, and even immunity. A diverse gut microbiome can lead to improved psychological well-being, showing a direct correlation between gut health and mood. Research indicates that specific bacterial species can produce neurotransmitters, affecting our mental states. Furthermore, microbial imbalances have been linked to conditions like obesity, diabetes, and metabolic syndrome. Regular exercise positively impacts these microbial populations, promoting the growth of beneficial bacteria while suppressing harmful ones. It has been observed that individuals who engage in consistent physical activity possess greater microbial diversity and richness. This diversity is beneficial, as it contributes to the resilience of the gut microbiome against disturbances, such as antibiotic treatments. Incorporating aerobic exercise, strength training, and even yoga can promote the growth of good bacteria. Interestingly, even moderate exercise is linked to positive changes in microbiome composition. Notably, these changes can occur within weeks, suggesting that creating an exercise routine could have immediate benefits for gut health. Embracing a physically active lifestyle appears to be a natural and effective strategy to enhance gut microbiome functionality.
Exercise Types and Their Impact
Different types of exercise can exert varying effects on gut health. Aerobic exercises, such as running, cycling, and swimming, have shown the most significant impact on increasing microbial diversity. High-intensity interval training (HIIT) is also effective, as it combines both aerobic and anaerobic benefits. Resistance training, though often overlooked, also contributes positively to gut microbiome health. It doesn’t just build muscle but can influence the gut environment by altering biochemical signals that promote a favorable microbiome. Engaging in consistent physical activity fosters the growth of key bacterial taxa associated with health benefits. Moreover, incorporating exercises that engage the core, like Pilates, can enhance gut motility as well. Activities that encourage more movement throughout the day, such as walking or group sports, provide key benefits for gut health. It’s essential to choose activities that one enjoys, as this leads to long-term adherence and better outcomes. Combining varied forms of exercise can further enrich the gut microbiome and improve overall health. It’s important to understand that finding an enjoyable active routine is foundational to reaping these microbiome benefits effectively.
Diet and exercise go hand in hand when it comes to enhancing gut microbiome health. Consuming a balanced diet rich in fiber complements the effects of regular exercise. Fermentable fibers serve as food for beneficial gut bacteria, stimulating their growth while supporting gut diversity. Including a variety of plant-based foods ensures a broader range of dietary fibers, allowing different bacterial species to thrive. Nutritionists recommend focusing on whole foods, such as fruits, vegetables, legumes, and whole grains. This fiber-rich diet can lead to better metabolic health, especially when paired with an active lifestyle. Additionally, fermented foods such as yogurt, kefir, and sauerkraut contribute beneficial bacteria that can boost the diversity of the gut microbiome. Therefore, integrating these foods with regular physical activity creates a synergistic effect. This combination not only enhances gut microbiome diversity but also maximizes health benefits, including better digestion and increased nutrient absorption. Furthermore, being mindful of sugar intake is essential, as excessive consumption can promote the growth of harmful bacteria. In essence, a coordinated approach focusing on both diet and exercise creates the optimal environment for a healthy gut microbiome.
Exercise, Stress Reduction, and Gut Health
Stress is known to adversely affect gut health, leading to conditions such as irritable bowel syndrome and dysbiosis. Exercise serves as a natural stress-relief mechanism that helps mitigate these negative effects on the gut microbiome. Engaging in physical activity can lower cortisol levels, the stress hormone, thereby positively affecting gut bacterial populations. Moderate exercise has been shown to enhance the production of endorphins, the body’s natural mood lifters. This mechanism not only improves mental well-being but also benefits gut health indirectly. Additionally, practices like yoga and tai chi not only involve physical movement but also promote mindfulness, further reducing stress. These forms of exercise encourage better breathing patterns and relaxation, supporting the gut-brain axis. Such activities have been proven to influence microbial diversity positively, proving that mental states intertwine with physical health. Creating a holistic approach by combining exercise with stress management techniques can transform gut health significantly. This is critical for individuals dealing with chronic stressors who may experience gut-related issues. Implementing exercise as a way to enhance mental health thus reciprocates positive effects on gut microbiome health, reinforcing its importance in overall wellness.
Regular monitoring of one’s gut health is essential for understanding the impact of exercise on the microbiome. Recent advancements allow individuals to analyze their microbiome using at-home testing kits, providing insights into their gut composition. This proactive approach can help individuals make informed lifestyle adjustments in response to their unique gut microbiome profiles. Tracking dietary habits, physical activity levels, and stress can illuminate patterns, highlighting the importance of alignment among these factors. Using this data strategically, one can alter their routines to better facilitate a healthy gut microbiome. Furthermore, individuals should be mindful of any personal health conditions, such as gastrointestinal disorders, that may require tailored approaches. Consulting healthcare professionals when interpreting microbiome results can ensure appropriate actions and necessary dietary or exercise modifications. The goal is to create a balanced, personalized strategy to enrich gut microbiome diversity effectively. Regularly updating one’s routine based on feedback from microbiome tests can provide measurable benefits over time. Ultimately, the integration of exercise and dietary practices, alongside regular monitoring, can foster a thriving gut microbiome and promote a healthier lifestyle.
Conclusion
Ultimately, the intricate relationship between exercise and gut microbiome health underscores the significance of maintaining an active lifestyle for holistic health. Regular physical activity fosters greater microbial diversity and positively impacts gut function, equipping individuals to combat various health disorders. Importantly, integrating consistent exercise routines with mindful dietary choices synergistically enhances gut microbiome health. It’s essential to explore different exercise modalities to find enjoyable activities that encourage consistency. The incorporation of a variety of beneficial foods alongside exercise can yield a profound impact on gut health. By addressing stress through physical movement, individuals can create a more favorable microbiome environment. With ongoing research shedding light on the importance of the gut microbiome, individuals are encouraged to prioritize their gut health. Engaging in a community of support and resources can further augment efforts. By focusing on this balance of physical activity, nutrition, and stress management, we can build a more resilient and diverse gut microbiome. As the understanding of the gut microbiome evolves, remaining proactive about one’s health will ensure engagements with this dynamic area of body resilience tremendously improve overall well-being.
In conclusion, fostering a balanced gut microbiome through exercise is a powerful way to enhance overall wellness. Discovering personal motivations for staying active, enriching dietary choices, and monitoring progress effectively ensures vital benefits for gut health. Implementing these strategies leads to long-lasting positive impacts on health. This dedication to well-being is a significant step towards a healthier lifestyle. Optimizing gut microbiome diversity is paramount for long-term health maintenance. Always approach changes with a holistic view, considering exercise, diet, and mental well-being. Celebrating small victories in your journey towards a healthier gut is also essential, as it reinforces a consistent, active lifestyle.