How Stress and Diet Interact to Impact Gut Wellness
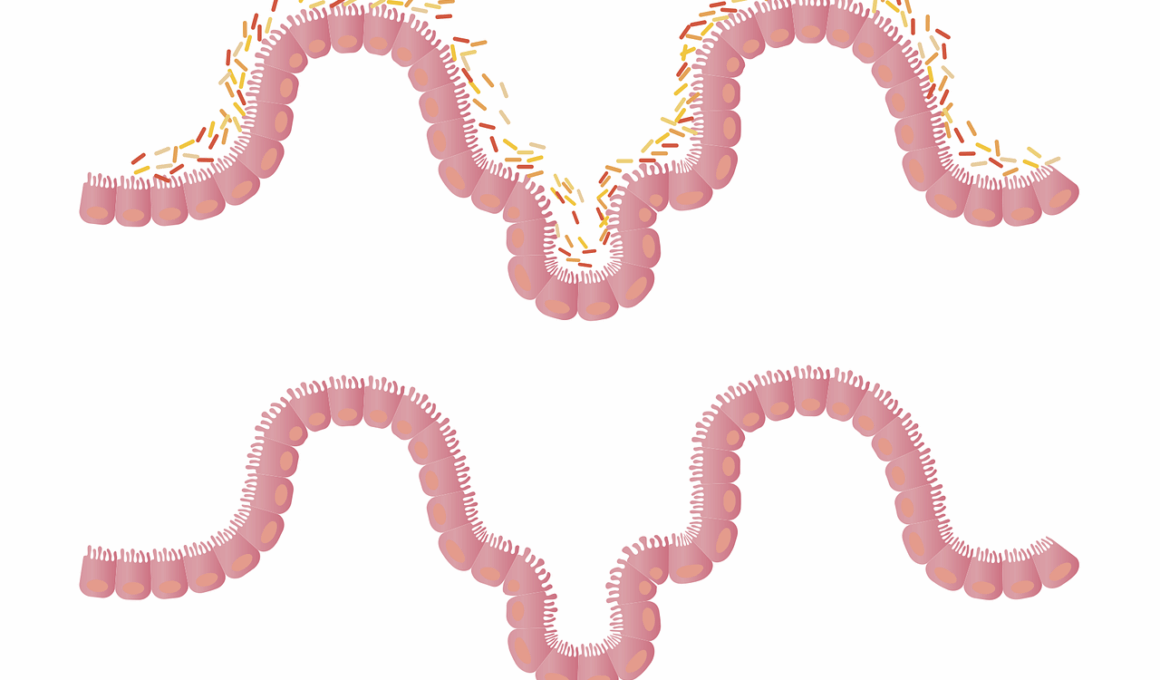
The connection between stress and gut health has gained considerable attention in recent years. Stress can significantly impact the gut microbiome, altering its composition and function. A healthy gut microbiome is essential for overall well-being, influencing immune function, digestion, and mental health. Diet plays a crucial role in maintaining gut health, as it directly affects the microbiome. Consuming a balanced diet rich in prebiotics, probiotics, and fiber can help promote a healthy gut environment. Foods like yogurt, fermented vegetables, and whole grains are excellent choices. On the other hand, diets high in sugar and processed foods can lead to gut dysbiosis or microbial imbalance. In addition to managing diet, incorporating stress management techniques can further support gut health. Practices such as mindfulness, yoga, and exercise can alleviate stress and positively influence the gut-brain axis. By prioritizing both diet and stress management, individuals can create a supportive environment for their gut microbiome. Focusing on these aspects may lead to improved digestive health and overall well-being. Understanding this connection empowers people to make informed lifestyle choices.
Maintaining a healthy gut requires awareness of dietary choices, especially under stress. Research indicates that stress can lead to unhealthy eating patterns, such as cravings for comfort foods high in sugar and fat. These choices ultimately disrupt gut health, leading to digestive issues. Resisting unhealthy food cravings can be challenging during stressful periods, but developing strategies to counteract them is crucial. One effective approach is to stock healthy snacks, like nuts or fruits, readily available. This preparation can aid in resisting the temptation of less healthy options when stress arises. Additionally, planning meals can promote healthier choices and ensure that nutritious foods are prioritized. Meal prepping can save time and reduce the chance of turning to convenience foods that lack essential nutrients. The quality of foods consumed can either strengthen or weaken gut health, making it important to pay attention. Supplements like probiotics may also benefit gut health, particularly during times of stress. Consulting with a healthcare provider before starting any supplement regimen helps ensure safety and effectiveness. A proactive approach to diet can mitigate stress-induced gut health issues, supporting a balanced microbiome.
