The Importance of Diversity in Your Gut Microbiome
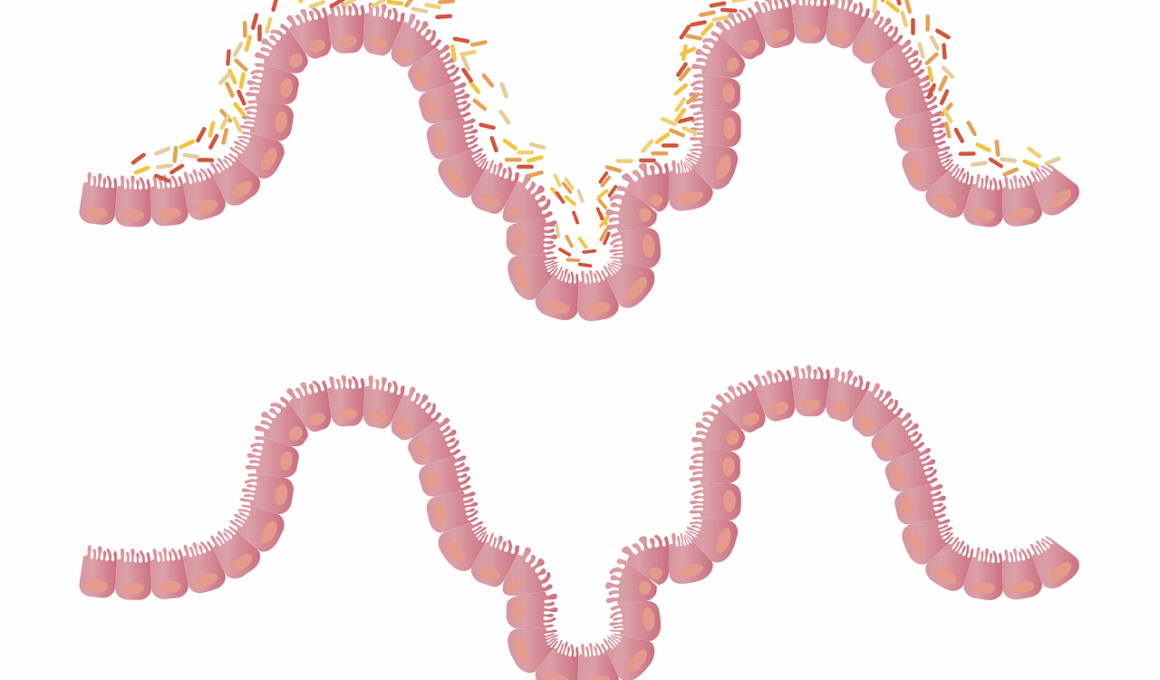
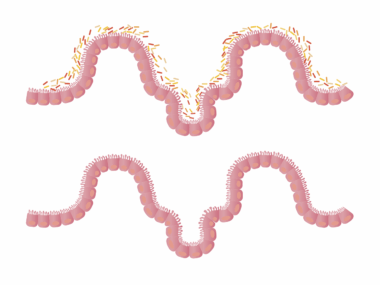
The gut microbiome consists of various microbes essential for our health. This diverse community includes bacteria, viruses, fungi, and protozoa. Each of these microorganisms plays a vital role in digestion, immune function, and even mental health. A healthy gut microbiome is rich in diverse species, which can lead to a balanced ecosystem in your gut. This balance allows for efficient nutrient absorption and protects against pathogens. Furthermore, maintaining diversity promotes the production of essential metabolites such as short-chain fatty acids. These metabolites are key to sustaining gut health and reducing inflammation. However, modern diets often lack diversity due to processed foods and antibiotic use. This can lead to a decrease in microbial diversity. A reduced diversity is associated with various health issues, including obesity, diabetes, and autoimmune disorders. Thus, prioritizing a varied diet can enhance gut microbiome health. Incorporating fermented foods, prebiotics, and diverse fruits and vegetables can help cultivate a robust microbiome. For specific recommendations, consulting a healthcare professional can provide personalized dietary guidance.
Diverse diets promote the growth of beneficial bacteria, which contribute to overall gut health. When you consume a variety of plant-based foods, it supports a wide range of microbes. These microbes perform countless functions, including breaking down dietary fibers and producing important vitamins. In contrast, a monotonous diet fosters survival of only a few species, potentially leading to dysbiosis. Dysbiosis refers to an imbalance of gut bacteria that may cause digestive issues. To ensure microbial diversity, focus on incorporating foods from various food groups. For instance, eat different colored fruits and vegetables, as these often contain unique phytonutrients. Additionally, try to include legumes, whole grains, nuts, and seeds in your meals. These foods provide both nutrients and diverse fiber sources for gut bacteria. Fermented foods are also excellent choices. Items like yogurt, kefir, sauerkraut, and kimchi introduce beneficial probiotics. Furthermore, prebiotics, found in foods such as garlic, onions, and bananas, stimulate the growth of good bacteria. Always remember to stay hydrated. Drinking sufficient water supports digestion and overall gut function.
