How to Adapt the Keto Diet for Heart Disease Management
The ketogenic diet has surged in popularity for weight loss, but its implications for heart health are critical. Managing heart disease while following a keto diet requires careful consideration of food choices. The traditional keto diet is high in saturated fats, which can raise LDL cholesterol levels. To adapt the keto diet for heart disease management, it is essential to focus on heart-healthy fats. These include omega-3 fatty acids found in fish, nuts, and seeds. Incorporating plenty of fiber-rich vegetables can also help maintain heart health while on a keto plan. Choosing lean proteins from sources such as poultry and fish is vital to manage cholesterol levels closely. It’s crucial to monitor blood lipid levels regularly and adjust fat intake based on the results. Moreover, hydration and electrolyte balance should not be neglected, as keto can lead to dehydration. A healthcare professional, registered dietitian, or nutritionist should be consulted to create a personalized meal plan that aligns with heart health needs and dietary preferences. Making gradual changes and introducing variety ensures sustainability on this low-carb journey towards better heart health.
Understanding the role of carbohydrates in the keto diet is crucial for heart disease patients. The typical keto plan drastically reduces carbohydrate intake to induce ketosis, where the body burns fat for energy instead of glucose. However, not all carbs are created equal; focus should be on low-glycemic index (GI) foods. Vegetables, particularly leafy greens and non-starchy varieties, should comprise a large portion of your carb intake. Foods high in fiber help maintain stable blood sugar levels and assist with proper digestion. Importantly, avoiding processed foods that are high in sugar, refined grains, and unhealthy fats is fundamental on this diet. Reading food labels to understand ingredients and nutritional content can significantly aid compliance with dietary restrictions. Additionally, portion control is critical; even healthy foods can contribute to weight gain if consumed excessively. Meal prepping or planning can help manage portion sizes and ensure nutritional balance. Engaging in regular physical activity is also important for heart health when following the keto diet. Combining a physical fitness routine with a well-planned keto diet can yield great results for heart disease management.
Choosing Healthy Fats for Heart Health
When considering fats in a modified keto diet for heart disease, not all fats are equal. Prioritizing unsaturated fats is key. Olive oil, avocados, nuts, and fatty fish provide essential nutrients that promote heart health, supporting cardiovascular function. These fats can help lower bad cholesterol (LDL) levels, making them a heart-friendly alternative to saturated fats often resultant from high-fat diets. However, moderation remains critical; fat is calorie-dense, and overconsumption can lead to weight gain, impacting cardiovascular health. It’s beneficial to limit saturated fat intake to no more than 10% of your daily calorie consumption. Trans fats, typically found in processed snacks and fast food, should be avoided altogether, as they increase heart disease risk. Instead, aim for a diverse range of sources of healthy fats, including chia seeds and flax seeds, which are rich in omega-3 fatty acids. Regularly incorporating these fats can create a satisfying diet while still being mindful of cardiovascular health. Always consult healthcare providers before making major dietary changes, ensuring the diet is safe and effective for individual needs.
Monitoring Health Markers and Adjusting Diet
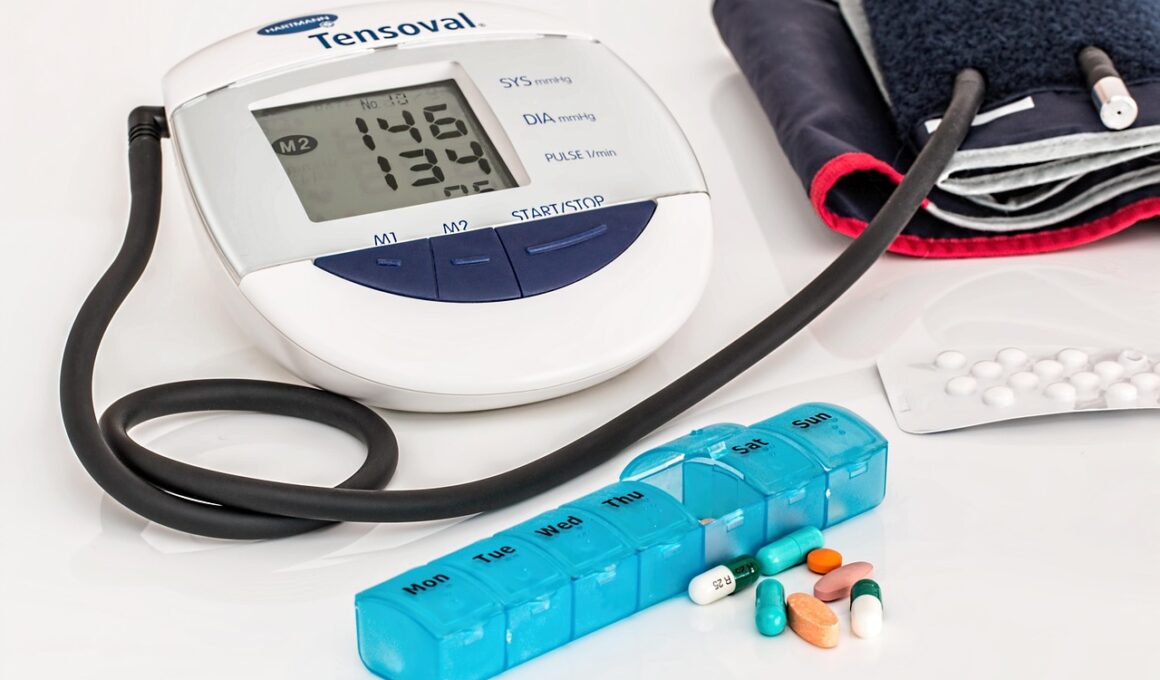
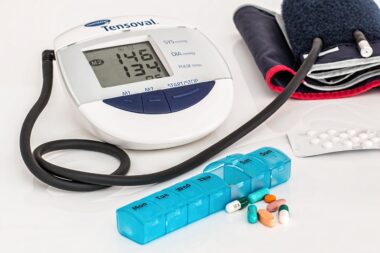
Monitoring health markers is essential while adapting the keto diet to manage heart disease effectively. Key indicators such as cholesterol levels, blood pressure, and triglycerides must be regularly assessed. In particular, aim to track your LDL and HDL cholesterol levels, as they are critical indicators of heart health. Keeping records helps identify what dietary changes positively or negatively impact heart health during your keto journey. Many patients might experience an increase in LDL cholesterol when starting keto, which could necessitate dietary adjustments. Consulting a healthcare professional aids in interpreting these markers and making informed decisions. Adapting fat sources or further increasing fiber intake could be necessary strategies. Additionally, incorporating regular cardiovascular exercises can support healthier cholesterol levels and enhance overall heart function. It’s also advisable to address any underlying conditions, such as hypertension or diabetes, which can significantly affect heart health. Most importantly, find support from peers or health coaches for motivation and accountability. A supportive network can inspire adherence to dietary changes whilst celebrating progress toward improved heart health.
