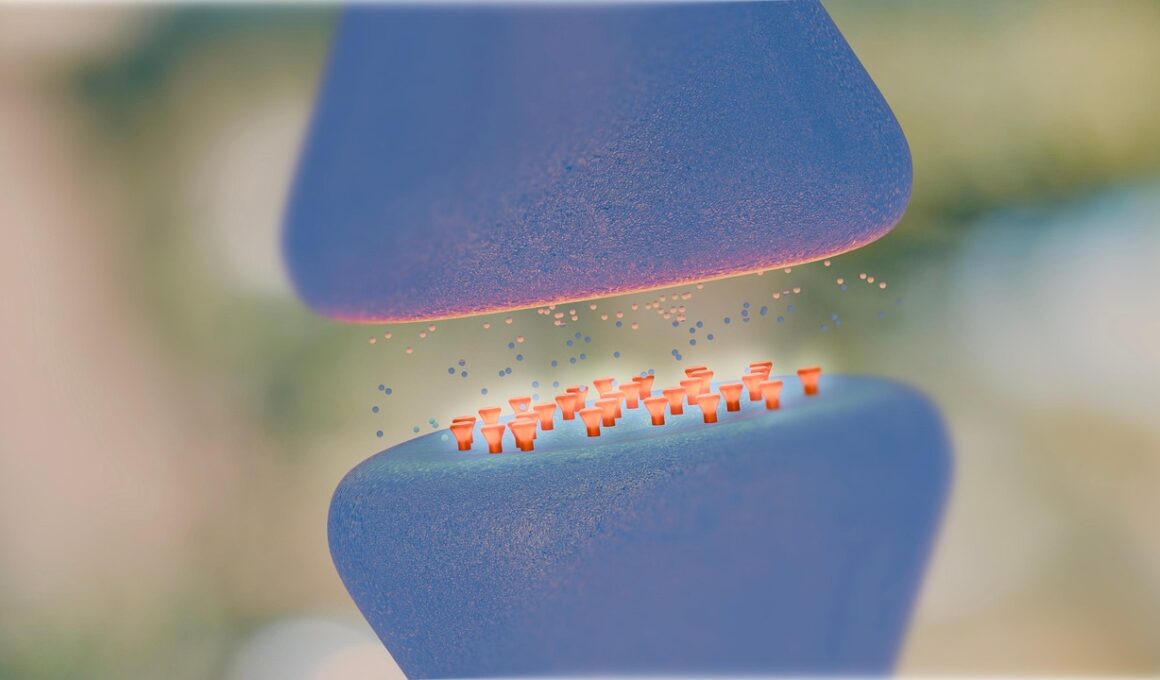
How Hormones Interact with Neurotransmitters
Hormones play a critical role in regulating various bodily functions, and their interaction with neurotransmitters is particularly significant. Hormones are chemical messengers released by glands in the endocrine system, while neurotransmitters are essential for communication between neurons in the nervous system. Understanding these interactions helps to reveal how they influence mood, behavior, and physiological processes. For example, cortisol, a stress hormone, can have a profound effect on neurotransmitter balance, impacting serotonin levels and mood stability. This open relationship ensures that changes in one system can lead to reactions in another, thus significantly affecting mental health. Furthermore, various factors such as diet, exercise, and sleep influence both hormone and neurotransmitter levels. By studying these interactions, researchers hope to develop better strategies for managing conditions like depression or anxiety where these systems may be out of balance. To promote hormonal balance, one can adopt healthy lifestyle practices including balanced nutrition and regular physical activity. Moreover, understanding these dynamics can empower individuals to seek targeted interventions or therapies, potentially leading to better mental health outcomes and improved quality of life. This interconnected relationship remains a dynamic field for ongoing research and clinical exploration.
Neurotransmitters are crucial for brain function and emotional regulation, and they work closely with hormones to facilitate brain communication. For instance, dopamine, serotonin, and norepinephrine often engage in complex relationships with hormones like estrogen and testosterone. These interactions can affect emotional well-being, cognitive functions, and stress response. Research indicates that fluctuations in hormone levels may lead to alterations in neurotransmitter activity, creating a feedback loop that affects both mental and physical health. In women, for example, hormonal changes during menstrual cycles can lead to mood swings, showcasing how estrogen impacts serotonin levels. Likewise, testosterone has been linked to dopamine release, impacting motivation and reward-driven behaviors. Furthermore, chronic stress can lead to elevated cortisol levels, which in turn can reduce serotonin and dopaminergic activity. This chain reaction can pose risks for developing anxiety disorders or depression. As ongoing studies delve deeper into these interactions, the importance of maintaining hormonal balance for optimal neurotransmitter function is highlighted. Therefore, recognizing signs of hormonal imbalance and addressing lifestyle factors can be vital in fostering mental health and achieving wellness.
The Impact of Stress on Hormones and Neurotransmitters
Stress is known to have profound effects on both hormones and neurotransmitters, leading to various physiological and psychological challenges. Under stress, the hypothalamus-pituitary-adrenal (HPA) axis is activated, resulting in the release of cortisol. Elevated cortisol levels can disrupt the regulation of neurotransmitters like serotonin and dopamine, leading to mood disorders and cognitive impairments. Chronic stress can create a cascading effect, where prolonged high cortisol levels harm neurotransmitter synthesis, making it difficult for the body to maintain equilibrium. Furthermore, neurotransmitter deficiencies can worsen the body’s overall stress response, creating a vicious cycle. Awareness of stress management techniques becomes essential to mitigate these influences. Techniques such as yoga, mindfulness, and meditation can help lower cortisol levels, positively impacting neurotransmitter activity. Engaging in regular physical activity also aids in balancing hormones and enhancing mood through increased endorphin release. Adopting a balanced diet rich in omega-3 fatty acids is beneficial for brain health, supporting neurotransmitter functions. Thus, implementing these strategies can significantly improve one’s ability to handle stress and support a healthy mind and body connection.
