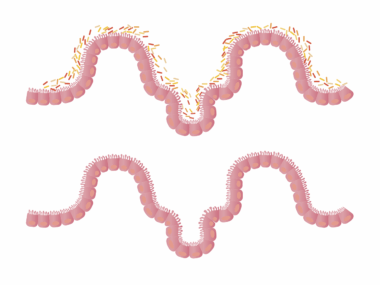
The Benefits of Omega-3 Fatty Acids in Digestive Health
Omega-3 fatty acids are essential fats known for their numerous health benefits. They are primarily found in fish, flaxseeds, and walnuts, and play a critical role in human health. One of the most significant areas where omega-3s have a positive impact is digestive health. Individuals suffering from digestive disorders, such as irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) or inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), often experience inflammation, discomfort, and disruption in their digestive processes. By incorporating omega-3 fatty acids into their diet, these individuals can benefit from the anti-inflammatory properties that help soothe their gastrointestinal tract. Studies have shown that omega-3s may enhance the gut barrier function, ensuring that the intestines operate efficiently and reducing symptoms associated with various digestive disorders. Consuming foods rich in omega-3s can also promote better absorption of nutrients, support a balanced microbiome, and enhance overall gut health. In this way, omega-3 fatty acids not only support digestive wellness but help protect against the development of further complications that can arise from chronic digestive conditions.
Furthermore, research indicates that omega-3 fatty acids can aid in the management of digestive disorders by modulating the body’s immune response. They influence the production of cytokines, which are proteins that are involved in the inflammatory process of the gut. By reducing the levels of pro-inflammatory cytokines, omega-3s contribute to lowering inflammation, ultimately assisting in alleviating discomfort and digestive disturbances. Individuals with conditions like Crohn’s disease or ulcerative colitis, both categorized as IBD, may find significant relief through increased omega-3 intake. Additionally, the consumption of these essential fats correlates with a reduction in the frequency and severity of flare-ups and symptoms associated with such conditions. Regular intake of omega-3s has also been linked to improved overall gastrointestinal function, enhancing the quality of life for those suffering from chronic digestive issues. To maximize these benefits, it’s essential to include a variety of omega-3 sources in your diet, ensuring a steady influx of these valuable nutrients. Thus, dietary changes focusing on omega-3 fatty acids can be a powerful strategy for managing digestive disorders.
Sources of Omega-3 Fatty Acids
Rich sources of omega-3 fatty acids include fatty fish such as salmon, mackerel, and sardines. Those who prefer plant-based options can consider flaxseeds, chia seeds, walnuts, and hemp seeds. Incorporating these food items into daily meals can significantly increase omega-3 intake. Furthermore, omega-3 supplements, such as fish oil or algal oil capsules, are also available for individuals who may not consume sufficient amounts of these foods. For those with allergies to seafood, algal oil is a fantastic alternative as it provides essential omega-3s derived from marine algae. It’s important to read labels carefully to ensure the supplements contain adequate amounts of both EPA and DHA, the two main types of omega-3 fatty acids beneficial for health. Consuming a variety of rich sources can help individuals maintain optimal levels of omega-3s, promoting digestive health and overall well-being. Additionally, adding omega-3-rich foods to meals can serve as an effective, tasty method to improve dietary variety and nutritional quality for all.
In addition, it is important to consider the balance of omega-6 to omega-3 fatty acids in the diet. Many individuals consume high amounts of omega-6 fatty acids due to the prevalent use of vegetable oils and processed foods. Maintaining an optimal ratio is crucial, as excessive omega-6 intake can lead to increased inflammation, counteracting the benefits provided by omega-3s. Striving for a balanced diet that includes sufficient omega-3 sources can enhance digestive health significantly. Increased consumption of omega-3s alongside a reduction in omega-6 rich foods can help support a healthier inflammatory response within the digestive tract. Emphasizing whole foods and reducing reliance on processed products can contribute to this balance. Along with a focus on omega-3 fatty acids, optimizing fiber intake can also be advantageous for digestive health. Fiber-rich foods, such as fruits, vegetables, and whole grains, can work synergistically with omega-3s to promote effective digestive processes while providing holistic dietary advantages.
Potential Risks and Recommendations
While omega-3 fatty acids are largely beneficial, it is vital to consult with healthcare professionals before making significant dietary changes, especially for individuals dealing with chronic health conditions. Under certain circumstances, high doses might lead to gastrointestinal disturbances or blood-thinning effects. Dietary guidelines recommend consuming fish and plant-based sources regularly but discourage relying solely on supplements to fulfill omega-3 requirements. Balance remains key, with an emphasis on obtaining nutrients from whole foods. Consuming two servings of fatty fish per week is often advised, along with regular incorporation of plant sources. Ensuring a proper balance with other nutritional components will allow omega-3 fatty acids to exert their protective effects effectively. Being mindful of mercury content in fish is also essential, making it important to choose cleaner sources of protein. By taking these precautions and recommendations into account, individuals can enjoy the benefits of omega-3 fatty acids in their diets without adverse effects, contributing to better digestive health alongside a holistic approach.
In conclusion, omega-3 fatty acids present a multitude of advantages for individuals suffering from digestive disorders. Their anti-inflammatory properties, ability to enhance gut barrier function, and positive impact on overall gastrointestinal health make them an integral part of managing chronic digestive issues. As we continue to understand the nuances of nutrition and its influence on chronic illness, incorporating omega-3-rich foods into our diets becomes increasingly crucial. By focusing on quality sources and balancing our intake of fatty acids, individuals can take proactive measures towards improving their digestive health. Future research will hopefully uncover even more insights into the specific mechanisms through which omega-3s affect digestive disorders. This knowledge can lead to better therapeutic strategies and dietary recommendations for those affected. Ultimately, adopting a diet rich in omega-3 fatty acids is not just beneficial for digestive health, but for overall well-being. Such dietary considerations empower individuals to make informed choices regarding their nutrition, leading towards better health outcomes in managing chronic digestive conditions over time.
For those interested in exploring the potential of omega-3 fatty acids for digestive health, it may be beneficial to visit reputable sources or consult registered dietitians for personalized dietary advice. They can assist in creating a balanced meal plan inclusive of omega-3 fatty acids that accommodates individual preferences and health concerns. Additionally, engaging with communities that focus on chronic illness and nutrition could provide valuable tips and shared experiences. Programs and workshops that educate about the benefits and sources of omega-3s may also enhance knowledge and inspire positive dietary changes. Furthermore, challenges in improving one’s diet can often be overcome through seeking support from health professionals or communities. Therefore, relying on both online resources and professional guidance can aid individuals in making empowering dietary decisions. Ultimately, omega-3 fatty acids are a valuable addition to a well-rounded diet geared towards improving digestive health and overall quality of life, promoting a holistic approach to wellness that encompasses body, mind, and nutrition.
. UPSERT input here