Impact of Antimicrobials on Gut Diversity
Antimicrobial medications, especially antibiotics, can drastically affect gut microbiome diversity. Antibiotics can eliminate not just harmful bacteria but also beneficial ones, creating a scenario where harmful microorganisms can flourish. This is particularly concerning if antibiotics are overprescribed or incorrectly used. A reduction in gut biodiversity can lead to various health problems, including gastrointestinal disorders, obesity, and allergies. Therefore, it is crucial to use antibiotics judiciously. Patients should always consult their healthcare provider regarding the necessity of antibiotics. Following a course of antibiotics, one might consider taking probiotics. Probiotics are live bacteria that can restore beneficial gut flora. Yogurt and probiotic supplements are examples. While the effectiveness of probiotics can vary, they generally support recovery in individuals post-antibiotic treatment. It’s also worth noting that not everyone needs supplements; sometimes, adequate nutrition can suffice. Post-antibiotic diet should emphasize fiber-rich foods, fermented items, and hydration. That way, individuals can help rebuild their microbial population. Education on appropriate antibiotic use can lead to better long-term gut health.
The connection between gut health and mental well-being has garnered considerable attention lately. Research indicates that the gut microbiome influences the brain and vice-versa, creating a complex gut-brain axis. A diverse microbiome can produce neurotransmitters like serotonin, positively impacting mood. A lack of diversity may destabilize this connection, potentially leading to conditions like anxiety and depression. Thus, ensuring a diverse gut environment might contribute positively to mental health. Foods high in omega-3 fatty acids, such as fish and flaxseeds, are instrumental in supporting brain function. Additionally, foods rich in antioxidants, like berries and dark leafy greens, protect against neuroinflammation. Transforming your diet to include these elements can enhance both gut and cognitive health. Regular physical activity also complements dietary changes, further supporting gut diversity and mental clarity. Engaging in activities like yoga promotes stress relief, which indirectly benefits gut health. Practicing mindfulness creates a holistic approach to maintaining both mental and gut health. Personalizing dietary and lifestyle approaches based on individual needs often results in better adherence and sustainable health improvements.
Benefits of a Plant-Rich Diet
A plant-rich diet is crucial for fostering gut microbiome diversity. Vegetables, fruits, whole grains, legumes, and nuts are packed with nutrients and dietary fibers essential for microbial health. Eating a wide variety of these foods increases the production of short-chain fatty acids. These acids are vital for gut health as they fuel colon cells and aid immune function. In addition, a diverse plant-based diet helps cultivate a more complex ecosystem of gut bacteria. Incorporating legumes like lentils and chickpeas provides versatile sources of protein and fiber that sustain various microorganisms. Whole grains contribute diverse forms of prebiotics that stimulate beneficial bacteria. Foods such as oats, quinoa, and barley promote balanced gut flora. Furthermore, tropical fruits like papaya and mango can introduce unique beneficial enzymes and fibers. Try new recipes that mix different plant foods to explore flavors and maximize health benefits. Listening to your body is essential; observe how you feel with new foods. Using these dietary strategies contributes to promoting a thriving, diverse gut microbiome that enhances overall health.
Stress management plays an integral role in maintaining gut diversity. The body’s stress response can disrupt the balance of gut microbiota. Chronic stress may lead to inflammation and negatively affect digestion. Practices such as meditation, yoga, and deep breathing can reduce stress levels significantly. Incorporating these techniques into daily routines allows for a holistic approach to gut health. Additionally, adequate sleep is crucial for restoring both mental and gut health. Poor sleep quality can exacerbate gut issues and create a vicious cycle of health concerns. Aim for at least seven to nine hours of restorative sleep each night for optimal function. Engaging in physical activities like walking or cycling can also alleviate stress and improve gut health. Balanced meals and hydration support digestion and nutrient absorption under stress. Make time for self-care and prioritize activities that induce relaxation such as reading or journaling. Connecting with community and spending time outdoors can further promote mental and gut health, yielding beneficial effects overall. Prioritizing self-care improves both psychological and gut well-being and fosters a healthier lifestyle.
Incorporating Functional Foods
In addition to a diverse diet, integrating functional foods can support the microbiome. Functional foods are those that provide health benefits beyond basic nutrition. Examples include probiotics, prebiotics, and fortified foods. Foods such as kimchi, sauerkraut, and kombucha are excellent sources of probiotics. These products introduce beneficial bacteria that enhance gut health and promote microbial balance. Prebiotic foods promote the growth and activity of beneficial flora. Examples of prebiotics include garlic, asparagus, and onions. Including these foods in meals can significantly impact gut biodiversity. Many commercial foods are fortified with additional nutrients, such as omega-3s and vitamins, promoting health. However, reading labels is essential to ensure that the food choices are genuinely beneficial. A combination of all these foods may enhance gut support significantly. Moreover, it is wise to introduce these functional foods gradually, monitoring how your body reacts. Each person’s microbiome is unique and may respond differently to new foods. Tracking changes in digestion and general well-being helps identify the most beneficial dietary additions for individual needs.
Overall, prioritizing diversity in gut microbiome is essential for maintaining optimal health. A varied diet nourishes a wide range of beneficial bacteria, ensuring a balanced gut environment. It’s vital to incorporate different food groups, hydrate adequately, and manage stress effectively. Exploring how various foods influence gut health reveals deeper connections between diet and overall wellness. This journey toward gut health is continuous, requiring consistent choices for lasting effects. Engaging healthcare professionals can provide personalized insights, ensuring tailored dietary recommendations. Remember, the path to gut health can directly influence overall health, including immunity, metabolism, and mental well-being. Taking small steps daily can foster an inviting gut atmosphere for flourishing diversity. Try new recipes, keep track of your energy and mood, and adjust choices accordingly. Creating a meal plan that incorporates various foods supports goals of promoting microbial health. It’s essential to remain open to new information and adjust strategies as needed. Remember, every individual’s needs differ; listening to your body is key. A diverse gut may promote longevity, reduce disease incidence, and improve quality of life. This knowledge empowers individuals to take charge of their gut health.