The role of nutrition in regulating hormonal and neurotransmitter activity cannot be overlooked. Certain nutrients play key roles in the synthesis of neurotransmitters as well as hormones. For example, amino acids serve as building blocks for neurotransmitters. Tryptophan, an amino acid found in turkey, eggs, and nuts, is essential for serotonin production. Similarly, phenylalanine, present in dairy products and meats, is needed for dopamine synthesis. Ensuring an adequate intake of vitamins and minerals is also crucial. Vitamins B6, B12, and folate aid in neurotransmitter synthesis and regulation, while magnesium contributes to the functioning of the HPA axis. Additionally, omega-3 fatty acids, prevalent in fish, flaxseeds, and walnuts, are vital for optimal brain function and hormone regulation. Furthermore, diet patterns, including high sugar and processed foods, can disrupt hormone balance, leading to inflammation and affecting neurotransmitter activity adversely. Adopting a nutrient-dense, balanced diet can support both hormonal and neurotransmitter functions, promoting mental well-being. Consequently, paying attention to nutrition can be as significant as understanding the intricate connections between hormones and neurotransmitters.
Exercise: A Natural Regulator of Hormones and Neurotransmitters
Exercise serves as a natural modulator for both hormones and neurotransmitters, offering myriad benefits for mental and physical health. When engaging in physical activity, the body releases endorphins, often referred to as ‘feel-good’ hormones, which contribute to improved mood and reduced feelings of stress and anxiety. Additionally, regular exercise has been shown to increase the production of serotonin and dopamine, key neurotransmitters that enhance pleasure, motivation, and overall emotional well-being. This boost in neurotransmitter levels can lead to an improvement in mood disorders and anxiety management. Notably, consistent moderate exercise can help regulate cortisol levels, promoting hormonal balance. Furthermore, studies reveal that exercises like aerobic activities can enhance neurogenesis, the creation of new neurons, supporting cognitive functions. To maximize the benefits, combining different types of workouts, such as strength training and aerobic exercises, is encouraged. Incorporating physical activity into daily routines can lead to holistic well-being. Not only does exercise help in managing stress, but it also strengthens the mind-body connection. Consequently, integrating exercise into daily life is a fundamental aspect of maintaining hormonal and neurotransmitter health.
Sleep’s impact on hormonal and neurotransmitter levels is a critical area of exploration in understanding overall health. Quality sleep is necessary for proper hormonal function, especially growth hormone and cortisol regulation. Sleep deprivation can lead to hormonal imbalances, manifesting as increased cortisol levels that can negatively affect neurotransmitter activity. Observational studies have shown that inadequate sleep can lower serotonin levels, which can lead to mood disorders and anxiety. Sleep stages, particularly REM sleep, are crucial for neurotransmitter cycling, ensuring that they are adequately synthesized and utilized. On the other hand, proper sleep allows the brain to process experiences and consolidate memories, which are vital roles for many neurotransmitters. Establishing good sleep hygiene is essential to optimize both hormones and neurotransmitters. Suggestions include maintaining a regular sleep schedule, creating a restful sleeping environment, and reducing caffeine intake. Mindfulness and relaxation techniques before bedtime can ease transitions to sleep, enhancing the body’s ability to recharge. A habitual focus on sleep can pave the way for improved hormonal balance and neurotransmitter function, significantly impacting overall mental health and resiliency.
The Future of Hormonal and Neurotransmitter Research
As science advances, the field of hormonal and neurotransmitter research continues to uncover more about their intricate relationships. Emerging research emphasizes the need for personalized medicine approaches, recognizing that individual variances exist in hormone and neurotransmitter interactions. Moreover, the interplay between these systems may illuminate pathways to better address mental health conditions. In exploring how chronic illnesses or lifestyle factors perpetuate changes, researchers hope to develop targeted therapies that could combat disorders rooted in hormonal or neurotransmitter imbalances. Innovations in biotechnology and genetics may enable deeper examinations and reveal new insights into gene expression related to hormonal regulation. For instance, understanding specific genetic markers related to neurotransmitter synthesis can lead to advancements in nutritional interventions or hormone therapy. Additionally, the impact of environmental factors, from pollution to diet, is an area of increasing study. Fostering collaboration across multiple disciplines, including psychology, endocrinology, and nutrition, will be crucial for advancing knowledge. By integrating these areas of research, we can enhance our understanding of the complex interplay between hormones and neurotransmitters, ultimately leading to improved health outcomes.
In conclusion, understanding how hormones interact with neurotransmitters is pivotal in recognizing their roles in mental health, behavior, and overall wellness. The delicate balance between these two systems can significantly affect emotional regulations, cognitive functions, and stress responses. By paying attention to factors such as stress management, nutrition, exercise, and sleep, individuals can adopt strategies to support both hormonal and neurotransmitter health. Likewise, ongoing research will pave the way for more effective interventions, helping to mitigate mental health challenges. As we further comprehend these intricate relationships, individuals will be better equipped to understand and manage their health proactively. Integrating findings from both neuroscience and endocrinology can lead toward a more holistic approach to health and well-being. Awareness about informing practices and lifestyle choices can empower individuals to make informed decisions. Through self-advocacy and education, improved wellness is attainable. Thus, exploring these connections can enhance not only individual health but also community well-being. Raising awareness concerning mental health issues rooted in hormonal and neurotransmitter systems will be essential for future progress. Ultimately, this intertwined knowledge reflects a broader understanding of human health dynamics.