Cross-referencing the keto diet with heart disease management involves being informed about potential pitfalls. One common misconception is that high-fat intake is universally beneficial; however, this isn’t true for everyone. Sustainable and positive outcomes require a balanced approach that prioritizes heart health. Foods high in refined sugars and unhealthy fats can provoke inflammation, which negatively affects cardiovascular health. It is important for individuals to personalize their approach, focusing on whole, nutrient-dense foods while avoiding overly processed options. Useful resources include reliable health websites, reputable cookbooks, and consulting with registered dietitians specializing in heart health. Many people also benefit from joining support groups for those managing heart disease while on a keto regimen. These communities offer shared experiences and can help answer questions and provide encouragement. Always remain vigilant about any symptoms or changes in well-being. Your body is the best indicator of how a diet is impacting your health. By keeping a food journal, individuals can gain insight into how their meals affect their heart health, allowing for better informed choices and sustainable health habits over time.
Incorporating Movement and Lifestyle Changes
Integrating movement into your routine enhances the benefits of a keto diet while managing heart disease. Regular exercise, combined with a healthy diet, improves overall cardiovascular function, increases energy levels, and reduces stress. Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic activity weekly, such as brisk walking, swimming, or cycling. Resistance training should also be included to promote muscle health and metabolic rate. Lifestyle changes, such as reducing sedentary behavior and implementing daily physical activity, have significant benefits for heart health. Each small step counts, so consider simple adjustments like taking the stairs instead of an elevator. Additionally, mental wellness is equally essential when following the keto diet. Stress management techniques, including mindfulness, meditation, or yoga, can contribute positively to heart health by reducing stress-induced inflammation in the body. Make time for rest and recovery as well, as it plays a pivotal role in maintaining sustained energy levels. Adopting a balanced approach to exercise and lifestyle changes promotes long-term adherence to the diet while also fostering overall well-being. Gradual changes yield lasting habits to support heart health.
In conclusion, adapting the keto diet for heart disease management requires a tailored approach that prioritizes heart-healthy choices. Focus on healthy fats, lean proteins, and an abundance of low-GI, fibrous vegetables to promote heart health. Regular monitoring of health markers aids in making necessary dietary adjustments while being mindful of portion sizes and the quality of food consumed. Engaging in regular physical activity and making lifestyle changes further support heart health. Consider collaborating with healthcare professionals, like registered dietitians, to develop a plan that aligns with individual health goals. Additionally, seeking support from trusted communities fosters motivation and accountability on this journey. Tracking progress via a food journal can provide helpful insights into dietary impacts on heart health. Remember that while the keto diet presents certain challenges, a well-planned approach can yield significant benefits when managing heart disease. Listen to your body, allowing flexibility in your meal choices, and celebrate each small victory along the way. Ultimately, the goal is to achieve a balanced diet that promotes long-term cardiovascular health while also supporting your overall wellness.
Readers should also consult trusted sources for additional guidance, ensuring they are informed about these dietary changes. Online resources from the American Heart Association and reputable health blogs can offer evidence-based information and recipes tailored for those with heart disease, making dieting easier and more enjoyable. With a little creativity in the kitchen, adhering to the ketogenic diet can be a journey that is both fulfilling and beneficial for heart health.