The Role of Probiotics in Stress Management
Probiotics are live microorganisms that can provide numerous health benefits, especially for gut health. Research shows that incorporating probiotics into the diet may help manage stress levels and enhance mood. Consuming foods rich in probiotics, such as yogurt, kefir, and kimchi, can support a thriving gut microbiome. Healthy gut bacteria play a key role in producing neurotransmitters like serotonin, which affect mood and overall mental health. When the gut microbiome is balanced, it can positively influence stress responses. A diverse microbiome often leads to better mental resilience, helping individuals cope with challenging situations more effectively. Moreover, certain probiotic strains have been studied for their benefits in reducing anxiety and depressive symptoms. These findings highlight the importance of choosing the right probiotic supplements. It’s essential to select strains that have been researched for their specific effects on stress and mood. While the benefits of probiotics are significant, they should complement a holistic approach including stress management techniques and a balanced diet. Individuals interested in enhancing their gut health through probiotics should engage with healthcare professionals for personalized advice.
Dietary fiber plays a vital role in gut health and can be particularly important in managing stress. Fiber-rich foods, such as fruits, vegetables, legumes, and whole grains, support a thriving microbiome by providing the necessary nutrients for beneficial gut bacteria. These microorganisms ferment fiber, producing short-chain fatty acids that promote gut health. When under stress, the gut may experience motility issues or discomfort, making it essential to consume adequate fiber to support digestive regularity. Furthermore, studies indicate that high-fiber diets can modulate stress responses, helping alleviate some negative consequences of stress on the body. Drinking plenty of water is equally important when increasing fiber intake, as it aids digestion and minimizes discomfort. Individuals should gradually introduce more fiber into their diets to prevent gastrointestinal upset. Additionally, incorporating a variety of fiber types is optimal for promoting a diverse microbiome. Balancing soluble and insoluble fibers can enhance overall gut function. Maintaining a fiber-rich diet is a proactive strategy to support gut health amidst stressful times and may contribute to improved emotional well-being.
The Impact of Sugar and Processed Foods
High sugar and processed food consumption can have detrimental effects on gut health, particularly during periods of stress. These foods can lead to inflammation and disrupt the balance of the gut microbiome, promoting the growth of harmful bacteria. Increased intake of sugary foods can lead to increased cravings, creating a vicious cycle that can be challenging to break. Reducing sugar intake stands as a crucial step toward improved gut wellness. Swapping out sugary snacks for healthier alternatives, such as fruit or dark chocolate, can satisfy cravings without harming gut health. Additionally, processed foods often lack essential nutrients and contain unhealthy fats, which can negatively impact overall well-being. Making gradual changes to incorporate more whole, nutrient-dense foods can help ease the transition away from processed options. Meal planning can significantly contribute to these changes, ensuring that healthier choices are consistently available. Individuals may also consider tracking their food intake to identify problematic eating patterns. Raising awareness about food choices can empower individuals to make more informed decisions about their diets amid stress, ultimately benefiting gut health.
Hydration is another critical factor influencing gut health and can be affected by stress. When stressed, individuals may neglect their water intake, which can lead to dehydration and digestive issues. Adequate hydration supports digestive function, nutrient absorption, and waste elimination. Drinking enough water is essential for maintaining a balanced gut microbiome and promoting overall health. Individuals are encouraged to aim for sufficient daily water intake, adjusting for activity levels and climatic conditions. Infusing water with fruits or herbs may make hydration more enjoyable, encouraging higher consumption. Stress management also plays an important role in promoting adequate water intake; practicing mindfulness can provide reminders to drink water throughout the day. Ensuring regular hydration can help mitigate some adverse effects of stress on the gut. Individuals seeking to improve their gut health should view hydration as a crucial component of their diet. Maintaining a healthy gut requires a comprehensive approach that includes hydration as well as mindful eating and stress reduction strategies. By prioritizing these elements, individuals can better support their gut microbiome and overall wellness.
Conclusion: A Holistic Approach to Gut Health
In conclusion, the intricate relationship between diet, stress, and gut health highlights the necessity for a holistic approach. Managing stress and making conscious dietary choices are essential components that contribute to a thriving gut microbiome. While probiotics and fiber can provide significant benefits, it’s vital to avoid high sugar and processed foods that can harm gut health. Hydration also plays an important role in maintaining a balanced gut environment. By incorporating stress management techniques such as mindfulness, yoga, and regular physical activity, individuals can foster resilience against stress and promote digestive wellness. Making gradual changes toward healthier eating habits can significantly benefit gut health, providing the necessary nutrients to support a diverse microbiome. Individuals should consider their unique situations when implementing these strategies, seeking advice from healthcare professionals as needed. By understanding the interplay between diet and stress, achieving better gut health and overall well-being is possible. Emphasizing the importance of both dietary patterns and lifestyle factors can empower individuals to take proactive measures for their gut health. A well-rounded approach yields lasting effects on gut wellness and enhances overall quality of life.